Three Standing Tests to Gauge Balance After 50
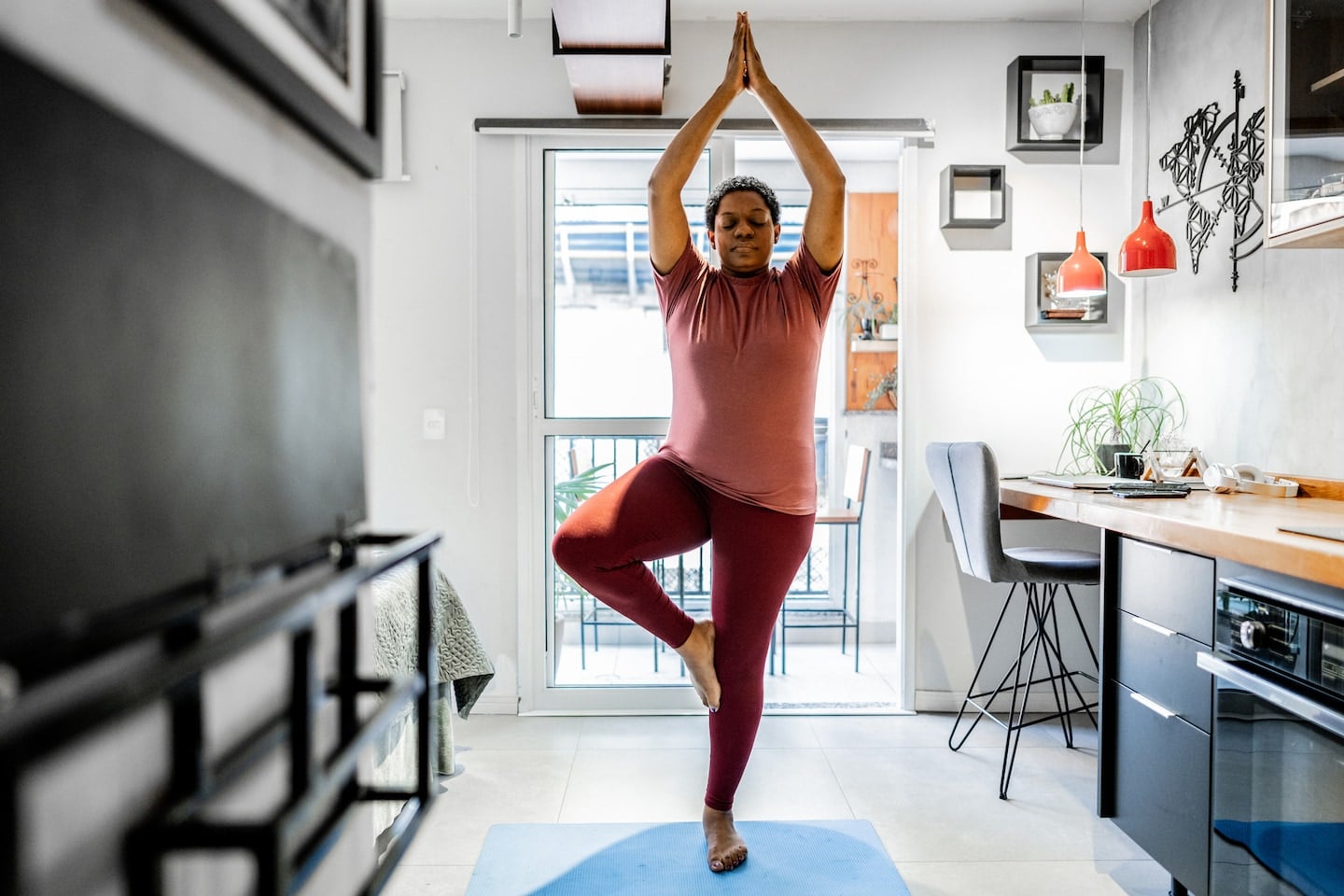
Balance tends to decline after 50 due to joint stiffness, vision changes, and reduced muscle mass, but three standing drills offer a practical test and training plan: Single-Leg Stand (eyes open or closed), Staggered Stance Overhead Reach (unilateral load), and Heel-to-Toe Line Hold (tandem stance). Perform 3 sets of 20–30 seconds per leg for the single-leg test, 3 rounds of 20 seconds per side for the overhead-reach hold, and 3 rounds of 30 seconds per side for the tandem hold. These moves engage core, hips, and stabilizers to boost multi-system coordination and reduce fall risk.