Two Weeks With a Glucose Monitor: From Sugar Jail to Data Overload
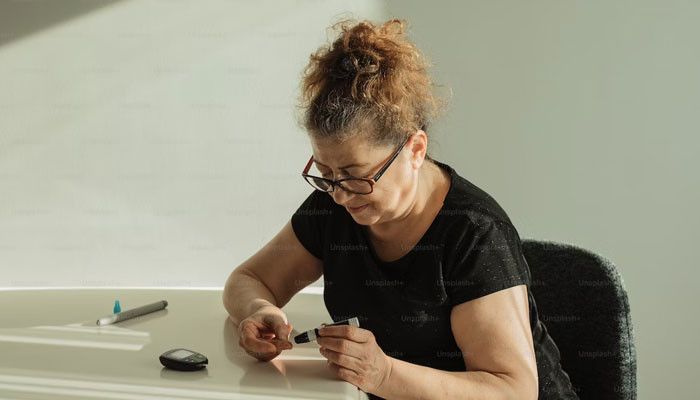
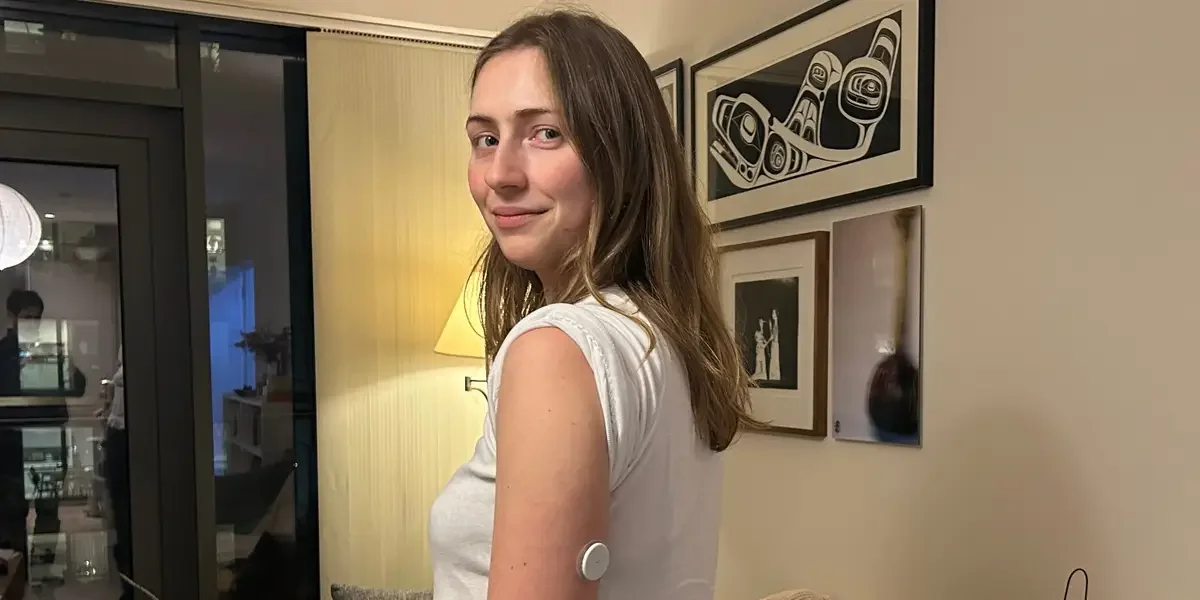
A health writer wore a continuous glucose monitor for two weeks to test if tracking glucose would boost energy. She found that some seemingly balanced meals caused spikes while some sweets didn’t, and the constant data led to guilt, obsession, and anxiety about “getting the line right.” The experience highlighted how CGMs can mislead non-diabetics and trigger unhealthy behavior, prompting experts to caution that such monitoring isn’t necessary for healthy individuals. Ultimately, she questioned whether pursuing perfect glucose stability is a healthy goal.