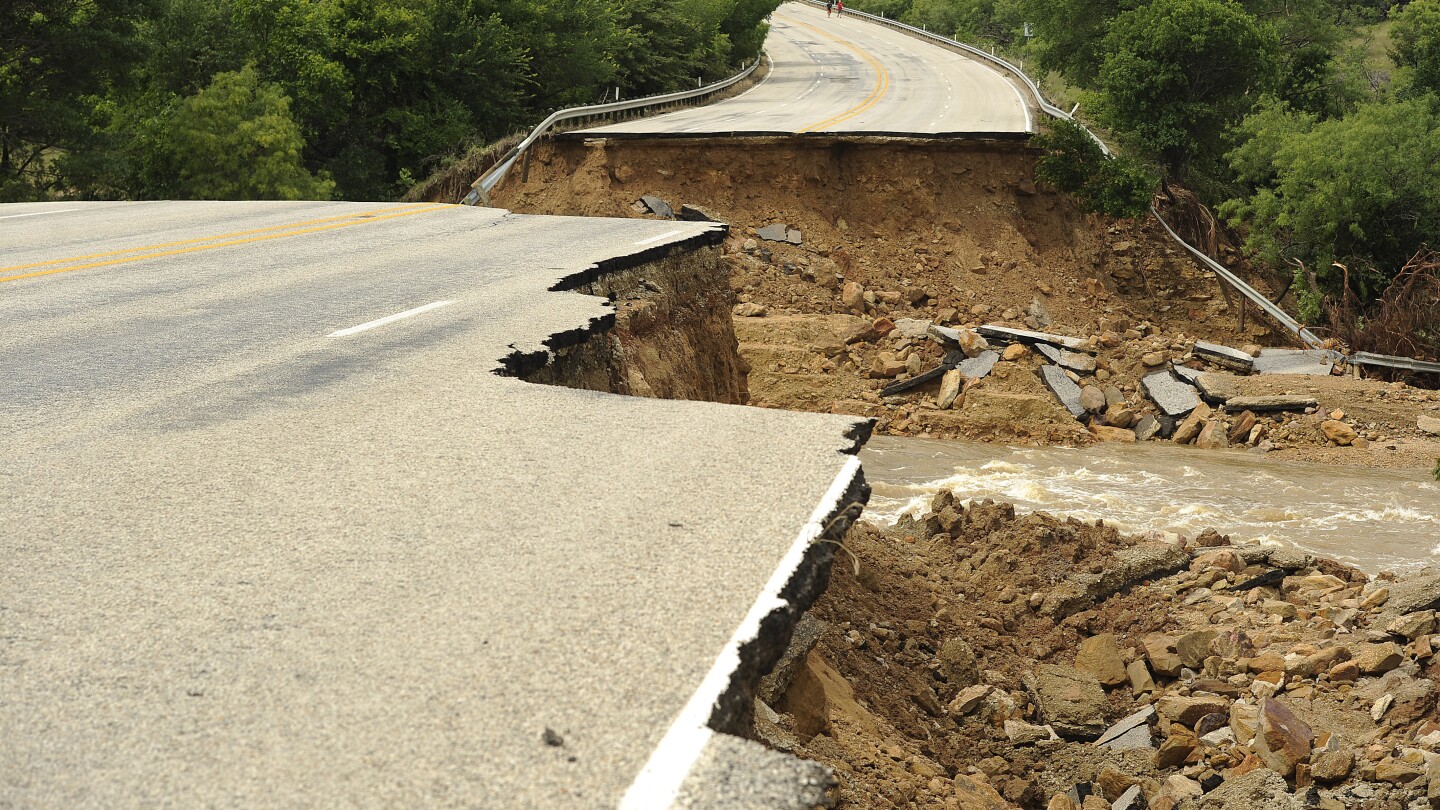
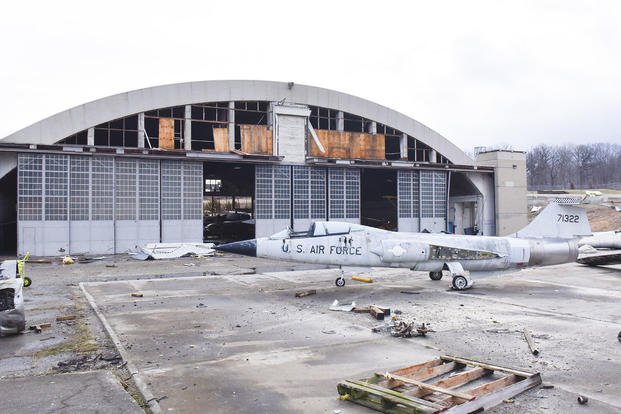
The Biden administration has awarded $830 million in grants to fund 80 projects aimed at strengthening the nation's infrastructure against the harmful impacts of climate change, particularly in areas affected by extreme weather events. The funds, part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, will improve bridges, roads, ports, rail, and transit across 37 states, Washington, D.C., and the Virgin Islands. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg emphasized the need for climate resilience, citing examples of infrastructure damage from extreme weather. The grants will support projects such as flood control, bridge replacement, stormwater infrastructure upgrades, and coastal management plans.