Cancer-Induced Nerve Damage and Inflammation Drive Immunotherapy Resistance
TL;DR Summary
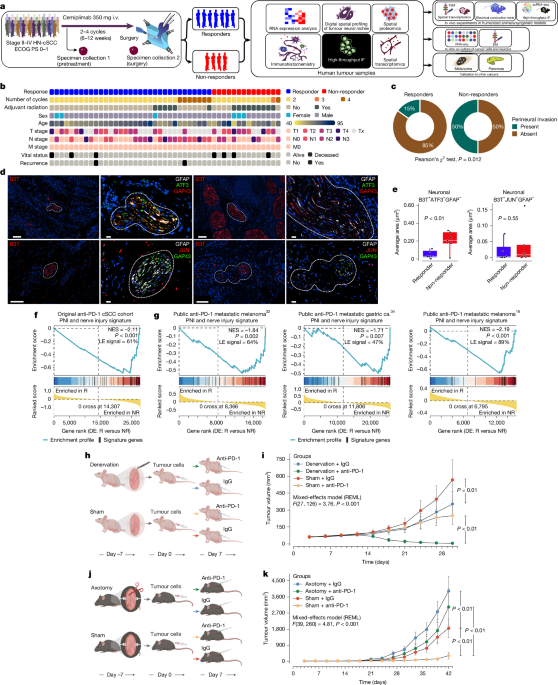
Cancer-induced nerve injury (CINI) promotes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy by causing myelin degradation and chronic inflammation, which leads to immune exhaustion. The study shows that nerve injury within tumors correlates with immunosuppressive activity and therapy resistance across multiple cancer types, and that blocking nerve injury signaling can improve immune response and treatment efficacy.
Topics:health#anti-pd-1-resistance#cancer-immunotherapy#cancer-research#nerve-injury#peripheral-nerve-fibers#tumour-microenvironment
- Cancer-induced nerve injury promotes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy Nature
- Cancer cells break down nerve covers causing immune exhaustion and therapy resistance News-Medical
- Nerve Damage from Cancer Triggers Chronic Inflammation and Undermines Immunotherapy Effectiveness BIOENGINEER.ORG
- Study Finds Cancer-Induced Nerve Damage and Chronic Inflammation Contribute to Immunotherapy Resistance geneonline.com
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
124 min
vs 124 min read
Condensed
100%
24,782 → 53 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature