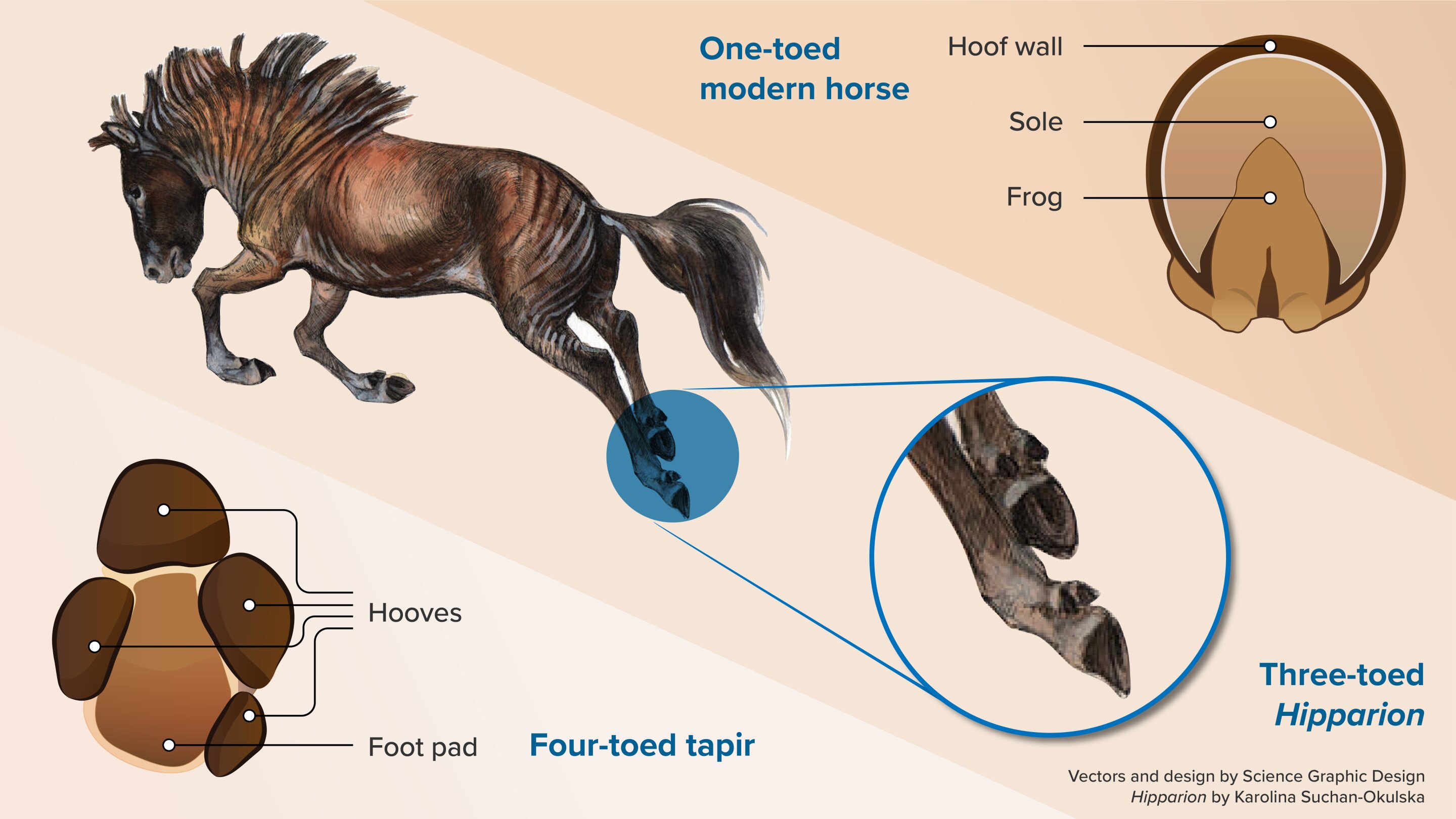
Moon Slowly Recedes, Extending Earth's Day by Fractions Each Year
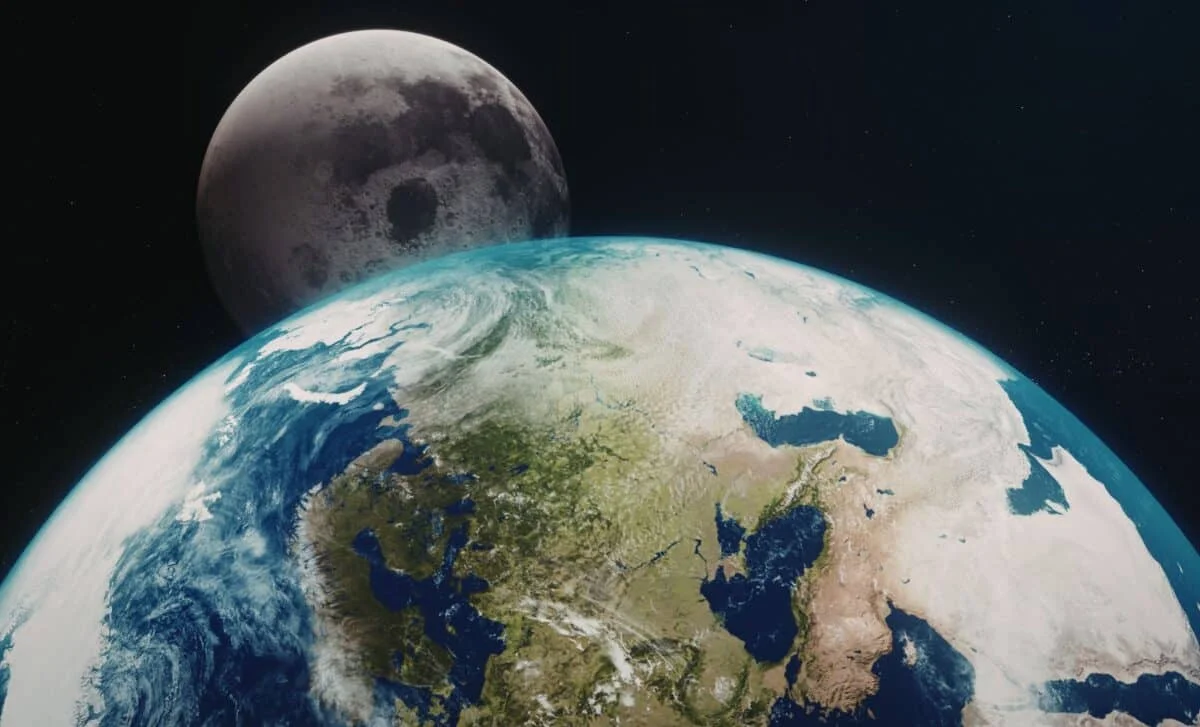
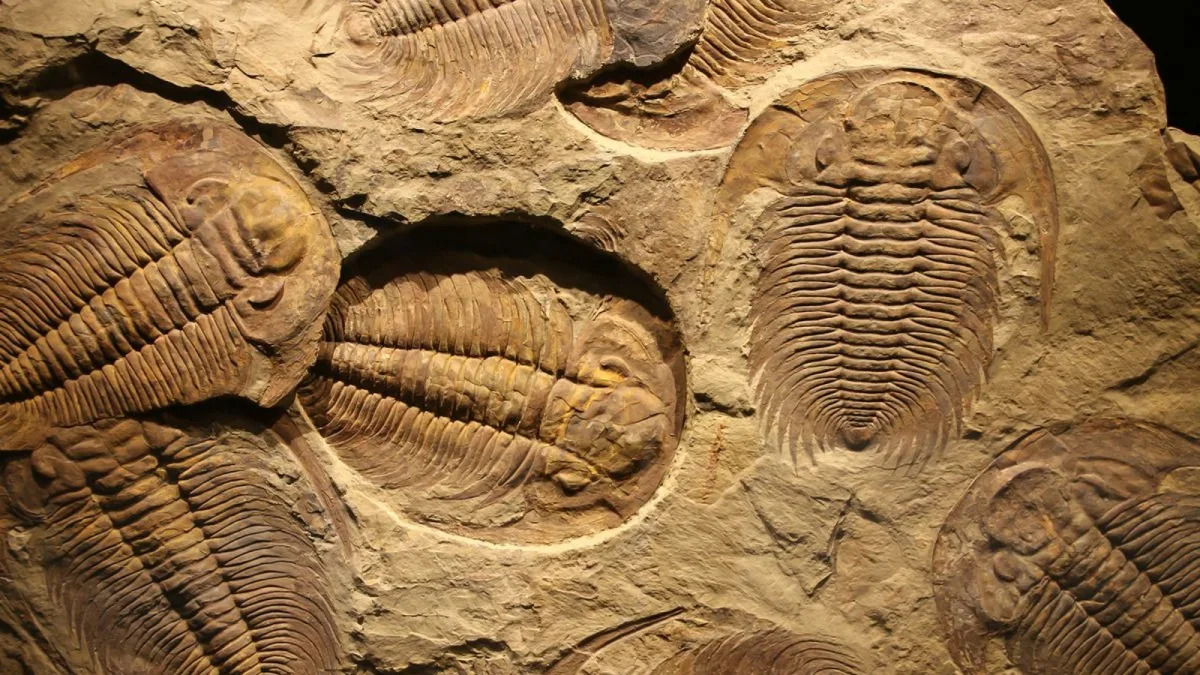
NASA measurements show the Moon is moving away from Earth at about 3.8 centimeters per year, transferring rotational energy from Earth to the Moon and gradually lengthening the length of a day. Fossil shells indicate shorter past days (roughly 23.5 hours around 70 million years ago), and the ongoing tidal evolution will continue to lengthen Earth's day by tiny amounts over millions of years.