Distant Gamma-Ray Burst at Redshift 7.3 Rewrites Early-Universe Star Deaths
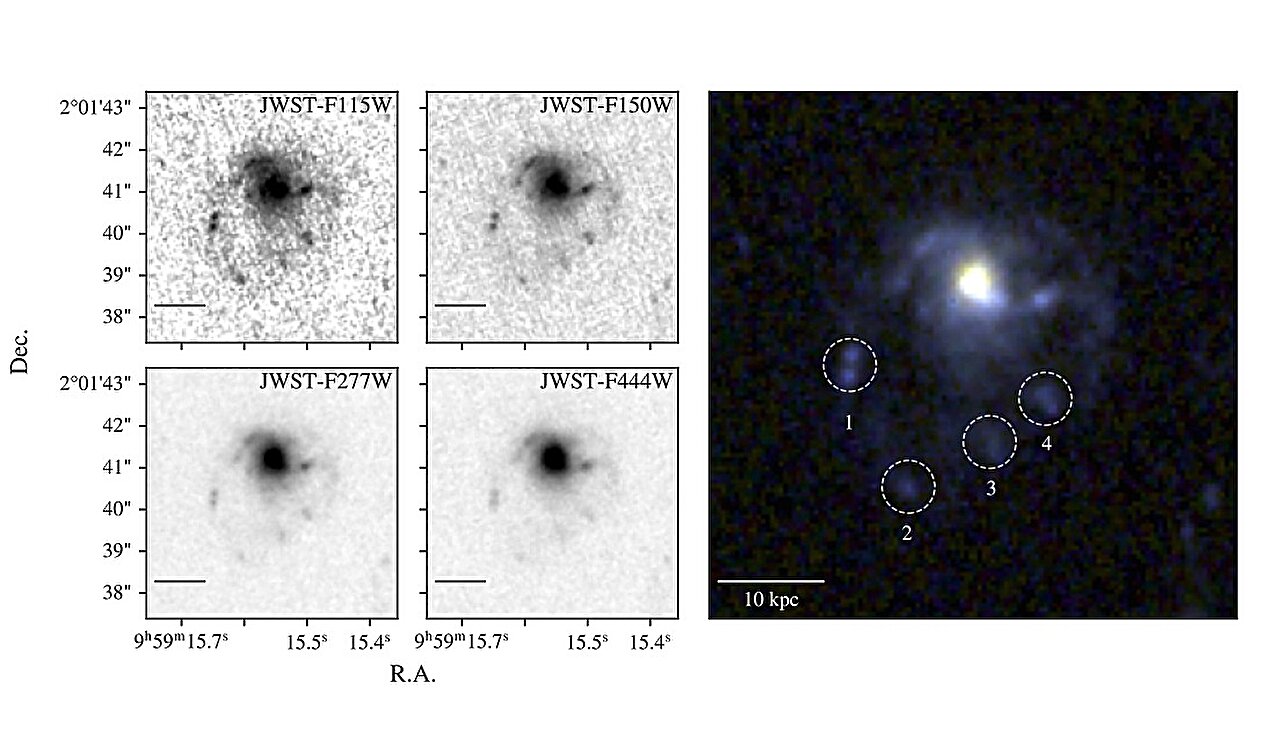
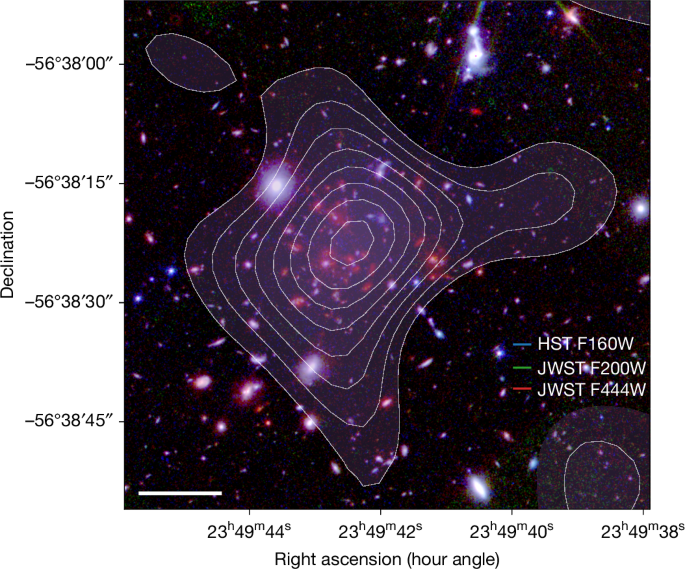
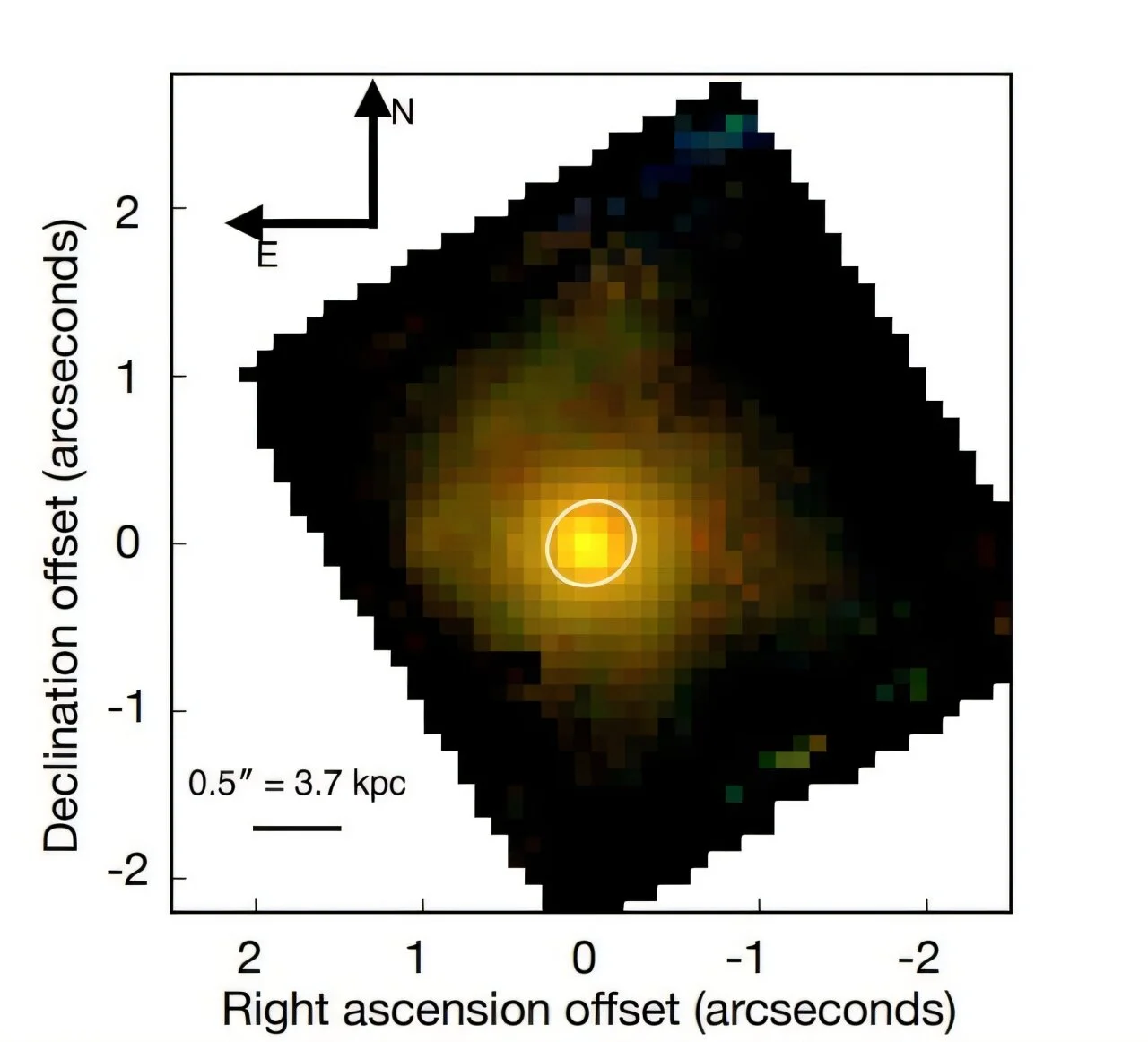
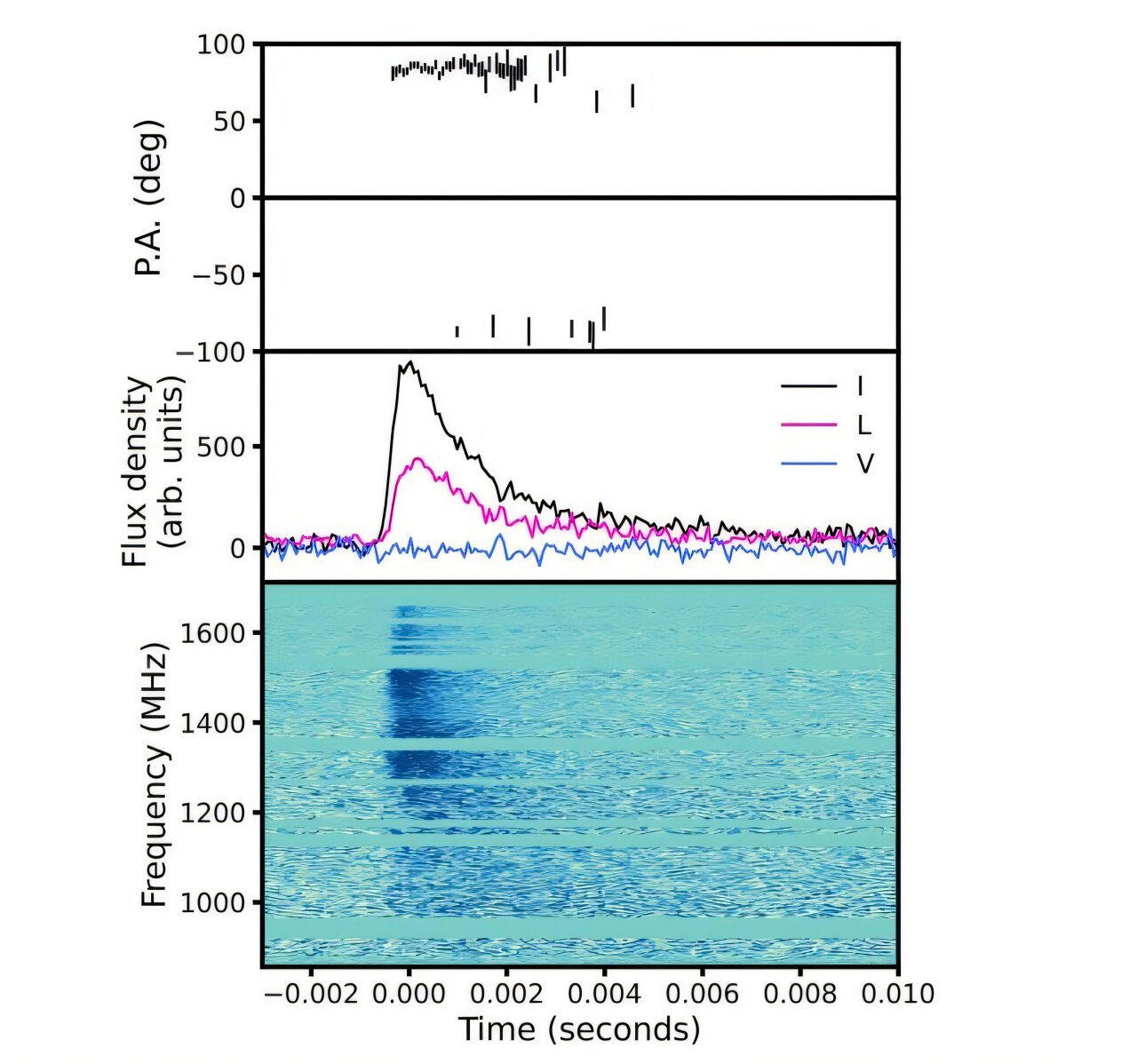
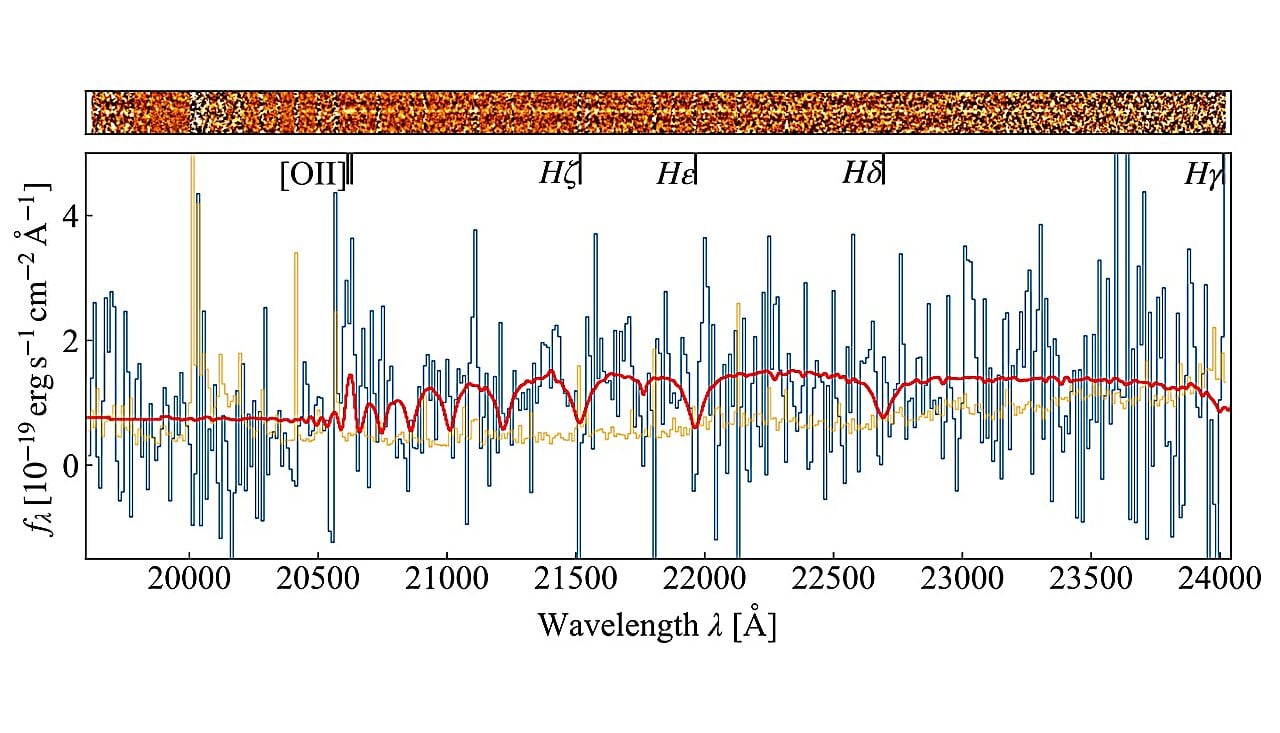
A ten-second, ultra-distant gamma-ray burst (GRB 250314A) at z=7.3 (~13.1 billion years old) sparked a rapid, global follow-up, with JWST resolving its explosion as a supernova similar to modern Type II events. The findings imply massive stars were dying and enriching their surroundings within the universe’s first billion years, challenging Population III star death models and suggesting comparatively mature stellar processes occurred far earlier than previously thought.