Resolving Quantum Interference in Photoionization with Attosecond Precision
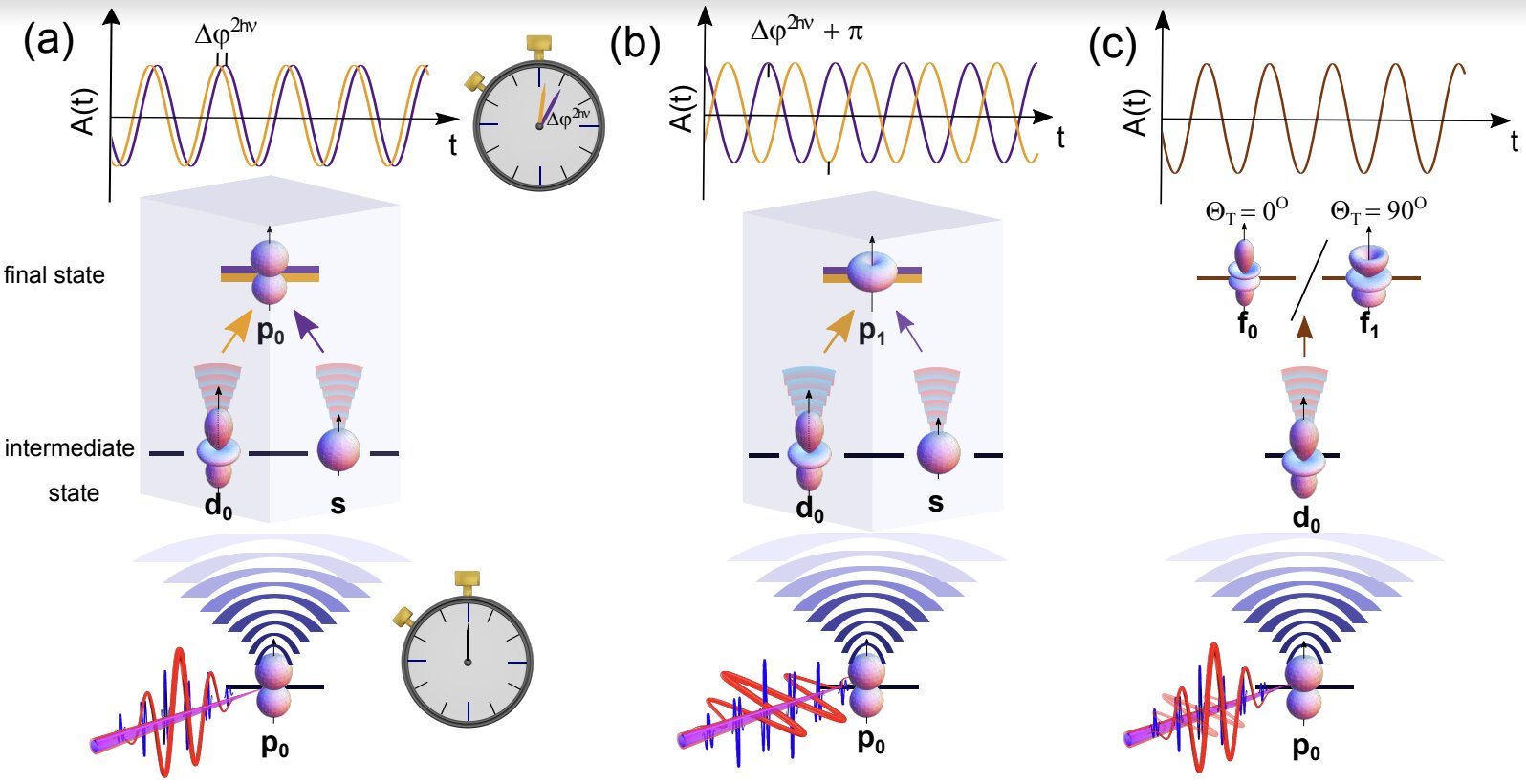
Researchers have developed a new method for conducting attosecond physics research by building on the RABBITT technique. By changing the polarization of laser pulses, they were able to measure individual contributions in photoionization and resolve quantum interference between different pathways. The experiments were conducted on helium, neon, and argon samples, and the results were validated through simulations. This method could provide insights into the fundamental dynamics of photoionization and potentially lead to advancements in controlling electrons using light for applications in electronic circuitry, photovoltaics, and radiation damage prevention in medical tools.