Trump pitches Big Tech to bankroll AI data-center power
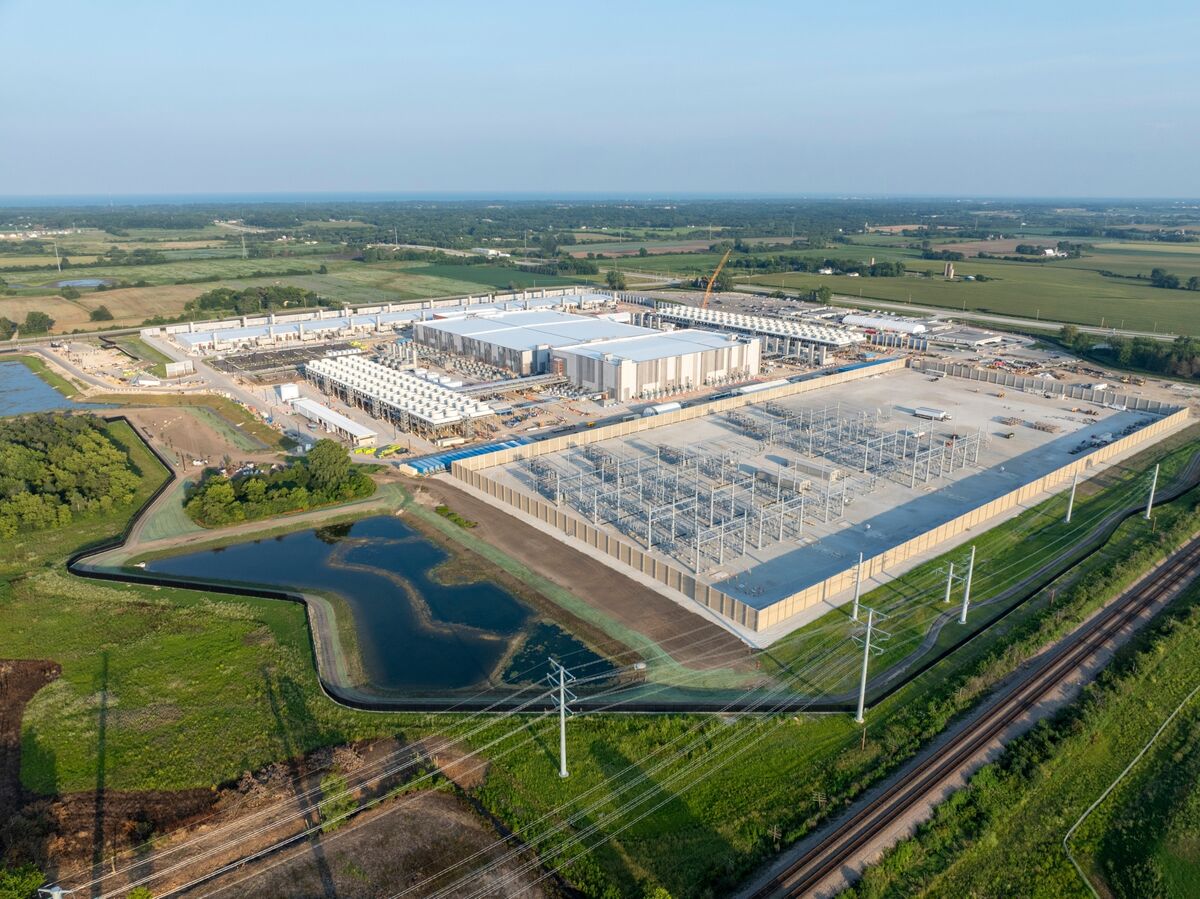
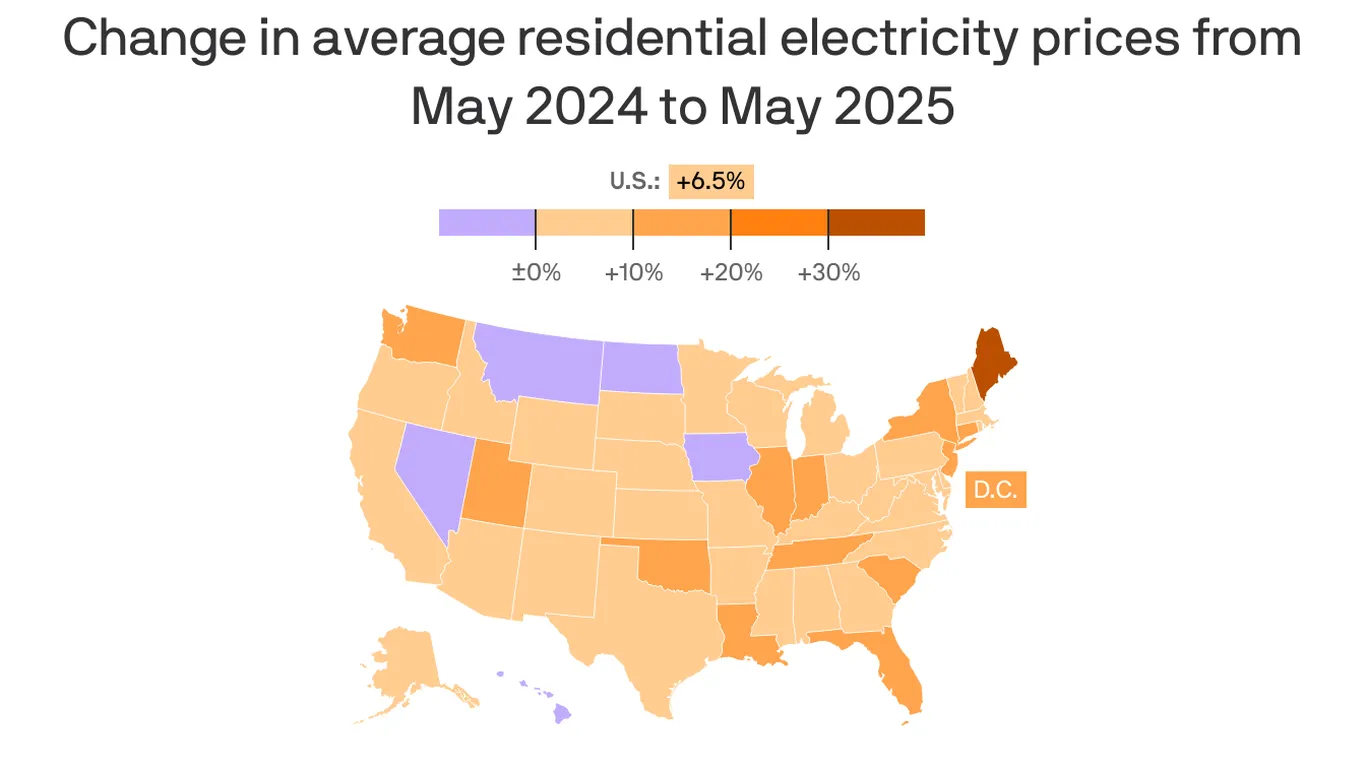
President Trump says he has secured a ‘rate payer protection pledge’ with Amazon, Google, Meta, Microsoft, xAI, Oracle and OpenAI to build or fund new electricity generation for AI data centers, with a March 4 signing event; details are scarce and enforcement questions loom, even as existing voluntary commitments and rising electricity costs intersect with growing data-center energy demand.