Antarctica sheds London-sized ice mass in 30 years, study finds
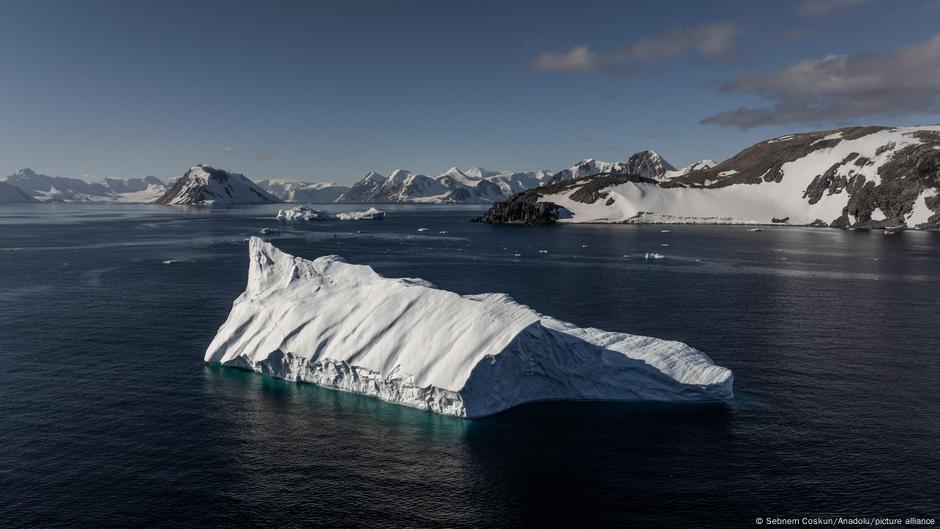
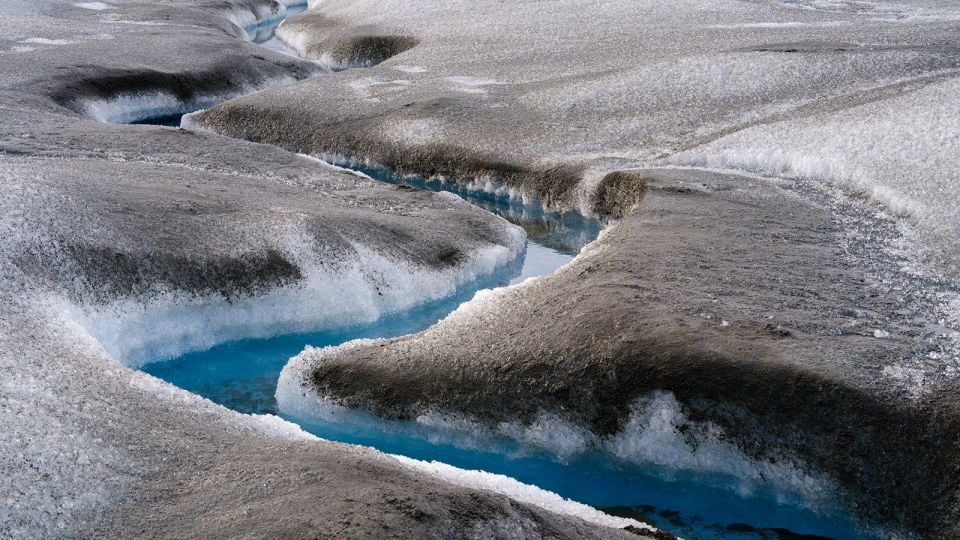
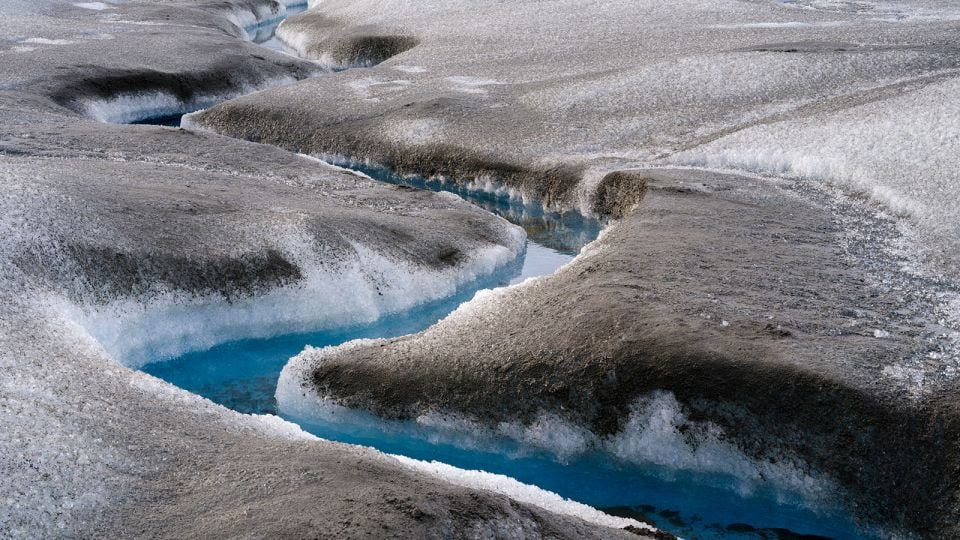
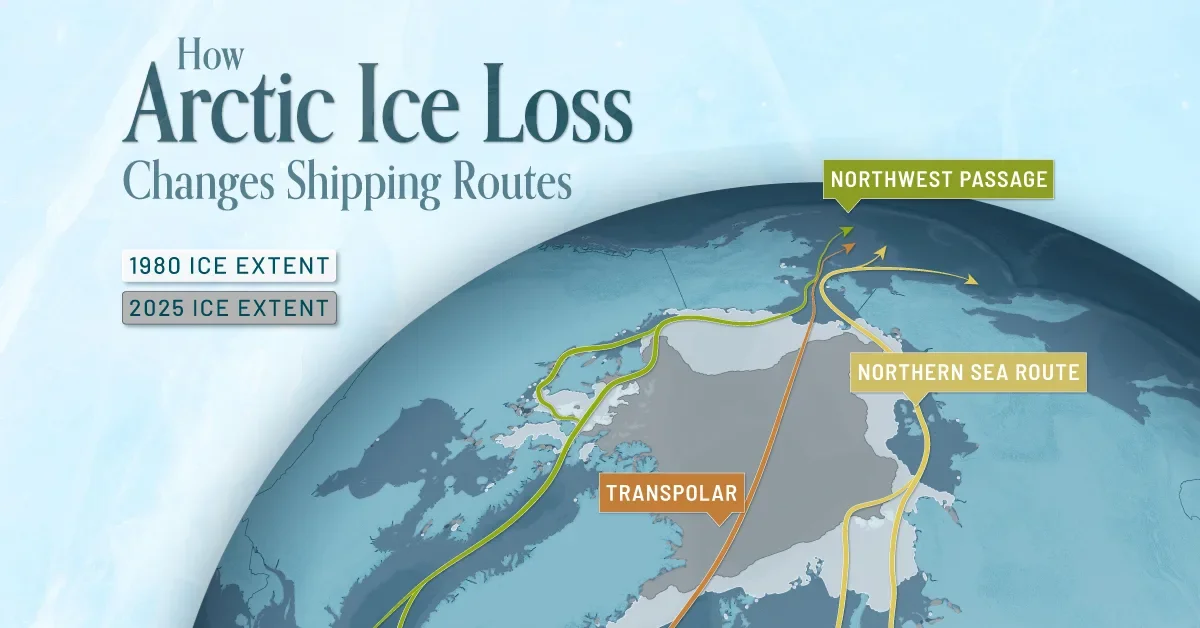
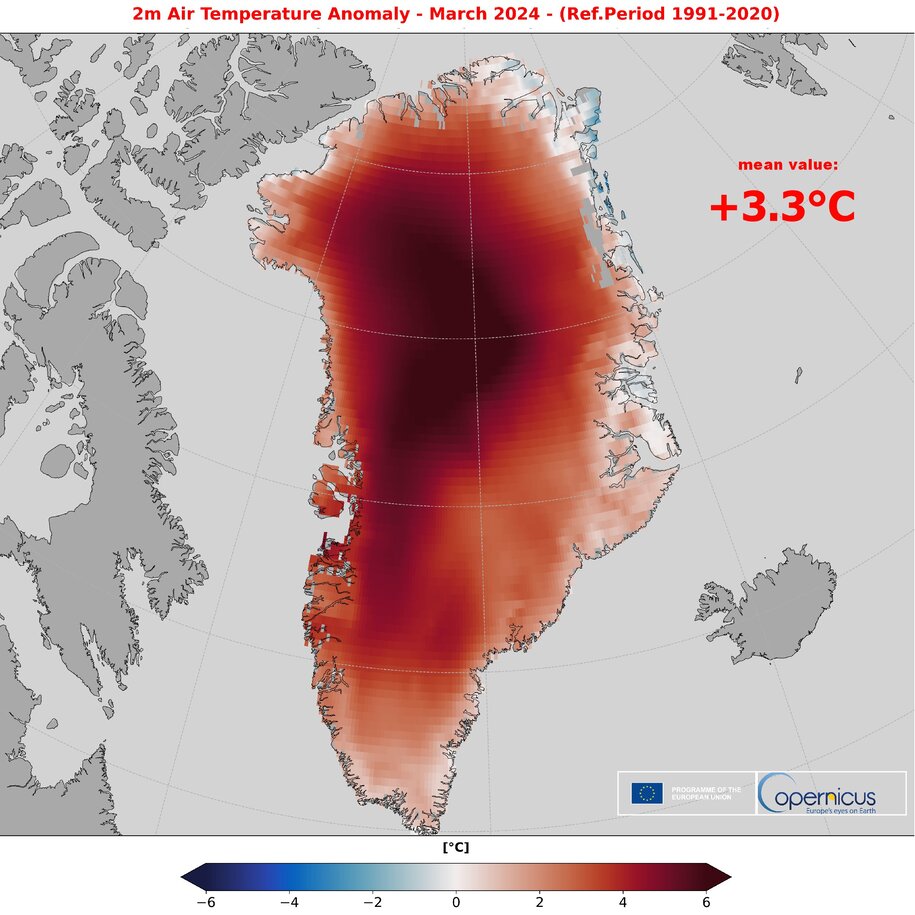
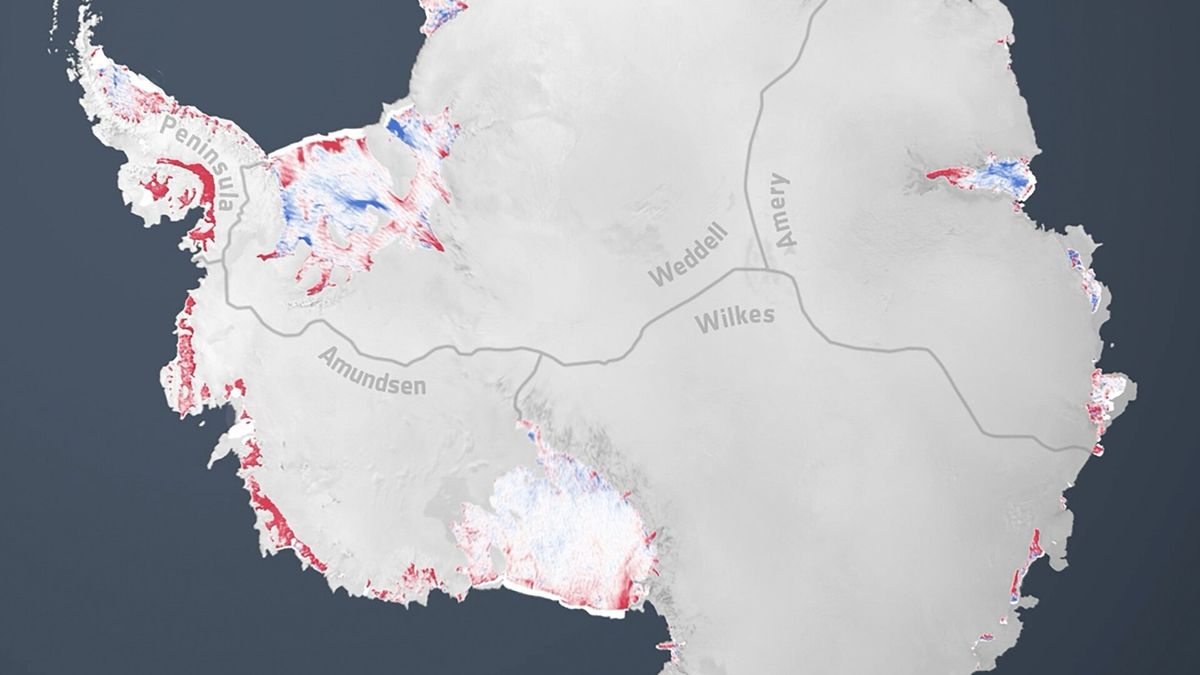
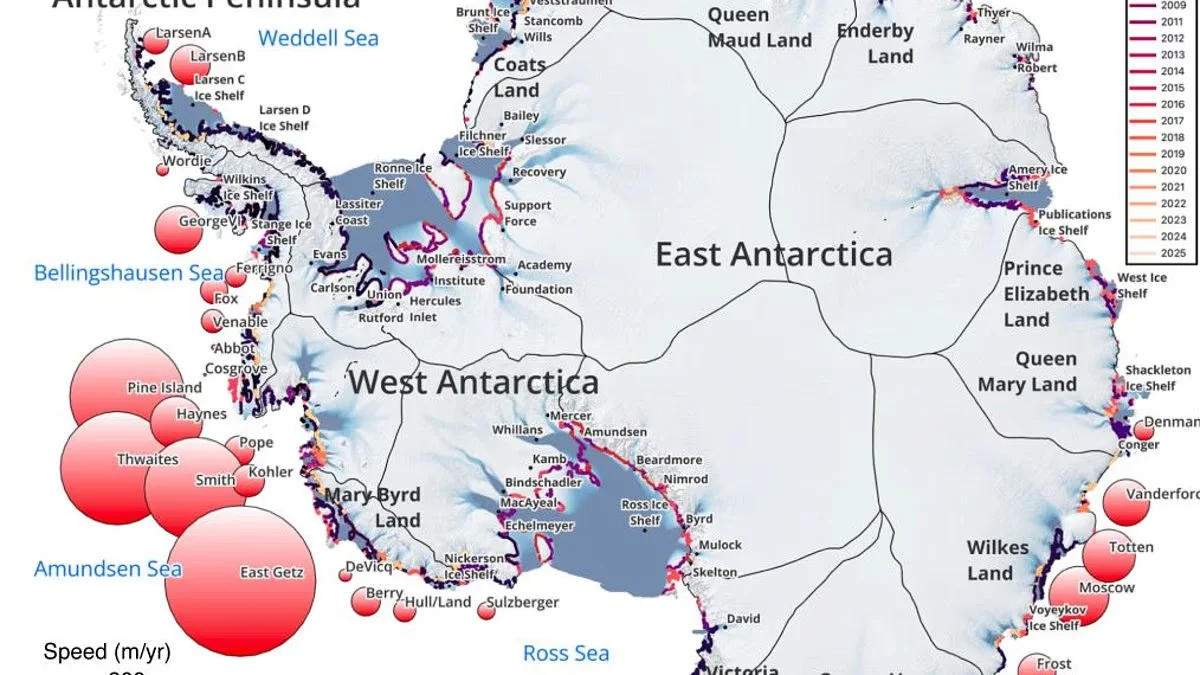
A satellite-based study shows Antarctica has lost ice covering an area eight times the size of Greater London in 30 years, driven by grounding-line migration concentrated in Western Antarctica and select East Antarctic regions. While 77% of the coast shows no grounding-line change since 1996, major glaciers such as Pine Island, Smith, and Thwaites have retreated by tens of kilometres, contributing to sea-level rise and underscoring the uneven nature of ice loss amid warming oceans.