8 Beauty Mistakes to Avoid for a Youthful Look
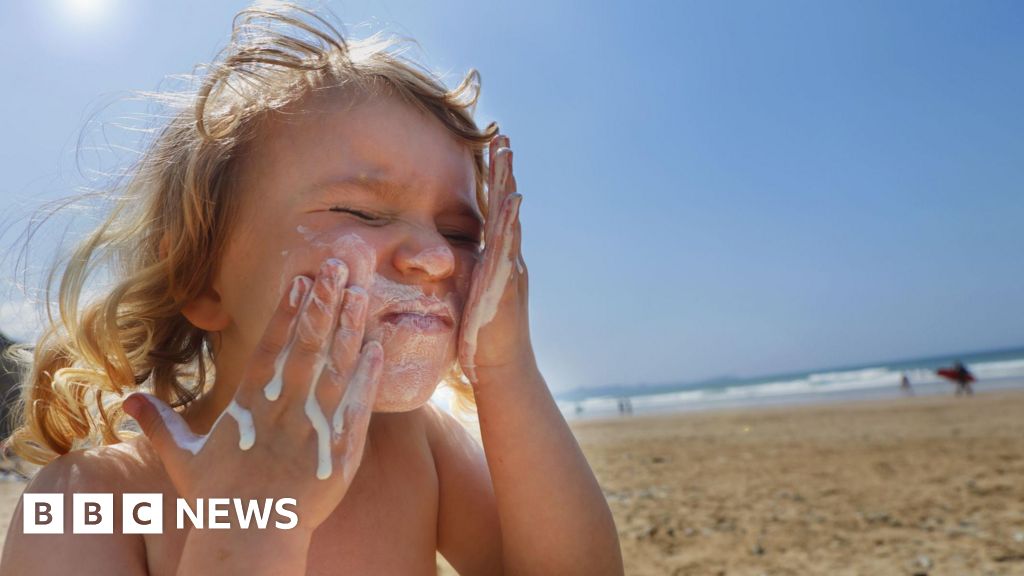
The article highlights eight common beauty mistakes that accelerate aging, such as neglecting sunscreen, sleeping with makeup on, over-exfoliating, neglecting neck and hands, using hot water on the face, touching the face frequently, using expired products, and following every skincare trend. Avoiding these habits and sticking to simple, proven routines can help maintain a youthful appearance and prevent premature aging.