Lego Unveils Sensor-Enabled Smart Bricks for Enhanced Star Wars Play
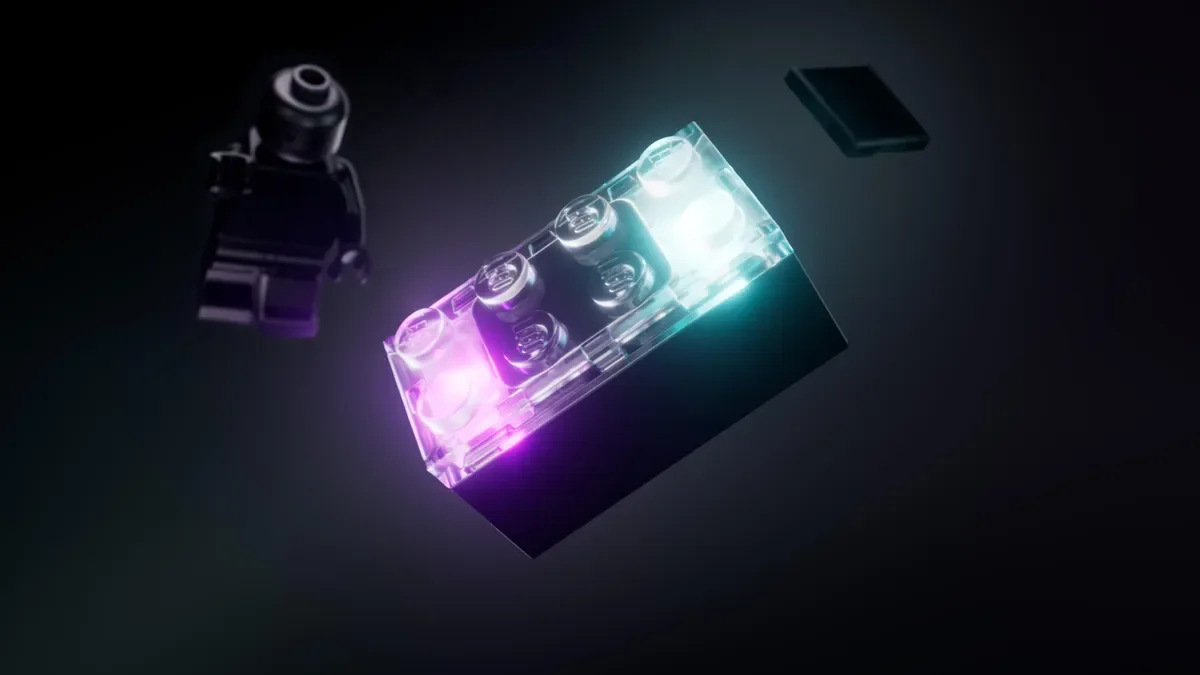
Lego is introducing new Smart Bricks with advanced sensor technology at CES 2026, capable of recognizing other bricks, activating effects, and playing music, with upcoming Star Wars sets that will feature interactive lights and sounds, enhancing play experiences with smart, connected components.