From glow to qubits: fluorescent proteins become inside-cell quantum sensors
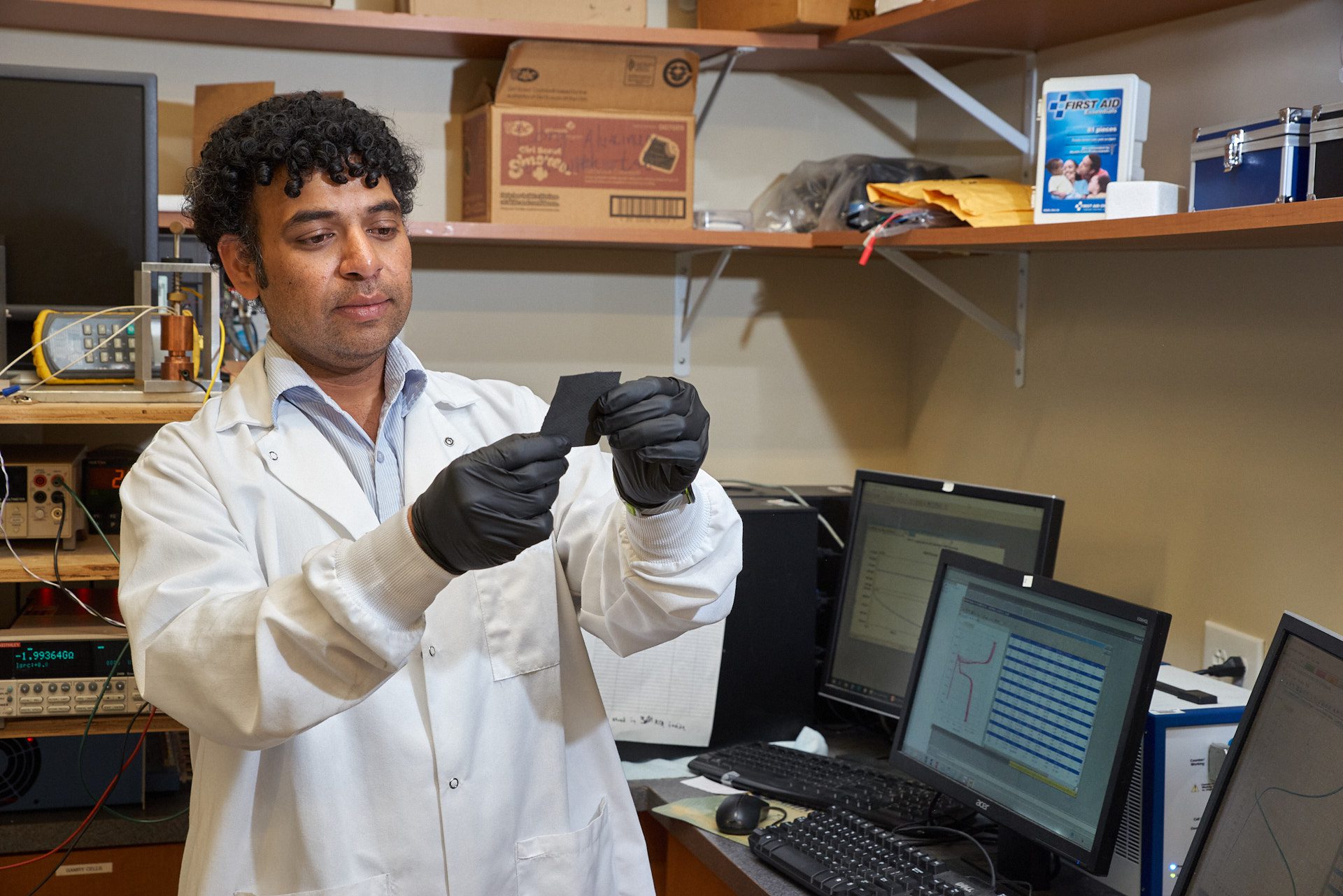
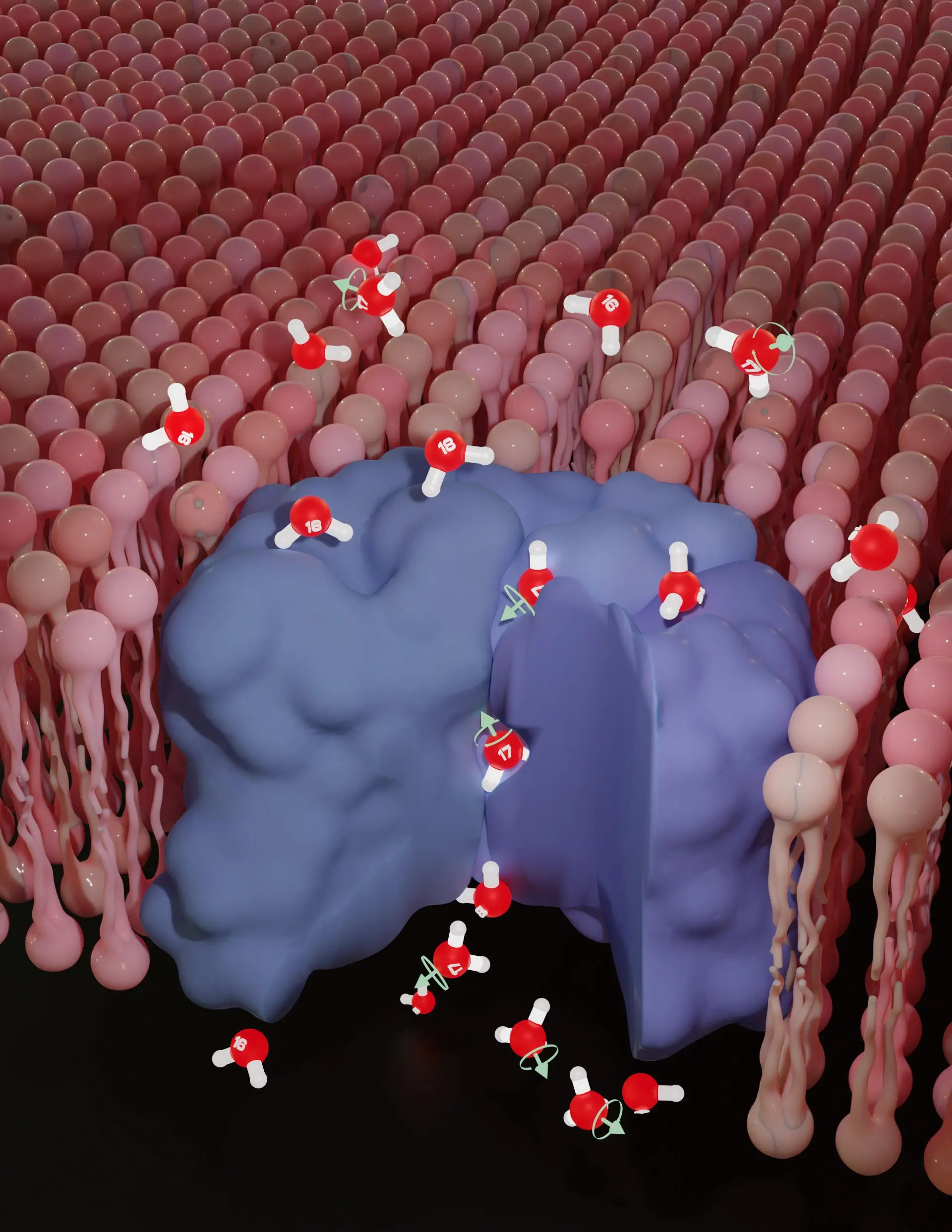
Researchers are turning fluorescent proteins into qubits to enable quantum sensing inside living cells, offering the potential for ultra-sensitive imaging of magnetic fields, neural activity and cellular stress. While proof-of-principle work exists and proteins are easier to place precisely in cells than NV-diamond sensors, challenges remain in protein stability and boosting sensitivity for robust biomedical applications.