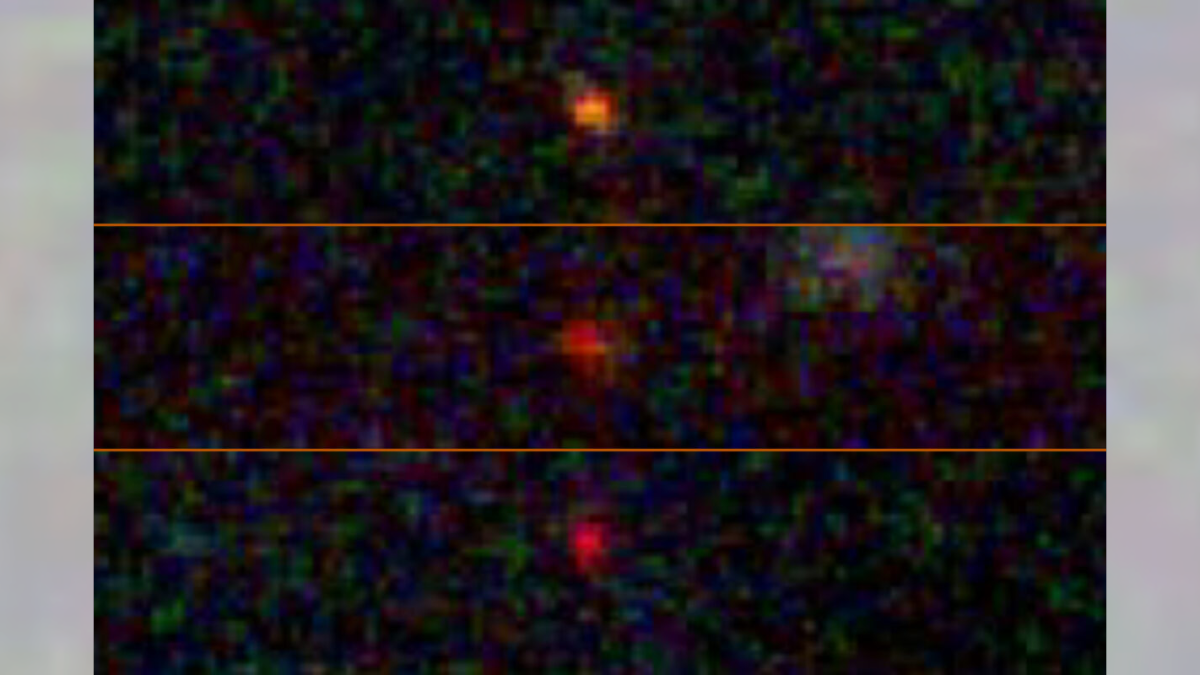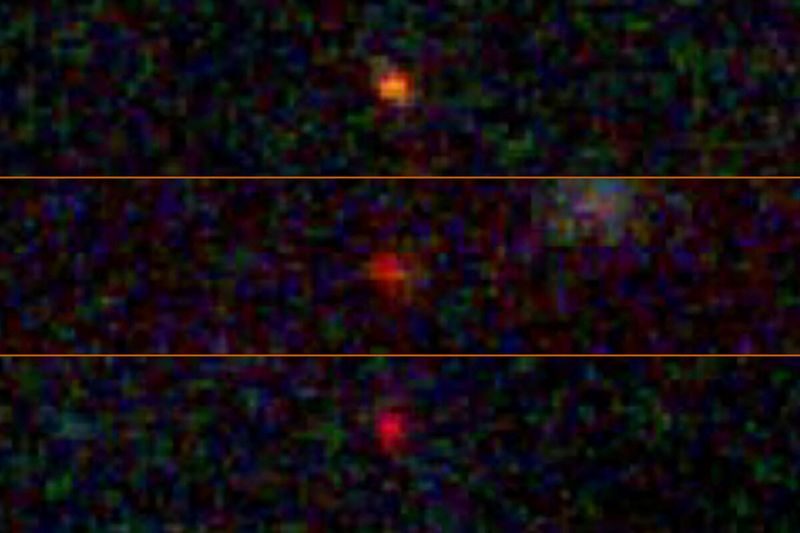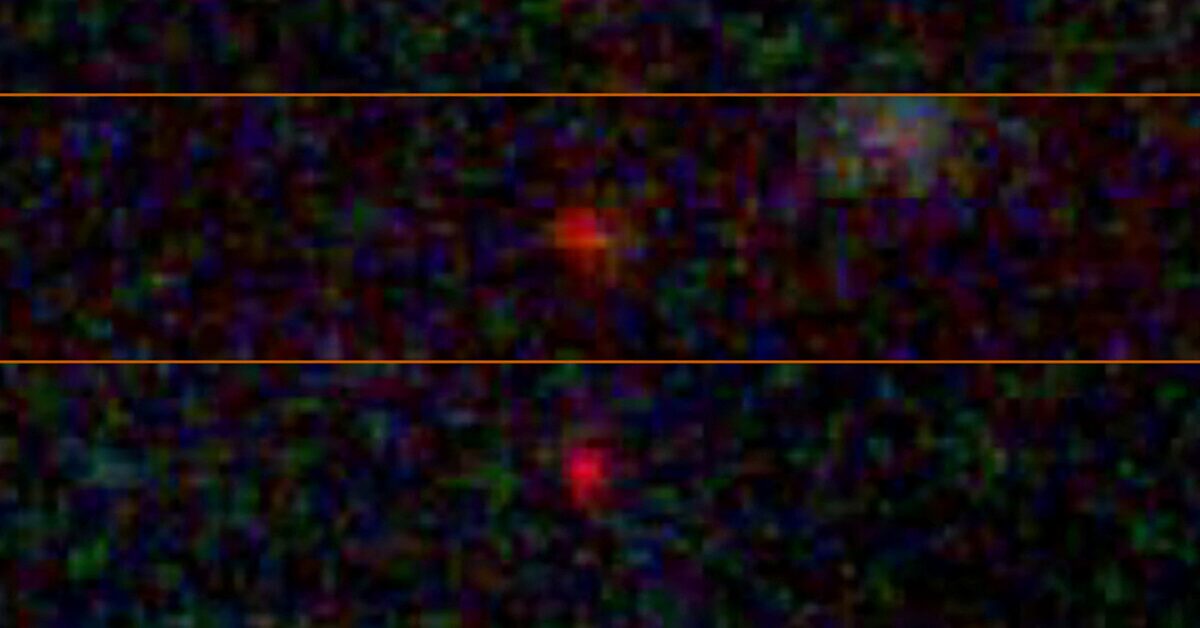
Dark stars could tie JWST’s three cosmic puzzles together
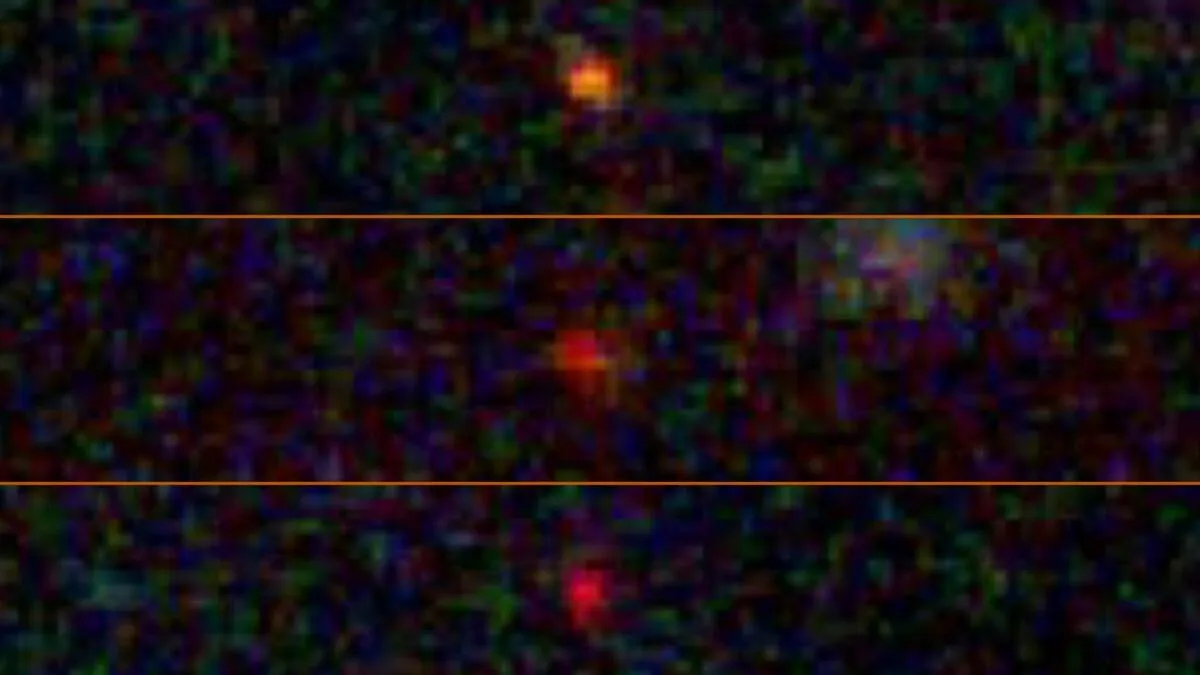
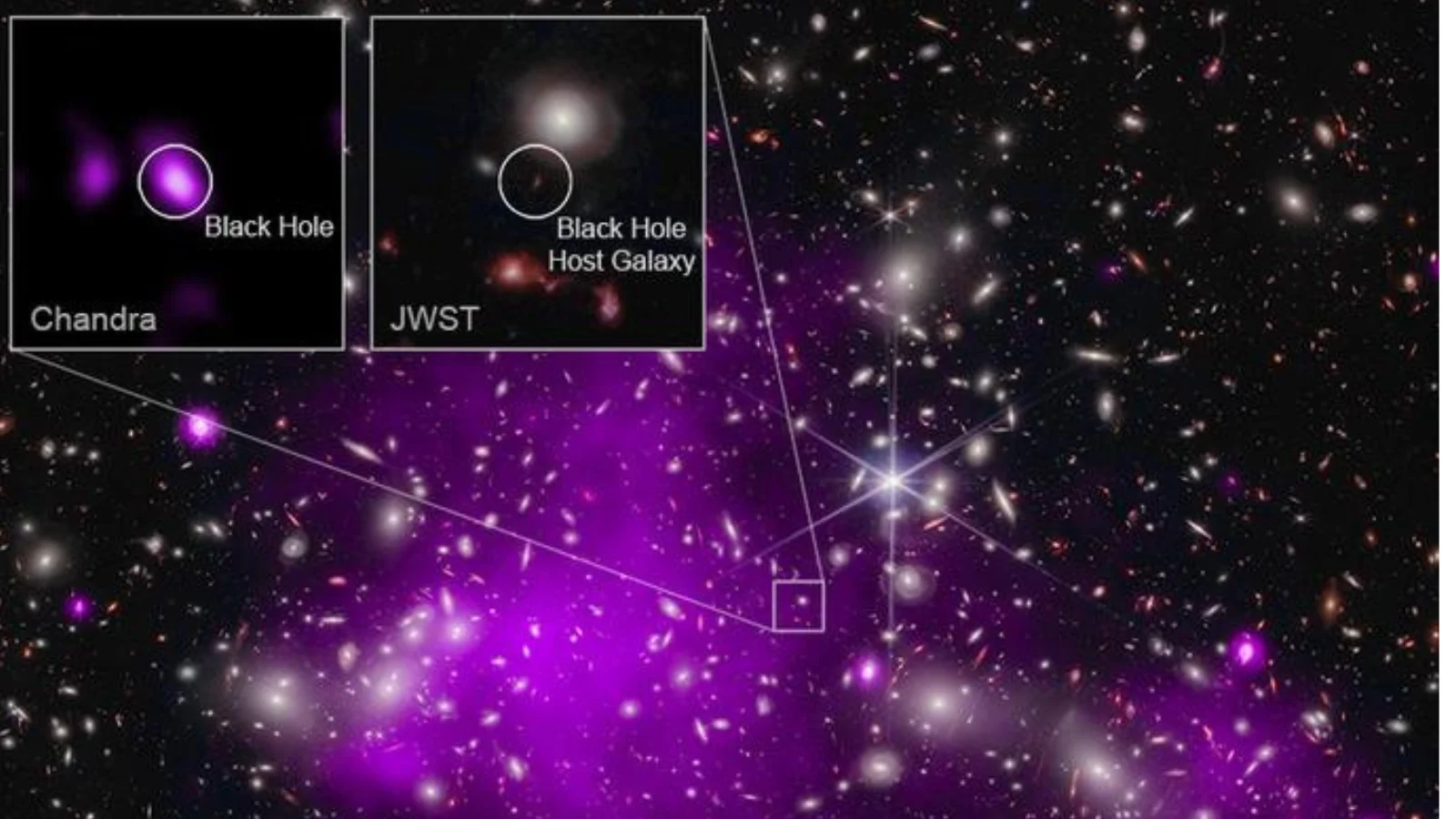
Dark stars—hypothetical early-universe objects powered by annihilating dark matter—could explain three JWST-era mysteries: the overabundance of supermassive black holes in the first billion years, the existence of ultrabright blue ‘monster’ galaxies, and the compact ‘little red dots’. If dark stars exhausted their dark matter and collapsed, they could seed rapid SMBH formation, aligning with JWST observations. The idea remains speculative but is supported by emerging hints, with a December 2025 paper proposing it as a single mechanism to address multiple puzzles.