Common regulatory variant in meiosis genes links crossover control to maternal aneuploidy risk
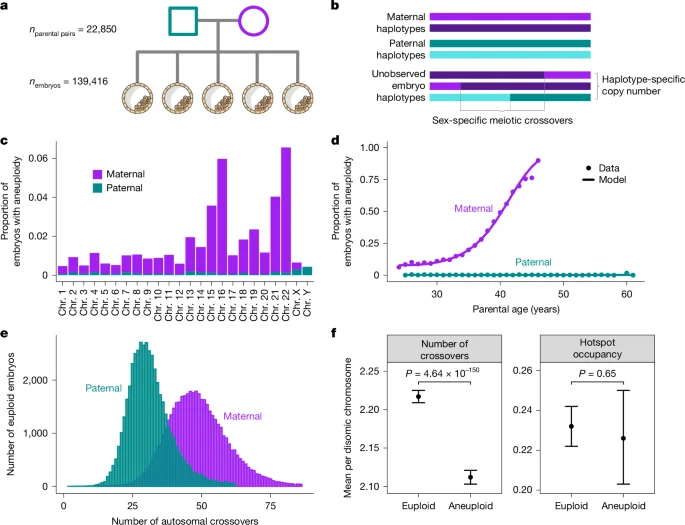
A large IVF-PGT analysis (139,416 embryos, 22,850 parental sets) maps crossovers and meiotic aneuploidy at scale and finds a common non-coding haplotype in SMC1B that associates with both lower maternal recombination and higher maternal meiotic aneuploidy, supported by functional assays and TWAS implicating C14orf39 and ubiquitin ligases CCNB1IP1/RNF212. SNP heritability for aneuploidy is negligible, suggesting environmental and rare-variant effects, while an inverse link between recombination rate and aneuploidy emerges. Evolutionary modelling suggests the risk allele is ancient and common, with complex fitness dynamics that can maintain it in populations. The work reveals a shared genetic basis for recombination and aneuploidy, with implications for fertility and genome evolution.