Cancer-Induced Nerve Damage and Inflammation Drive Immunotherapy Resistance
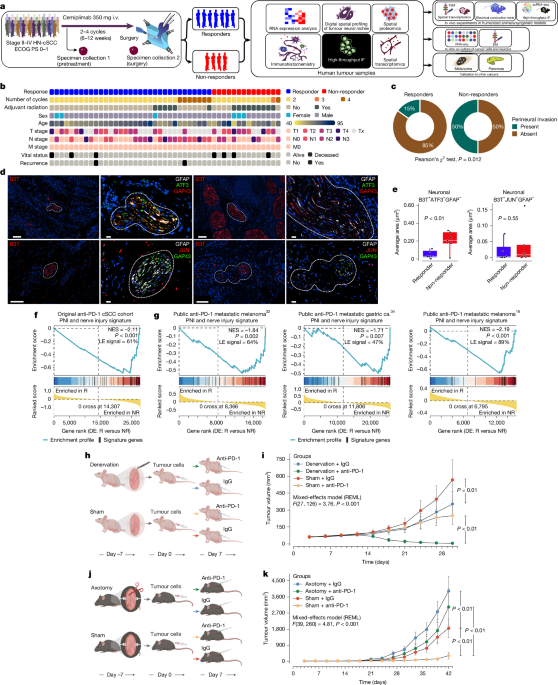
Cancer-induced nerve injury (CINI) promotes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy by causing myelin degradation and chronic inflammation, which leads to immune exhaustion. The study shows that nerve injury within tumors correlates with immunosuppressive activity and therapy resistance across multiple cancer types, and that blocking nerve injury signaling can improve immune response and treatment efficacy.
