NASA's Artemis II Mission Nears Launch, Marking a Historic Return to the Moon
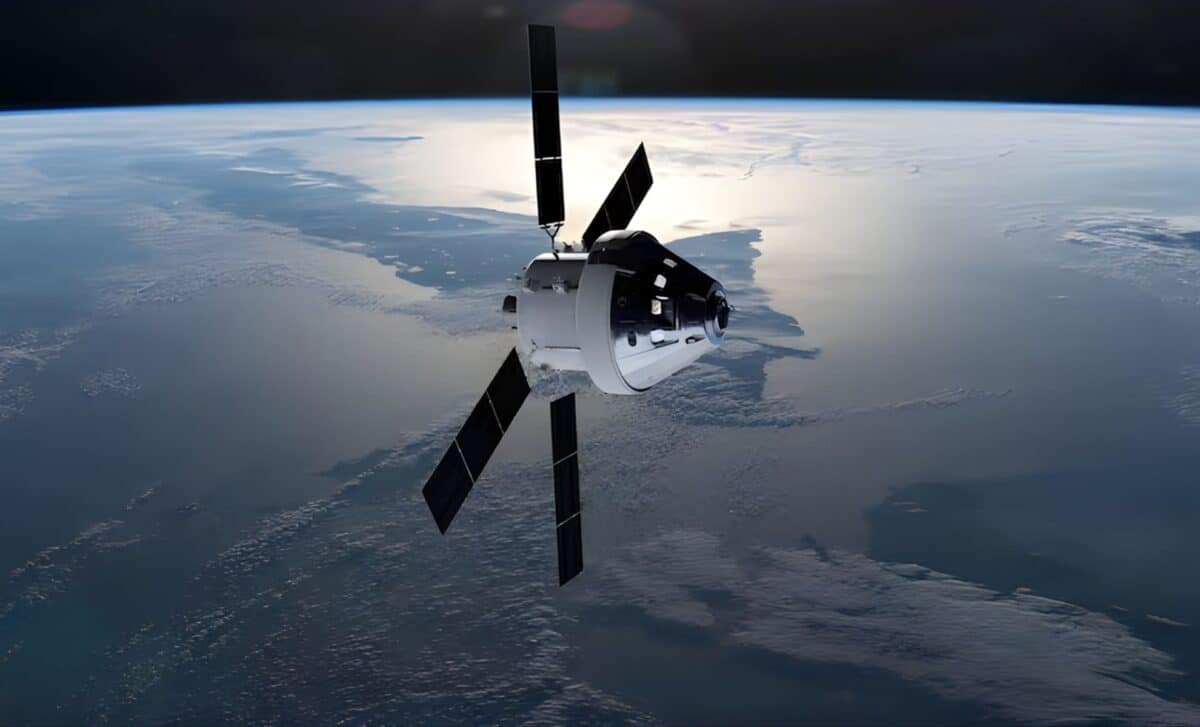
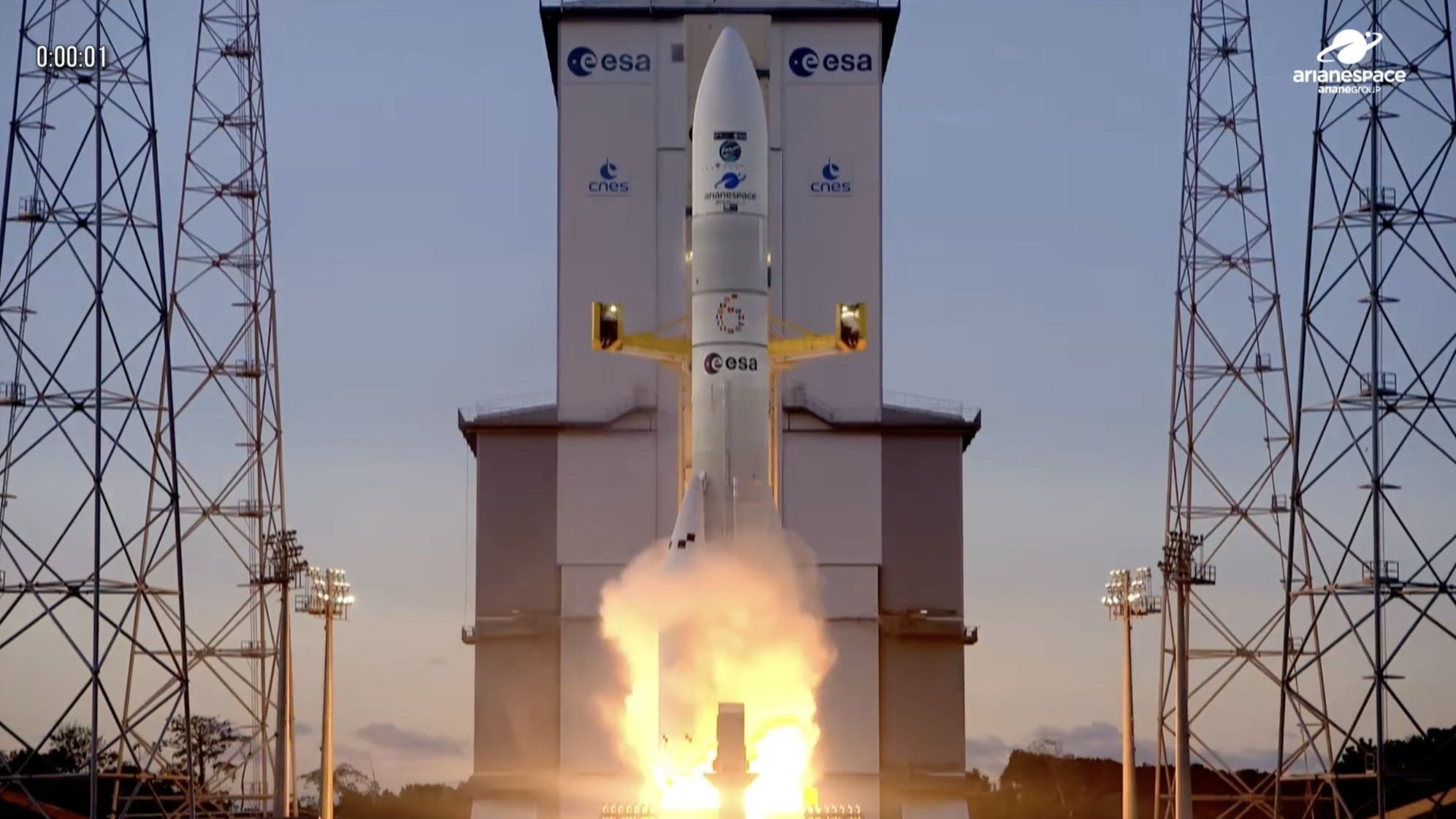
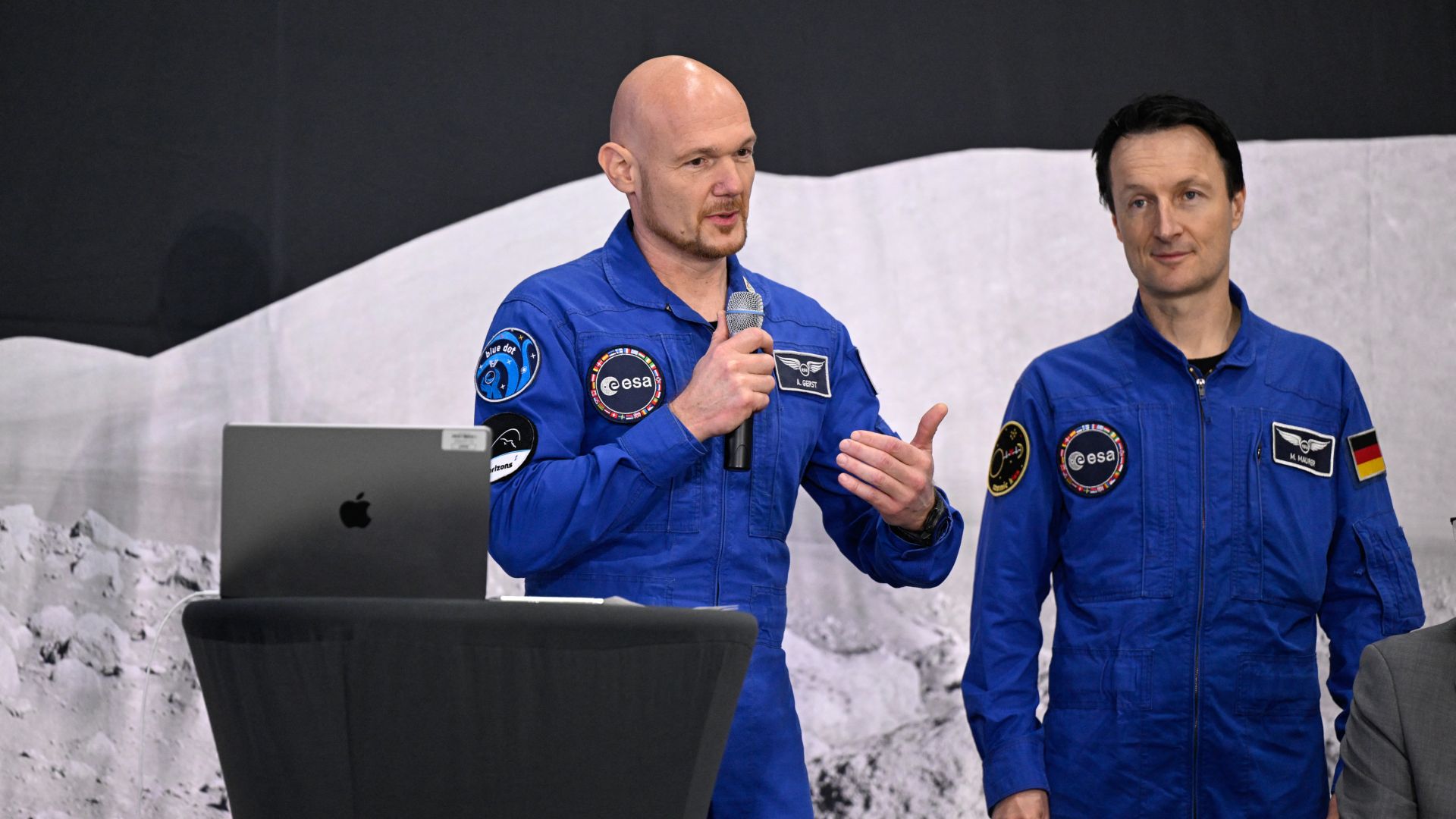
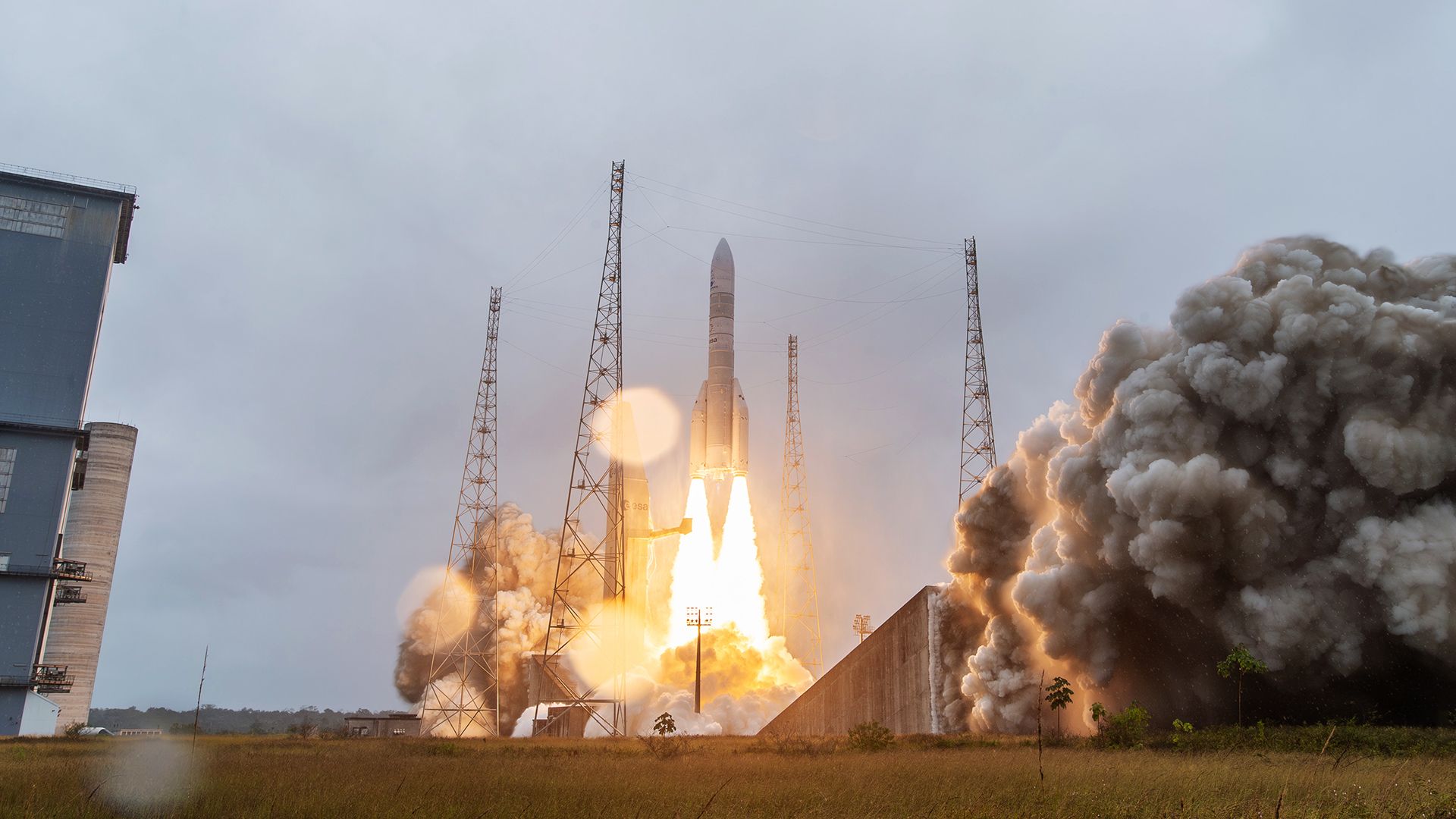
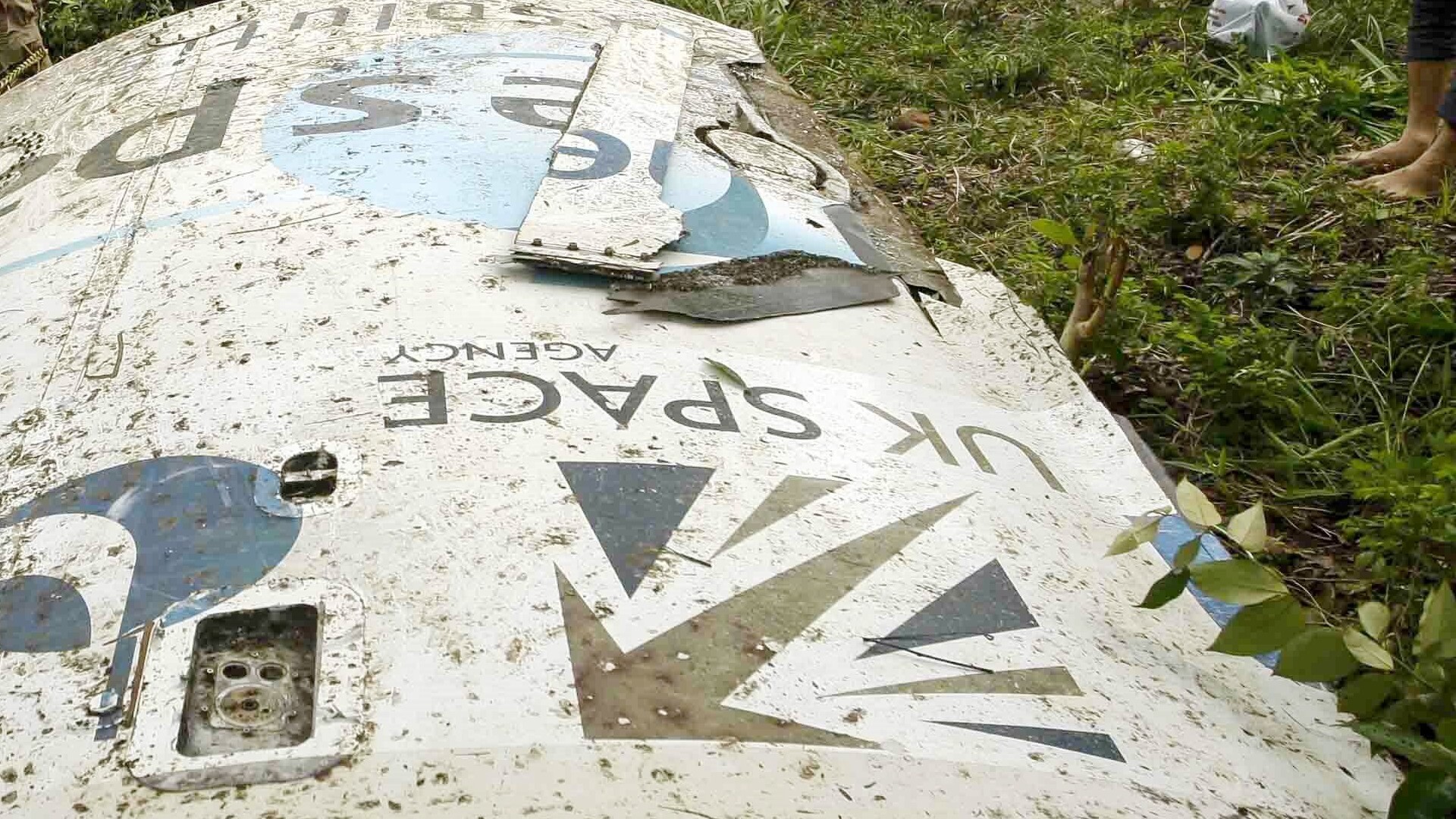
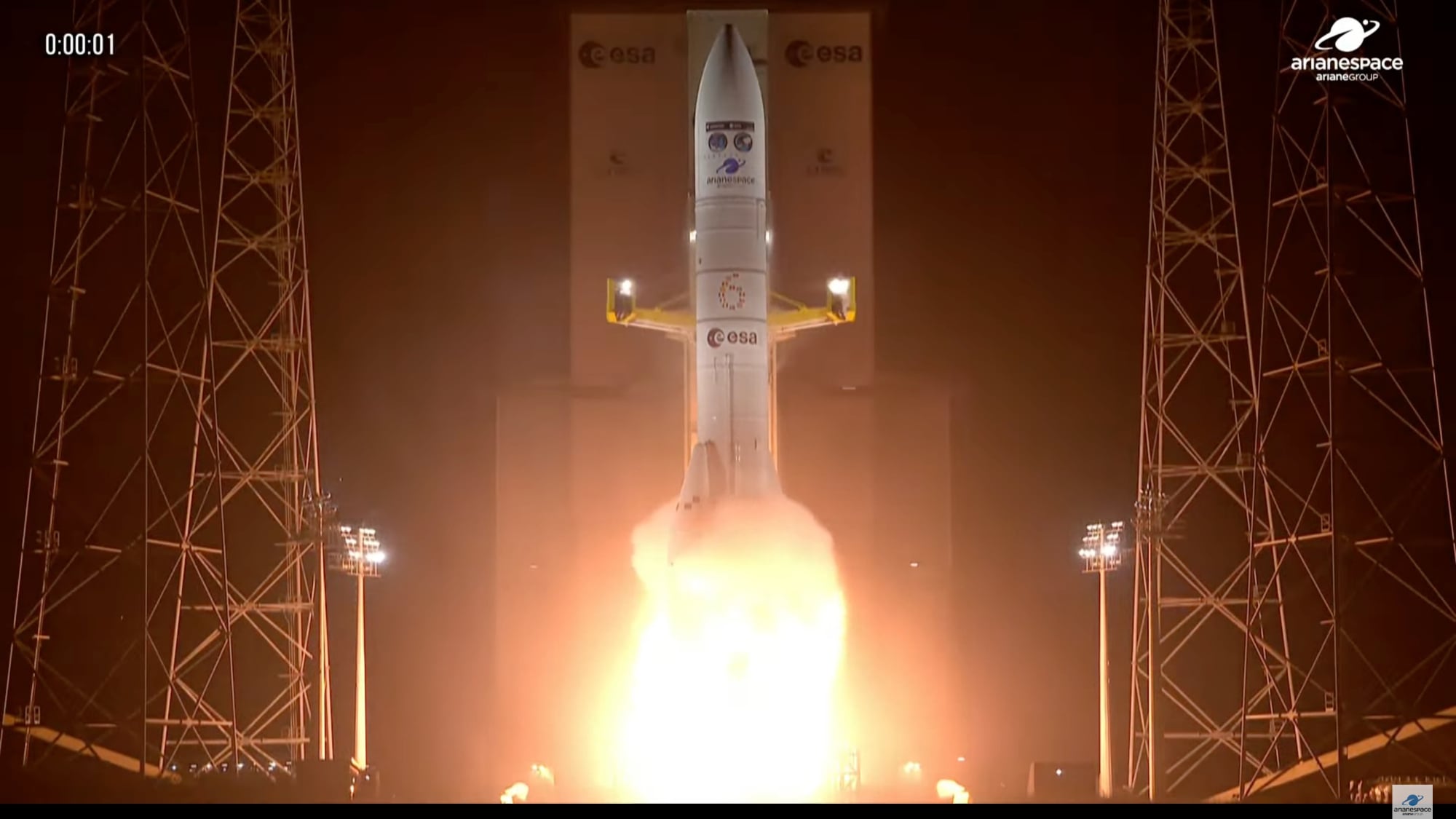
NASA's Artemis 2 mission, set for launch in 2026, will send four astronauts on a 10-day lunar flyby to test systems for future lunar landings, marking a significant step toward establishing a sustained human presence on the Moon, with European contributions playing a key role.