Cosmic predators: active black holes suppress star formation in neighboring galaxies
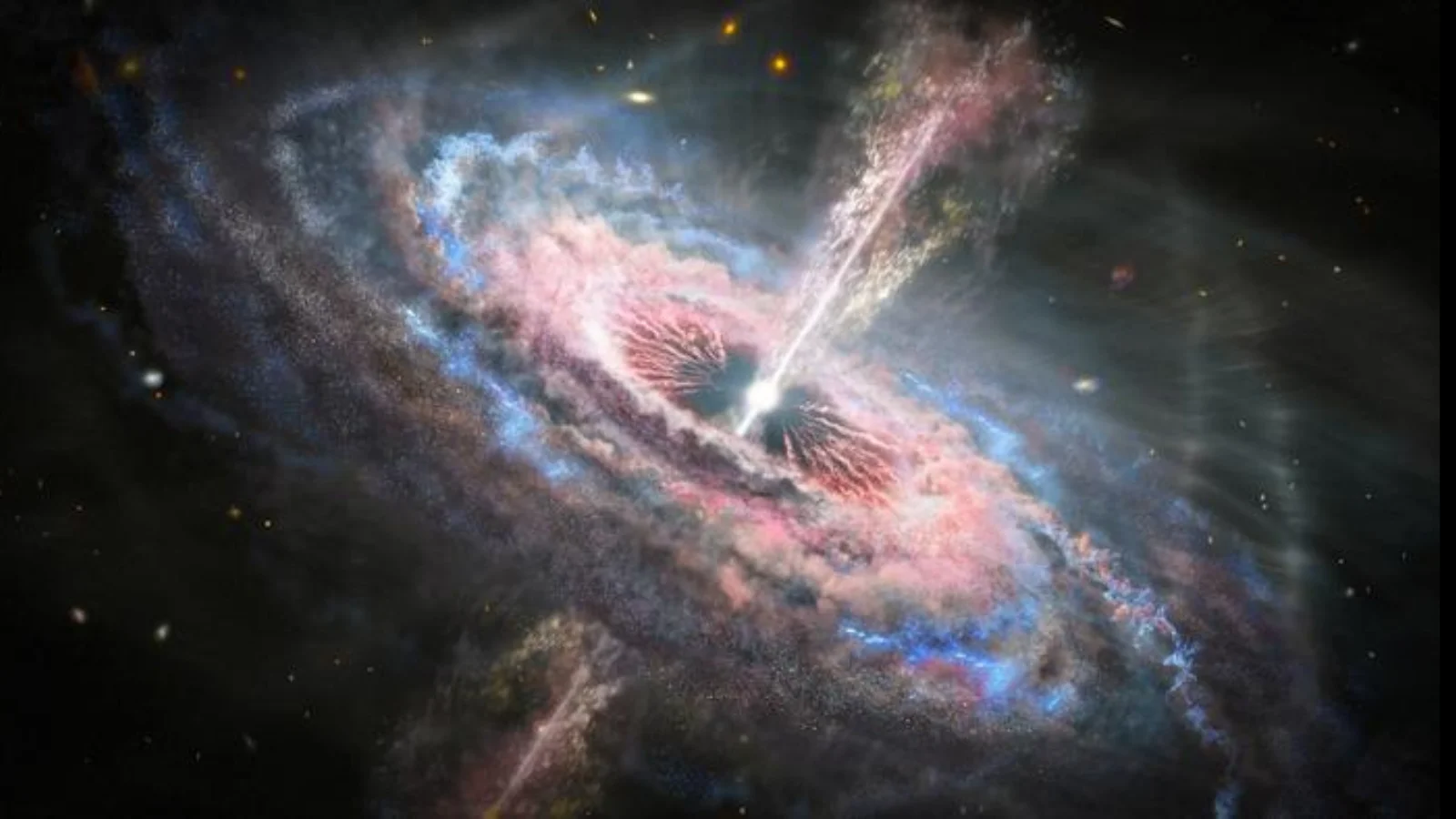
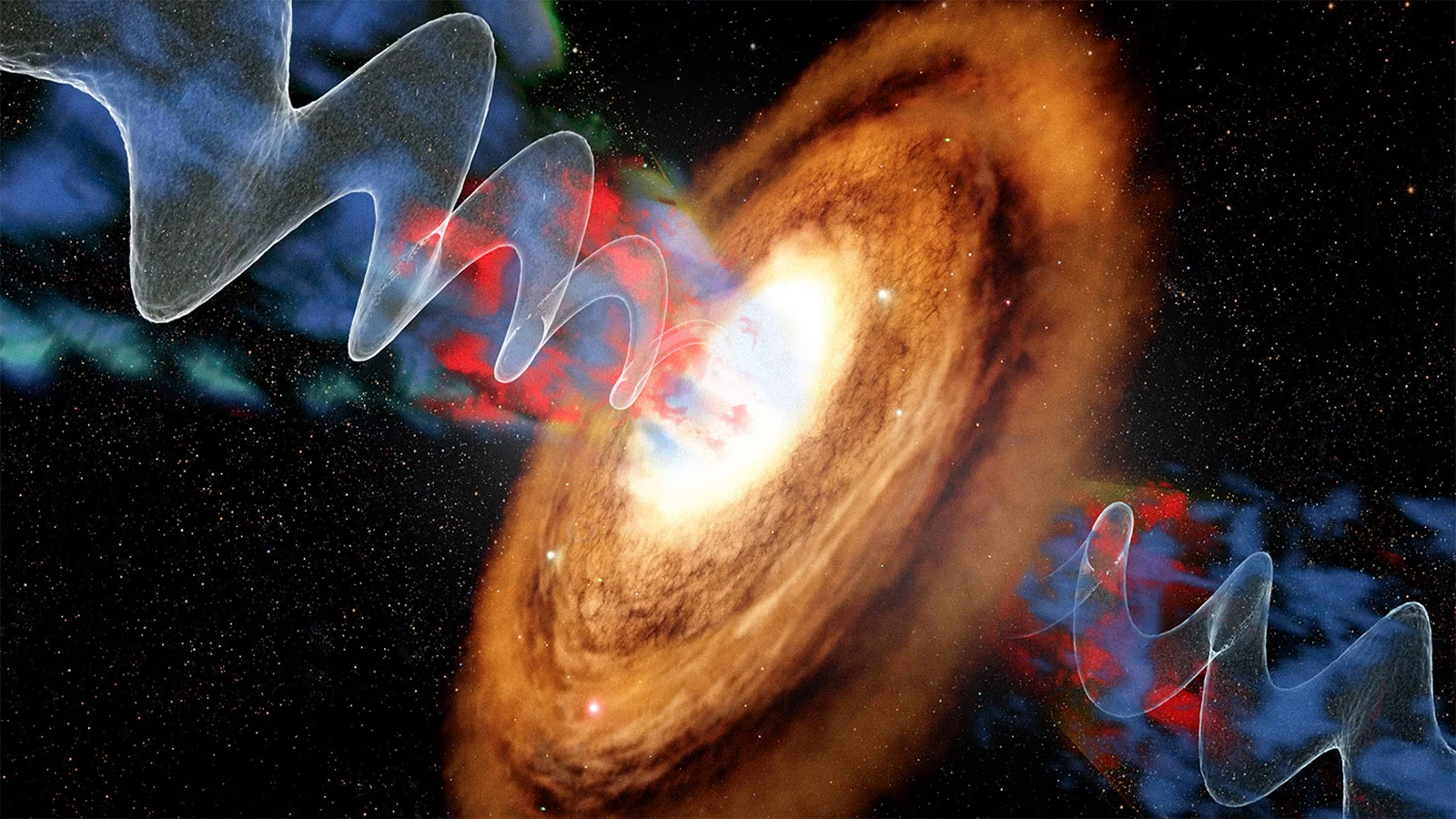
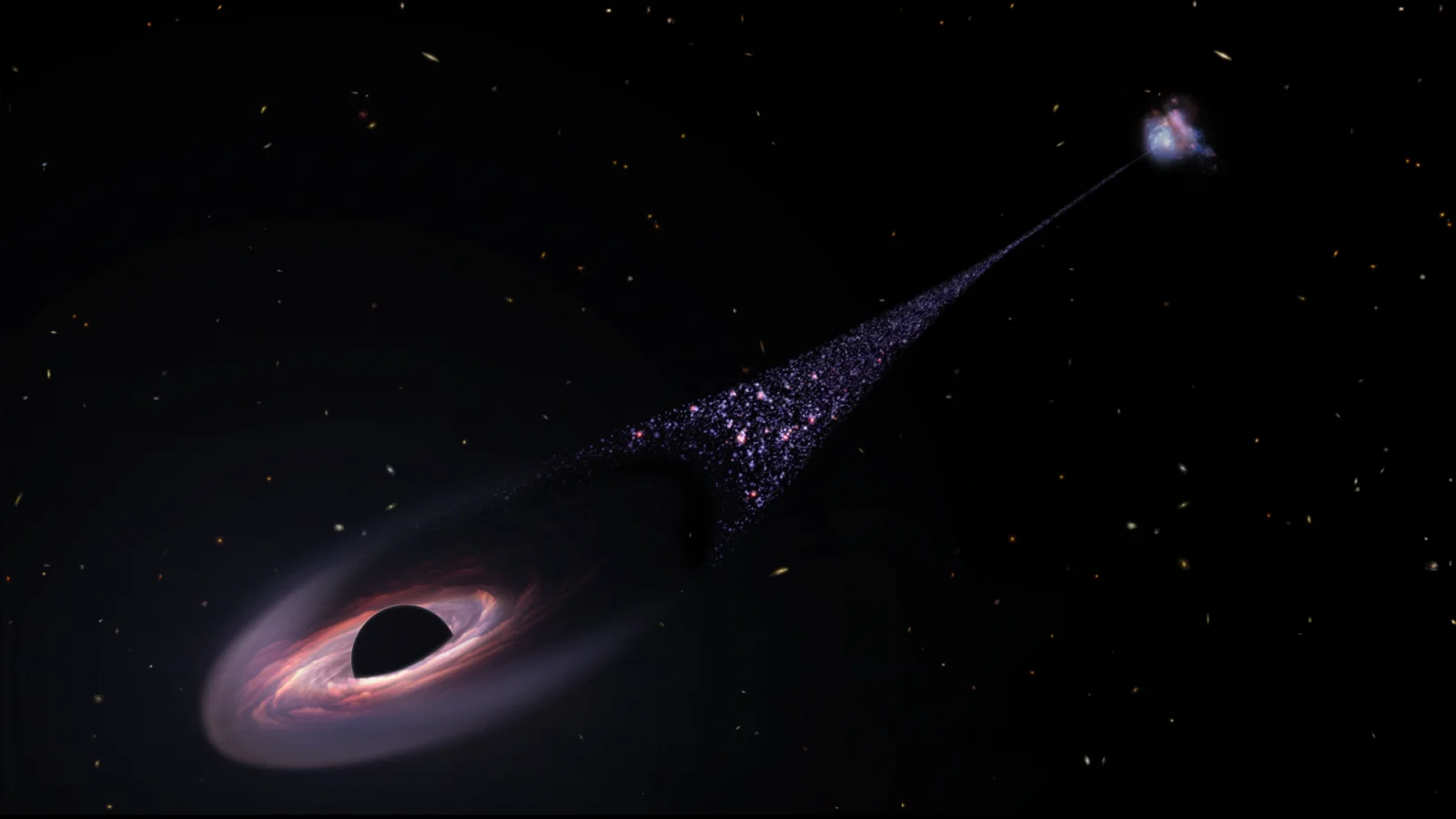
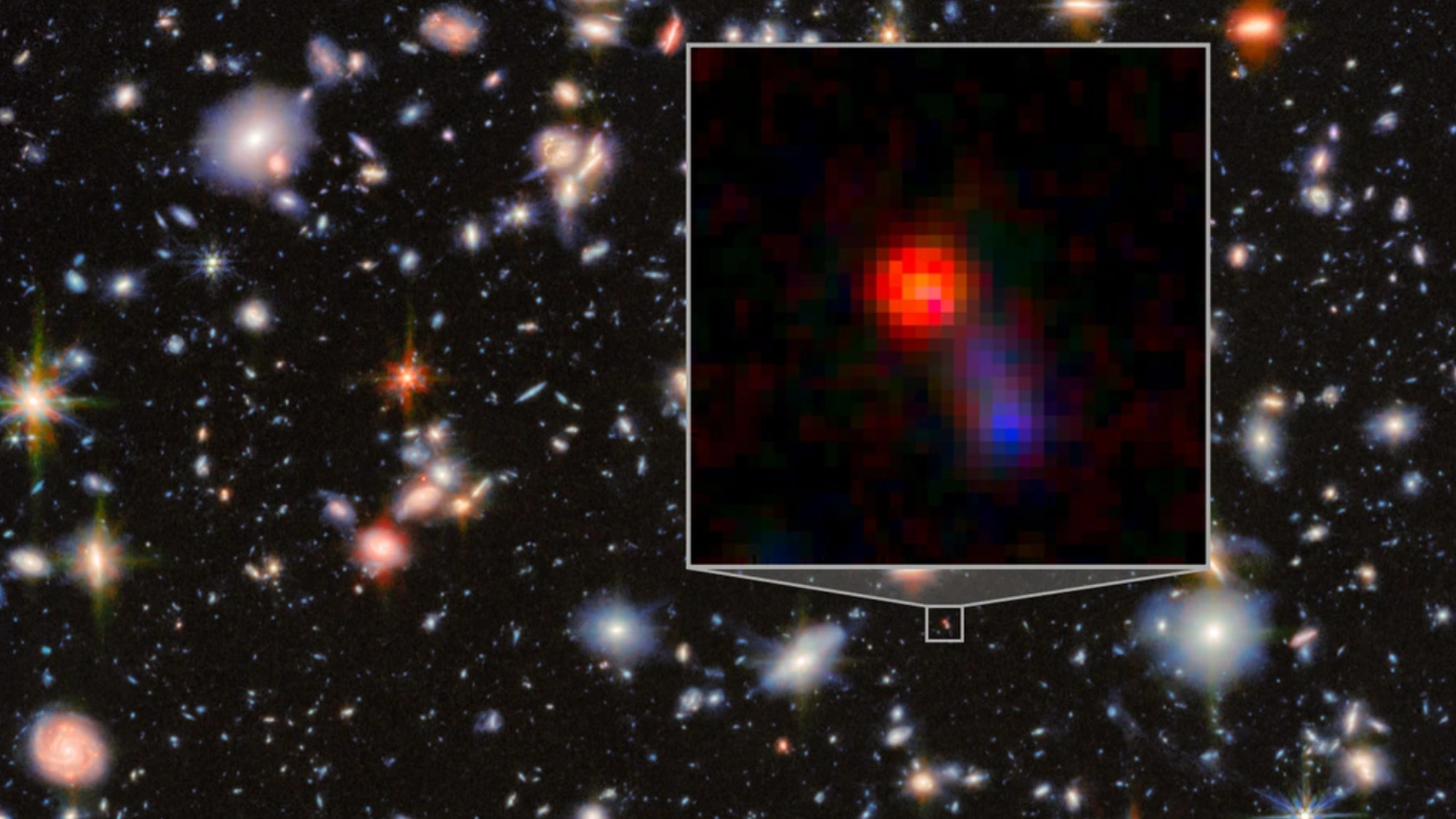
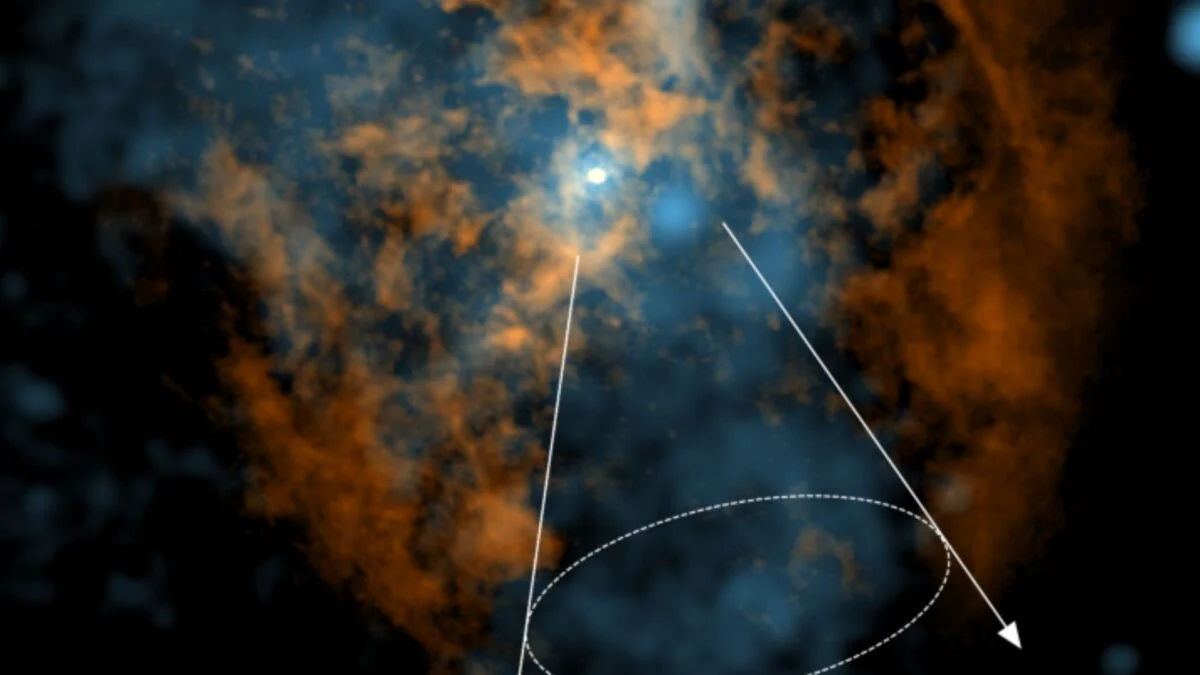
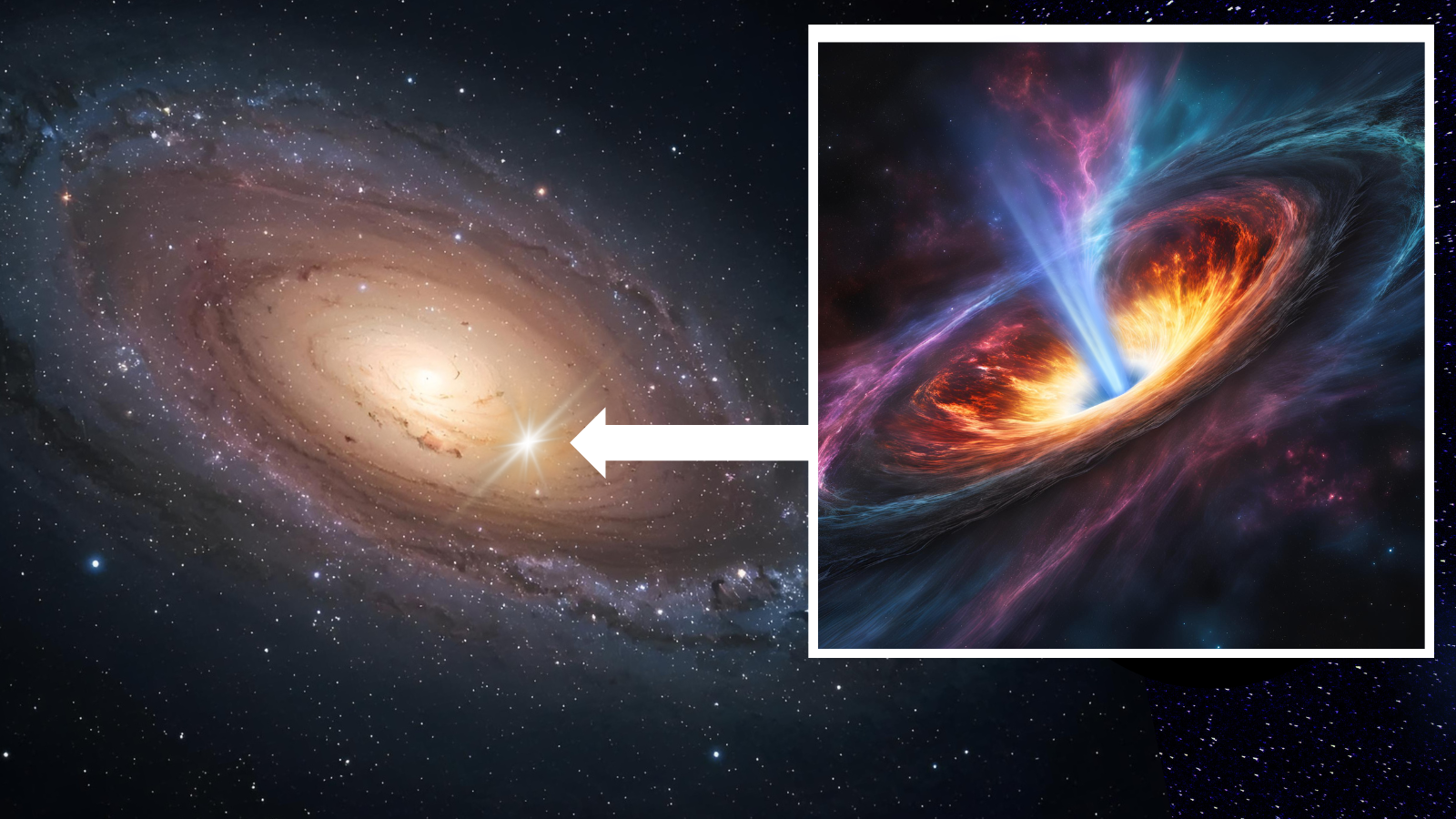
Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope found that one of the universe’s brightest quasars appears to quench star formation not only in its host galaxy but also in neighboring galaxies within about a million light-years. The study of quasar J0100+2802 showed reduced ionized oxygen in nearby galaxies, indicating suppressed star birth likely caused by intense radiation and outflows from the active supermassive black hole, suggesting a galactic “ecosystem” where massive black holes influence galaxy evolution beyond their own hosts, especially in the early universe.