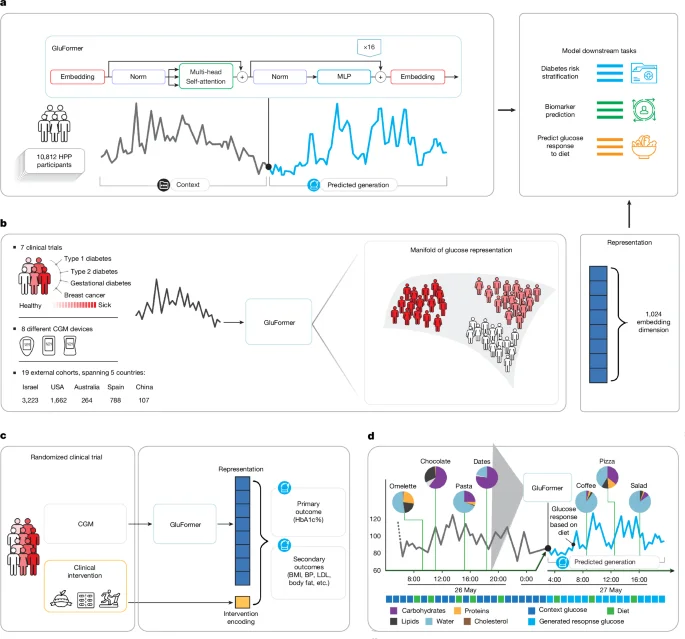
GluFormer: A universal model for decoding glucose patterns across diverse populations
Researchers introduce GluFormer, a self-supervised, autoregressive foundation model trained on over 10 million CGM measurements to learn transferable glucose representations across 19 external cohorts spanning 5 countries and multiple devices. The learned representations improve forecasting of glycemic metrics, stratify prediabetes progression better than baseline HbA1c, and identify higher long-term diabetes and cardiovascular mortality risk than HbA1c in follow-up data. A multimodal extension incorporating dietary data can simulate plausible glucose trajectories and predict individual glycemic responses to food, suggesting GluFormer as a generalizable tool to advance precision metabolic health.