Musk Pushes Public Medical Data to Train Grok, Triggering Privacy and Accuracy Concerns
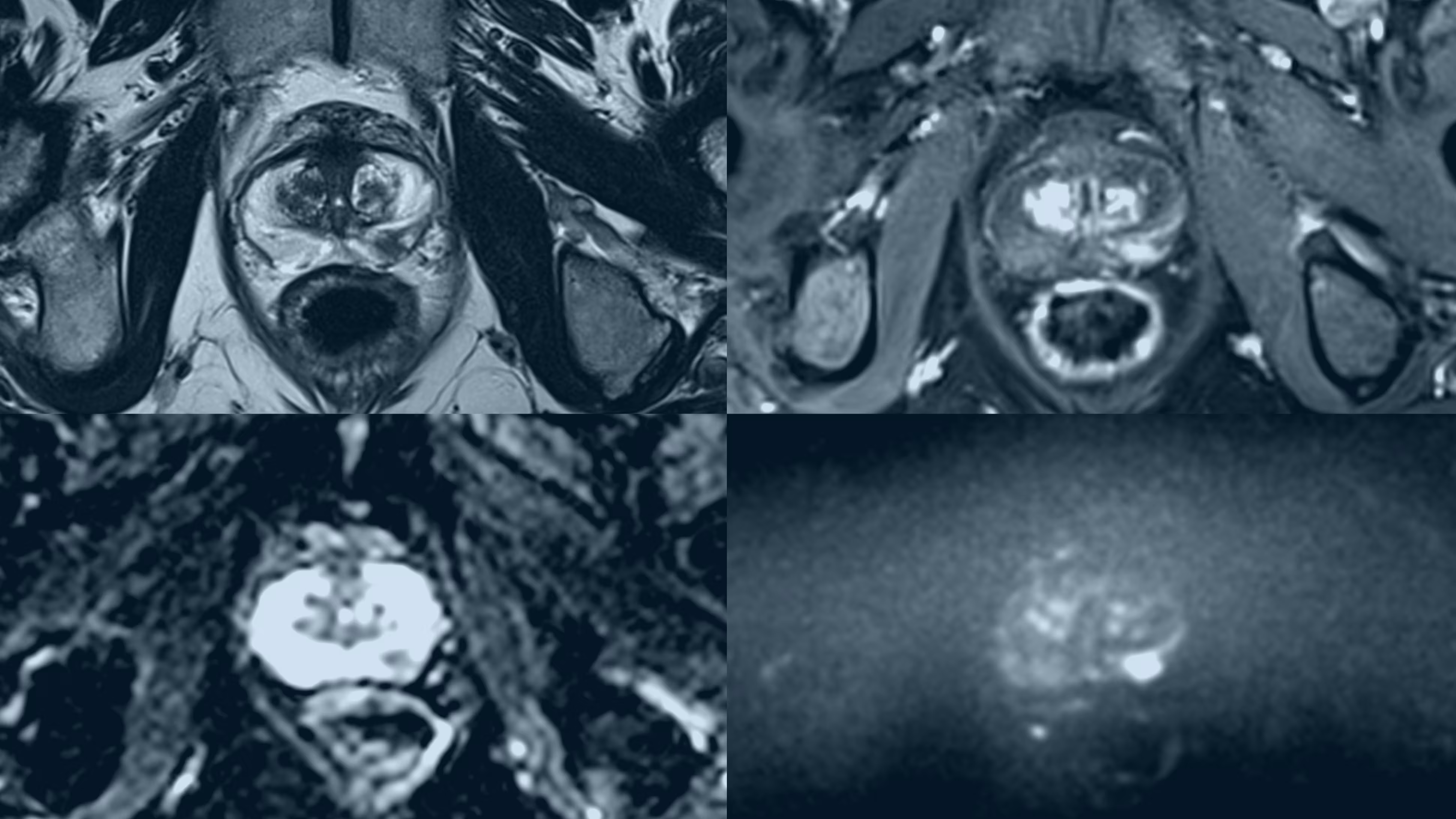
Elon Musk urged X users to upload medical data—including X-rays, MRIs and CT scans—to Grok to train the AI in interpreting images, a plan critics say risks patient privacy since social-media shares aren’t HIPAA-protected and data may not reflect diverse patient populations; Grok’s diagnostic accuracy remains mixed amid competition from health-focused AI like OpenAI’s ChatGPT Health.