Jacksonville Doctor's Research to Aid NASA's Space Bone Studies
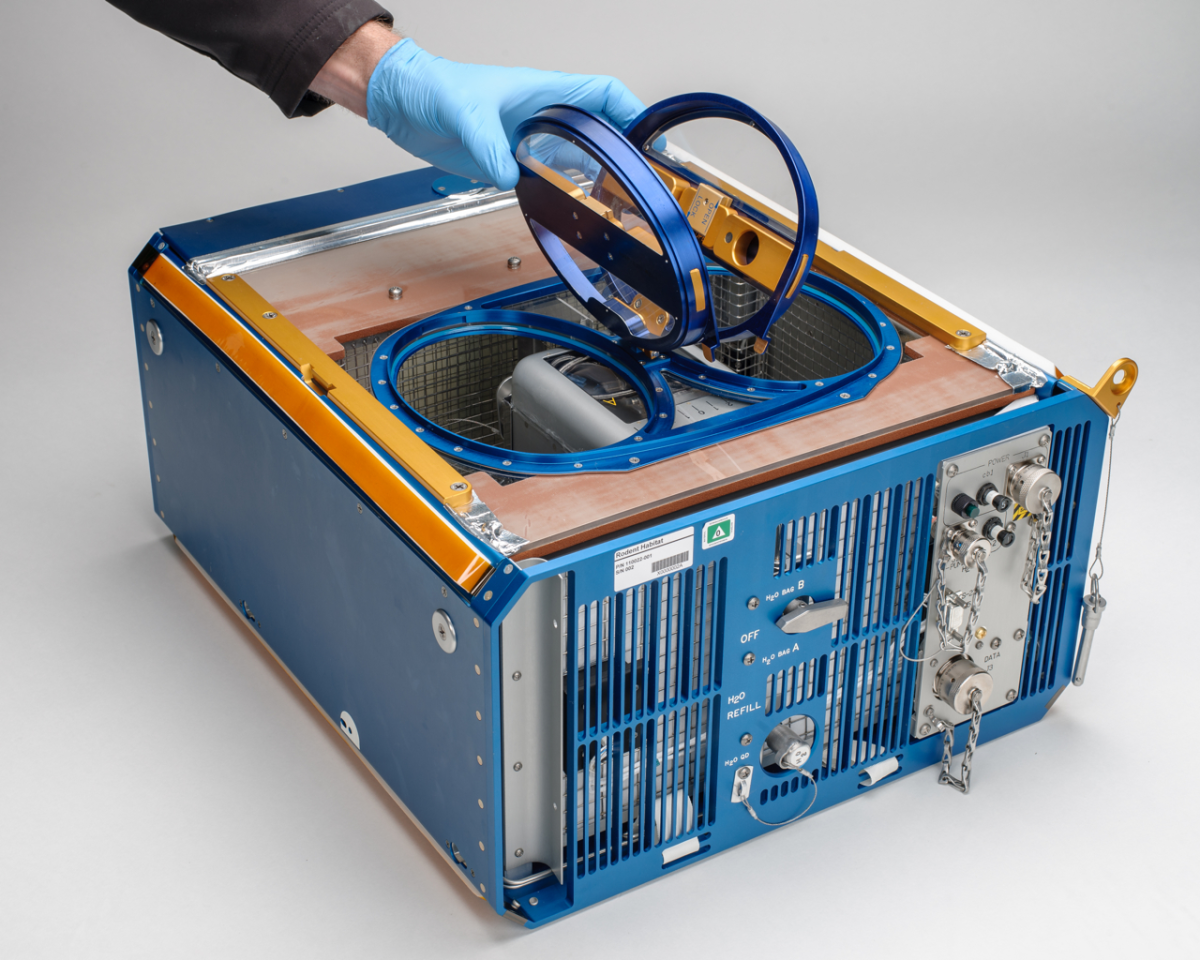
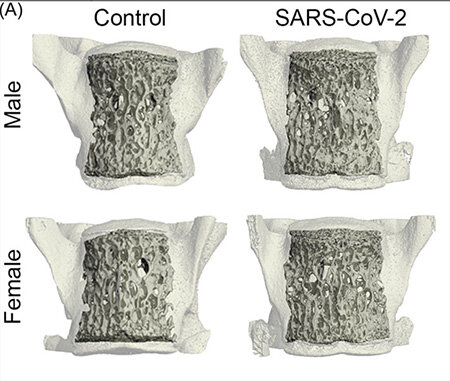
Jacksonville doctor Dr. Abba Zubair is leading research at Mayo Clinic that will be used by NASA during its upcoming space mission to study how microgravity affects bone-forming stem cells, aiming to develop treatments for bone loss conditions like osteoporosis and improve astronaut health during long spaceflights.