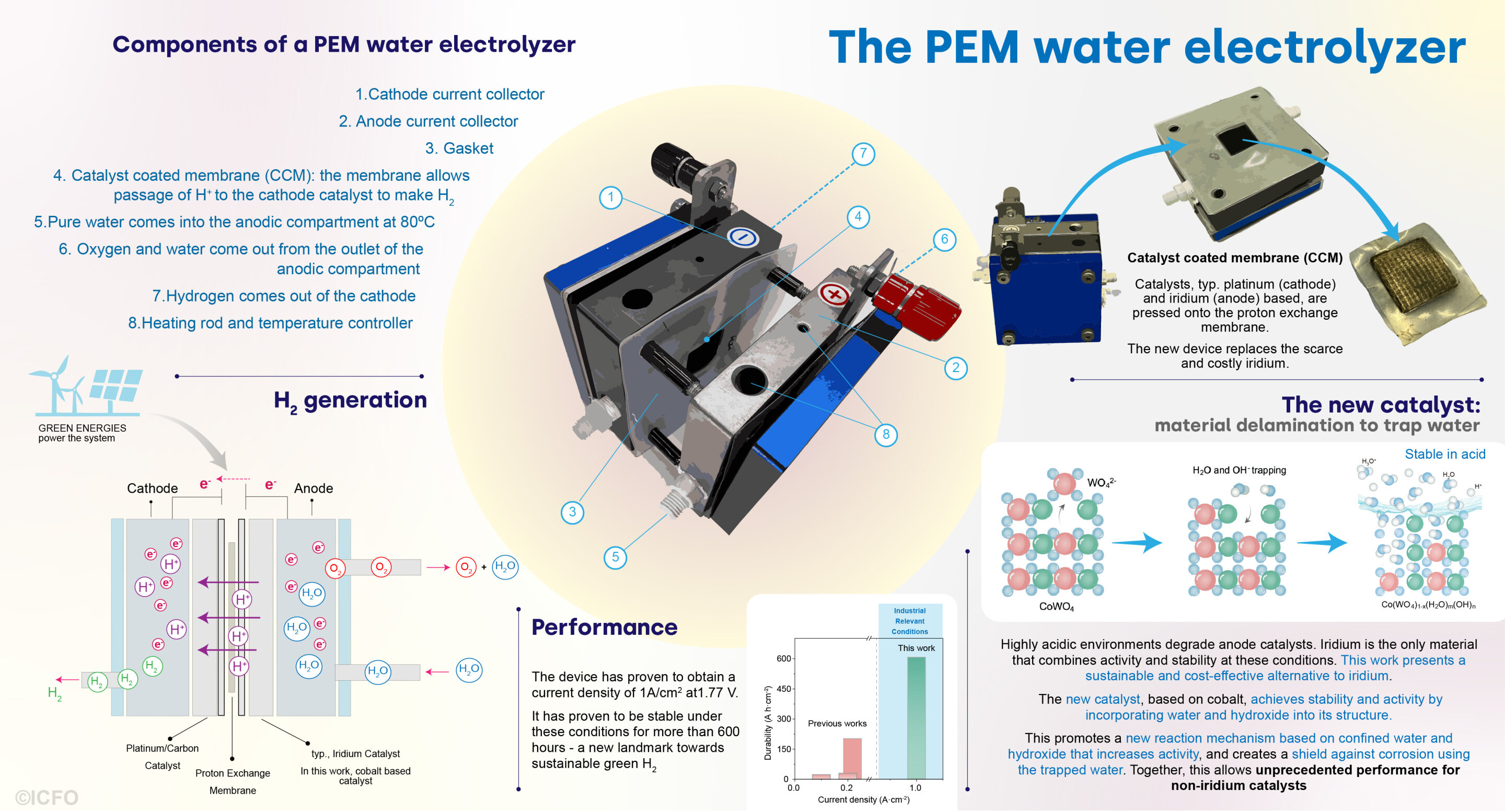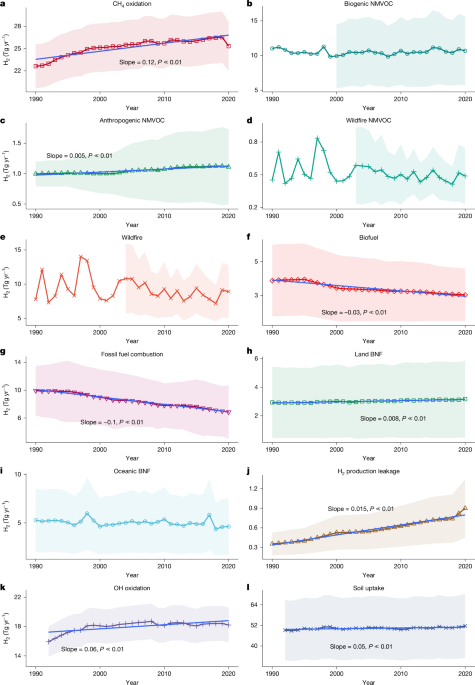
The Rising Importance of a Global Hydrogen Budget in Climate Change
The article discusses the global hydrogen budget, highlighting the current reliance on energy-intensive grey hydrogen, the potential shift towards green and blue hydrogen by 2030–2040, and the climate implications of hydrogen leakage, which acts as an indirect greenhouse gas. It presents a comprehensive analysis of hydrogen sources and sinks over the past three decades, estimates the recent decade's hydrogen budget, and projects future climate impacts, emphasizing the need for better data and understanding of hydrogen's role in the climate system.