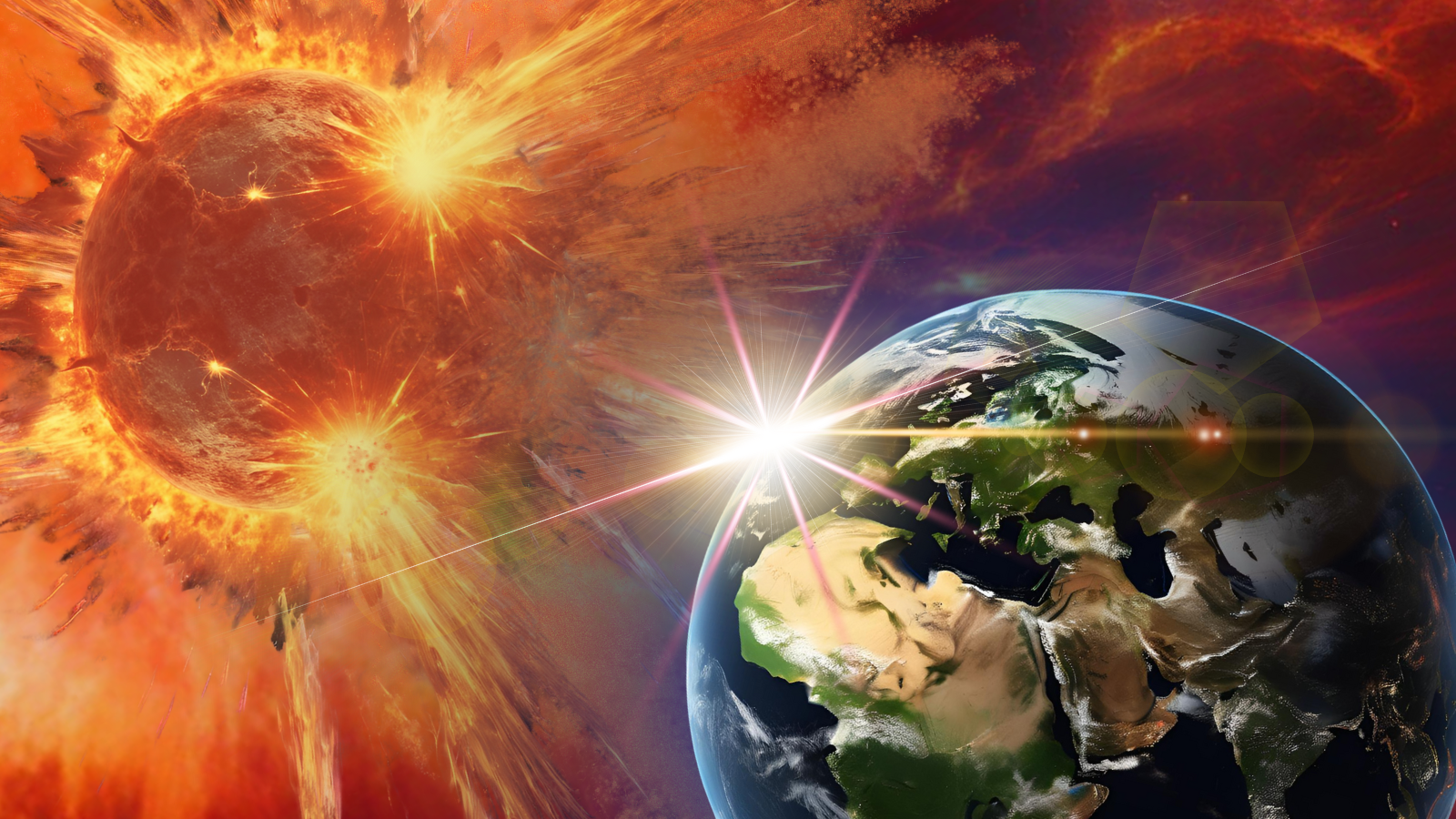
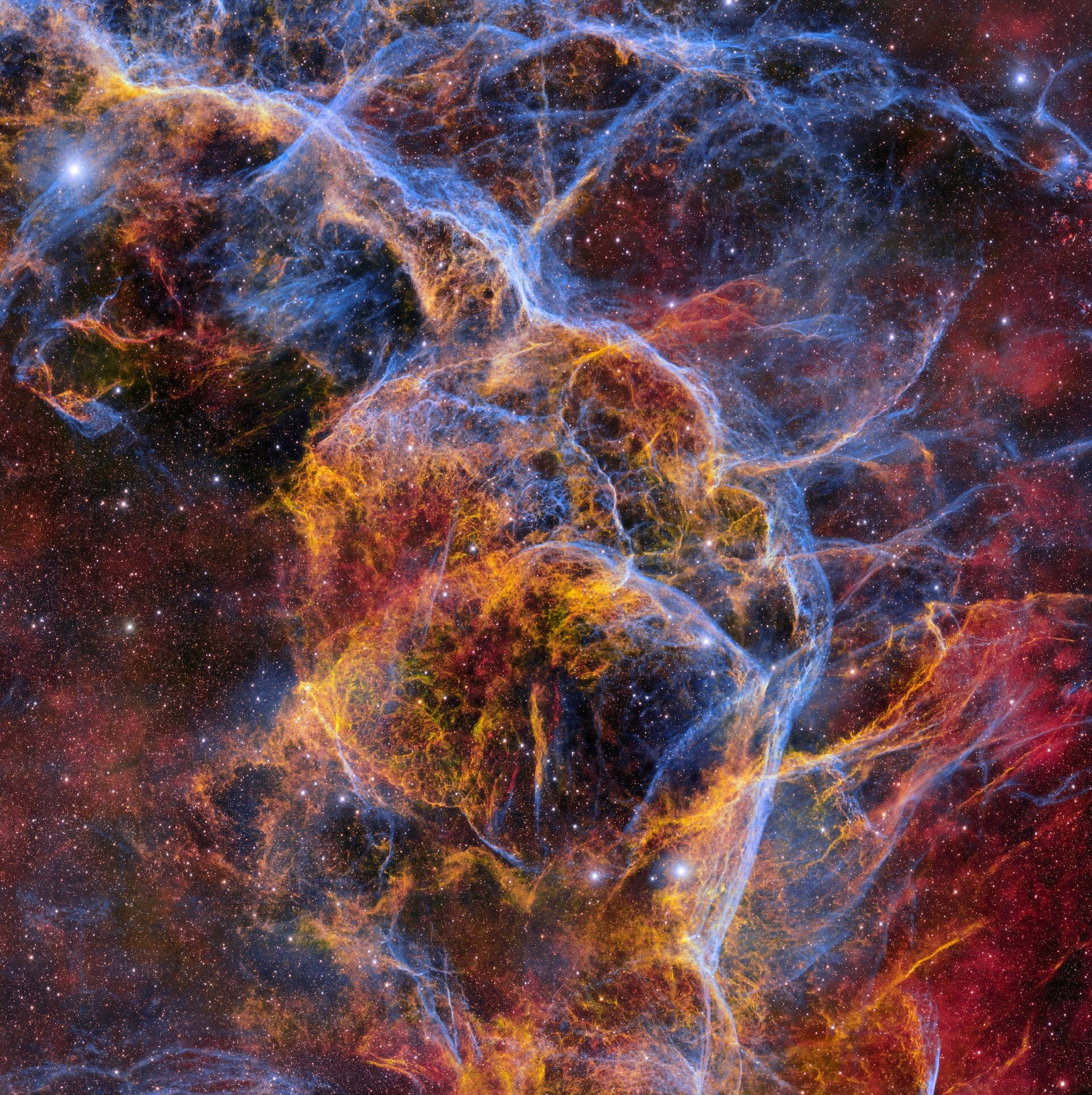
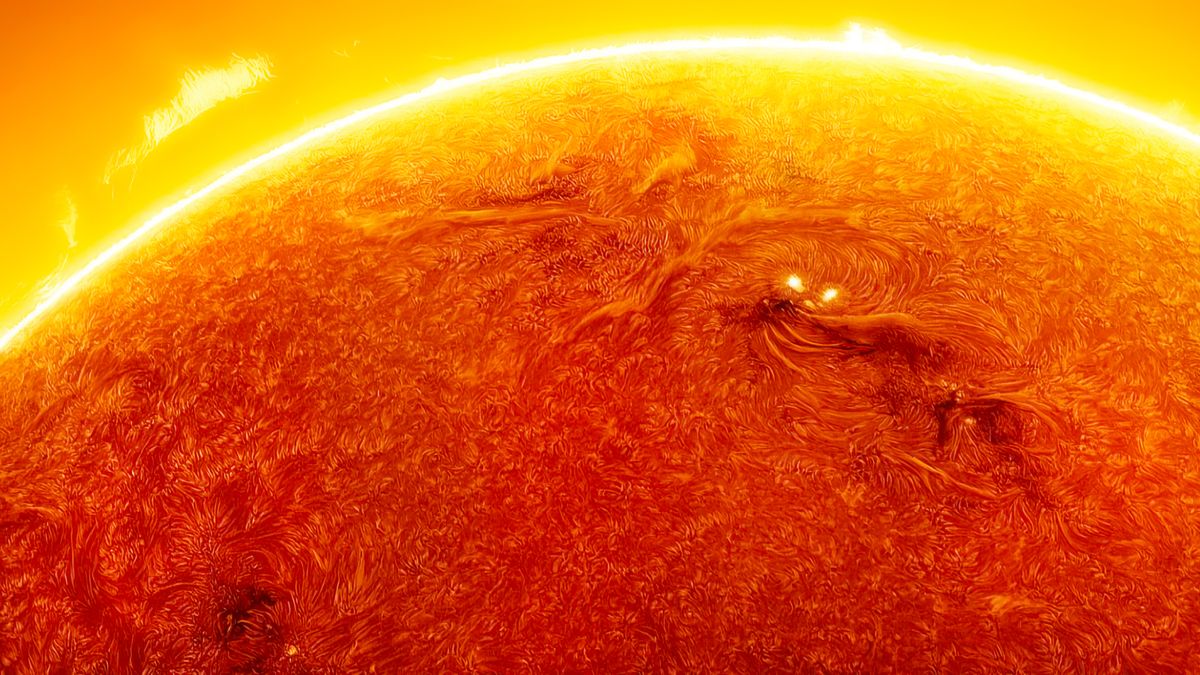
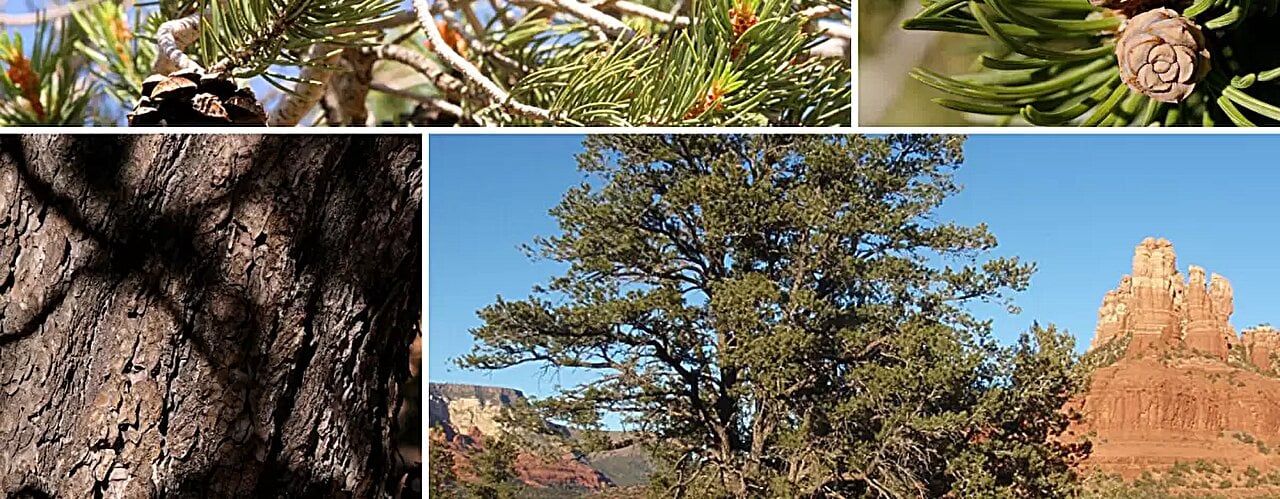
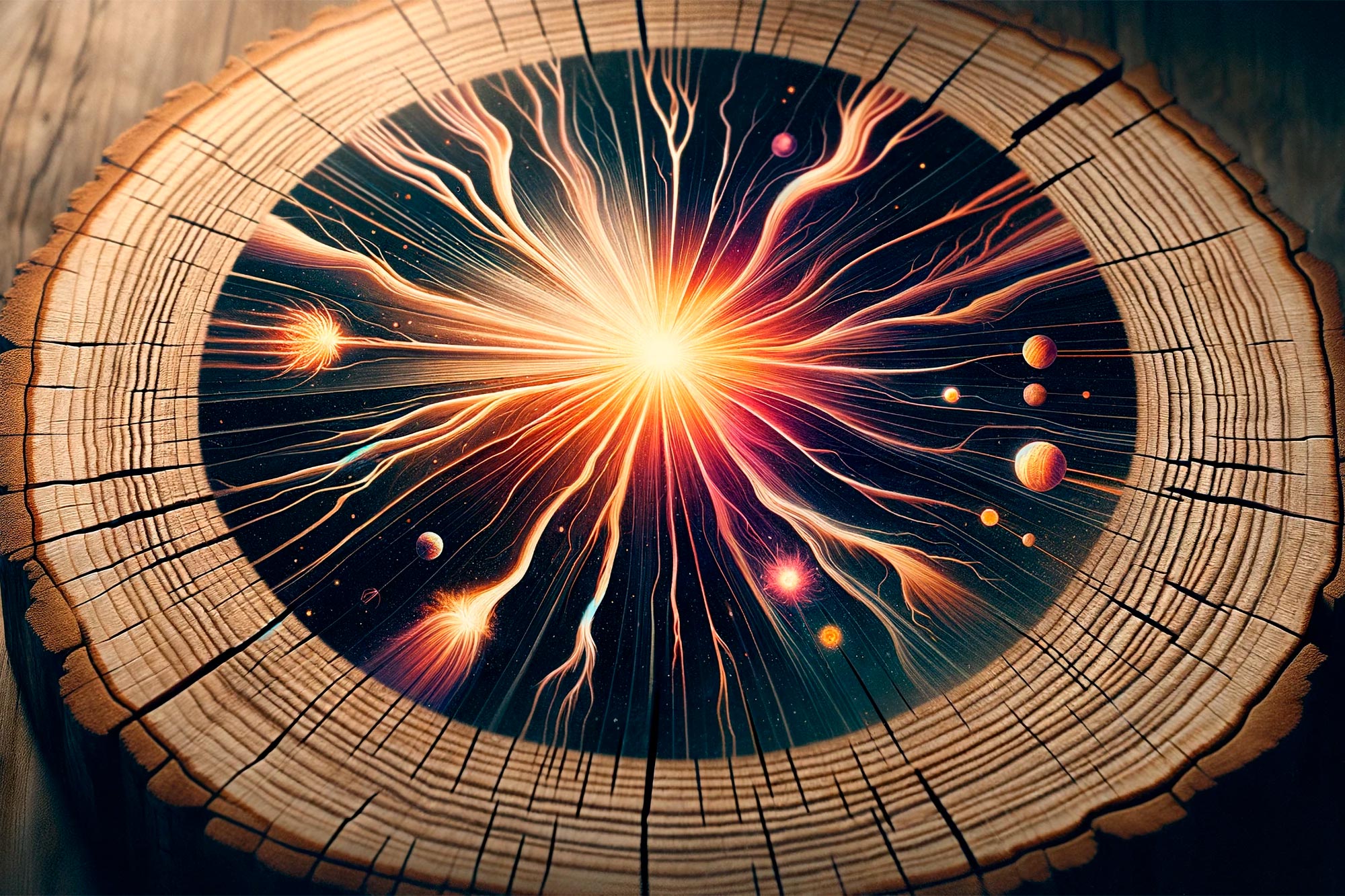
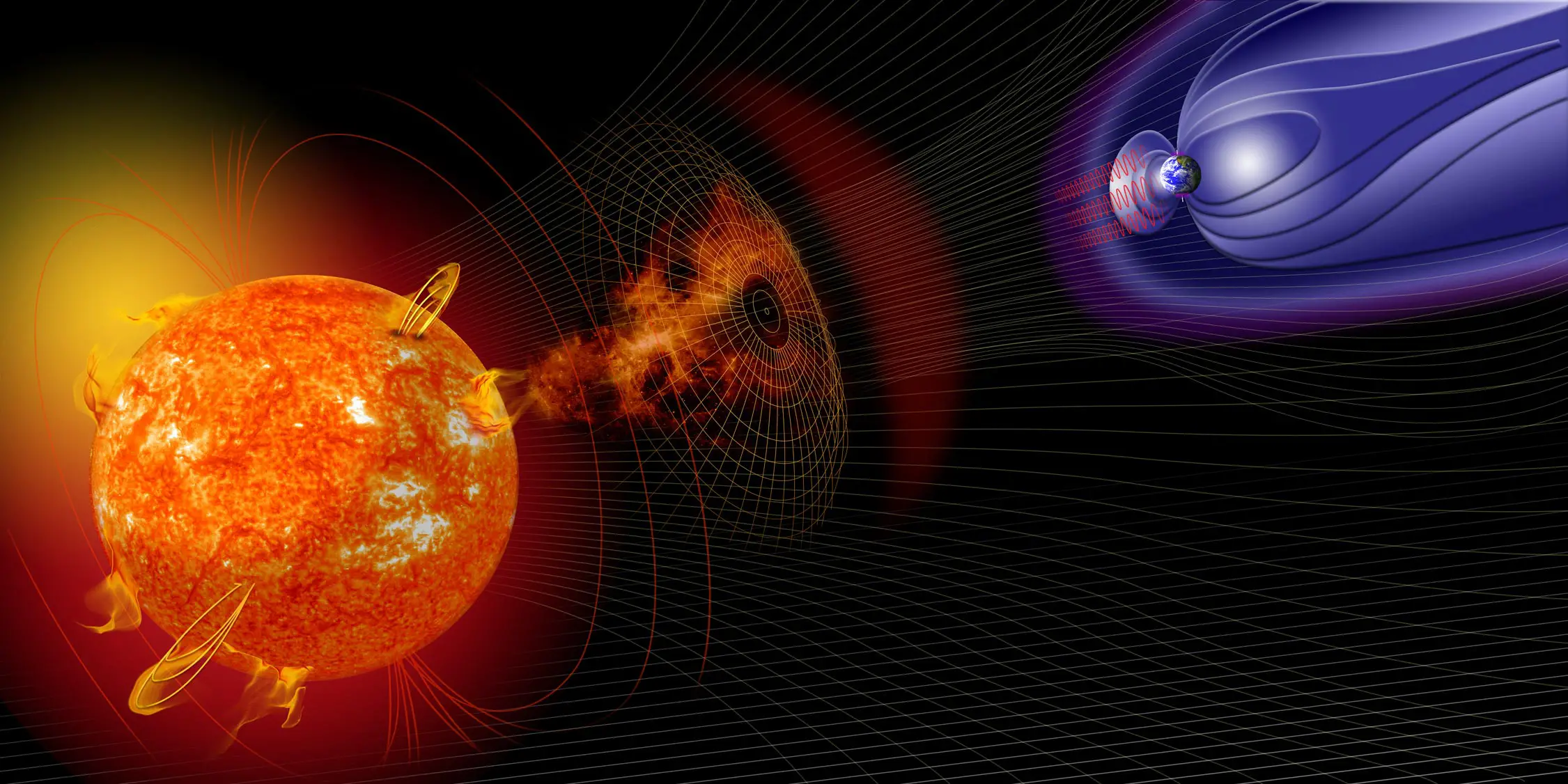
Supernovae's Potential Role in Earth's Past and Future Climate Changes
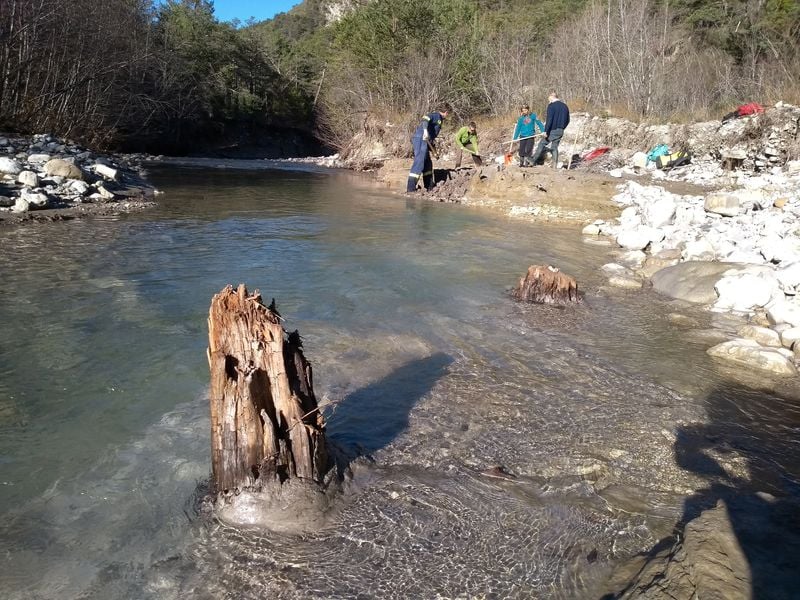
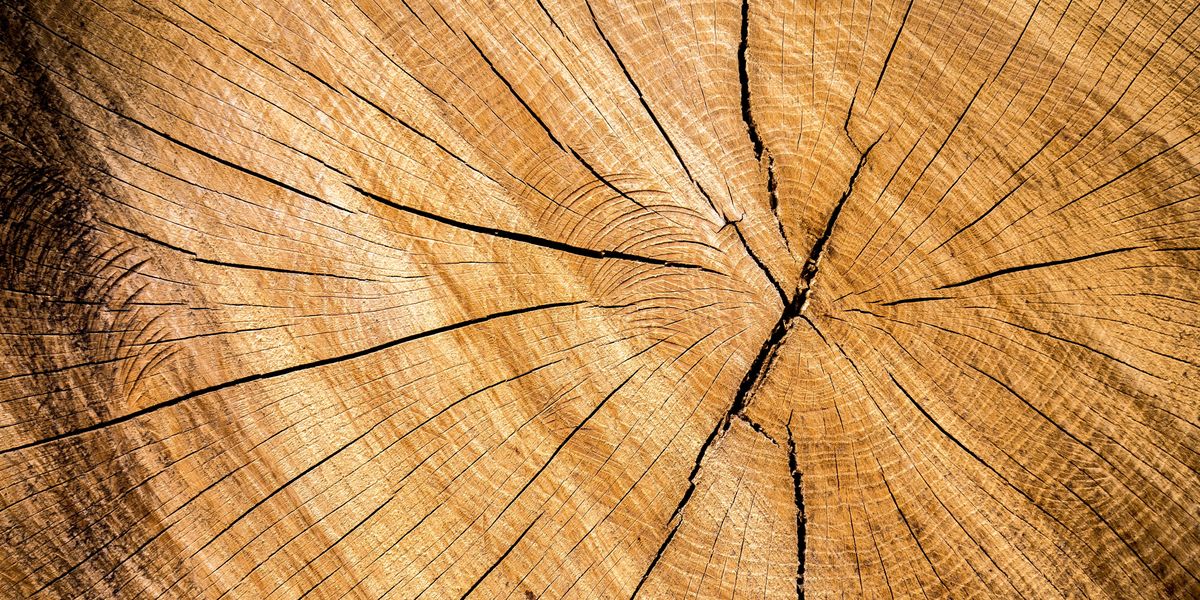
Research suggests supernovas may have caused significant climate changes on Earth in the past by damaging the ozone layer and affecting greenhouse gases, with potential implications for future events as nearby stars like Betelgeuse go supernova. Evidence from space telescopes and tree rings supports this theory, highlighting the importance of understanding supernova impacts on our planet.