
Economists Predict AI-Driven U.S. Productivity Growth Amid Mixed Results
Economists predict that the US will extend its productivity lead due to the ongoing AI boom, highlighting the significant impact of artificial intelligence on economic growth.
All articles tagged with #economists

Economists predict that the US will extend its productivity lead due to the ongoing AI boom, highlighting the significant impact of artificial intelligence on economic growth.

Economists say Europe's economic growth prospects heavily depend on Germany's increased spending, highlighting Germany's crucial role in the continent's economic outlook.

Economists widely oppose Zohran Mamdani's proposed rent freeze in NYC, arguing that while it offers short-term relief, it exacerbates long-term housing shortages, misallocates resources, and deepens inequality, emphasizing the need for increased housing supply rather than price controls.

A group of nearly 50 prominent economists, including former Federal Reserve Chairs Bernanke and Yellen, filed a brief urging the US Supreme Court to overturn President Trump's global tariffs, arguing they are based on misconceptions about the economy and won't effectively address trade deficits, with oral arguments scheduled for November 5.

Economists favor Christopher Waller to lead the Federal Reserve, but there is an expectation that President Trump will choose a loyalist for the position.

Economists warn that investors are underestimating the potential threat Donald Trump poses to the Federal Reserve, highlighting concerns about his influence on monetary policy and economic stability.
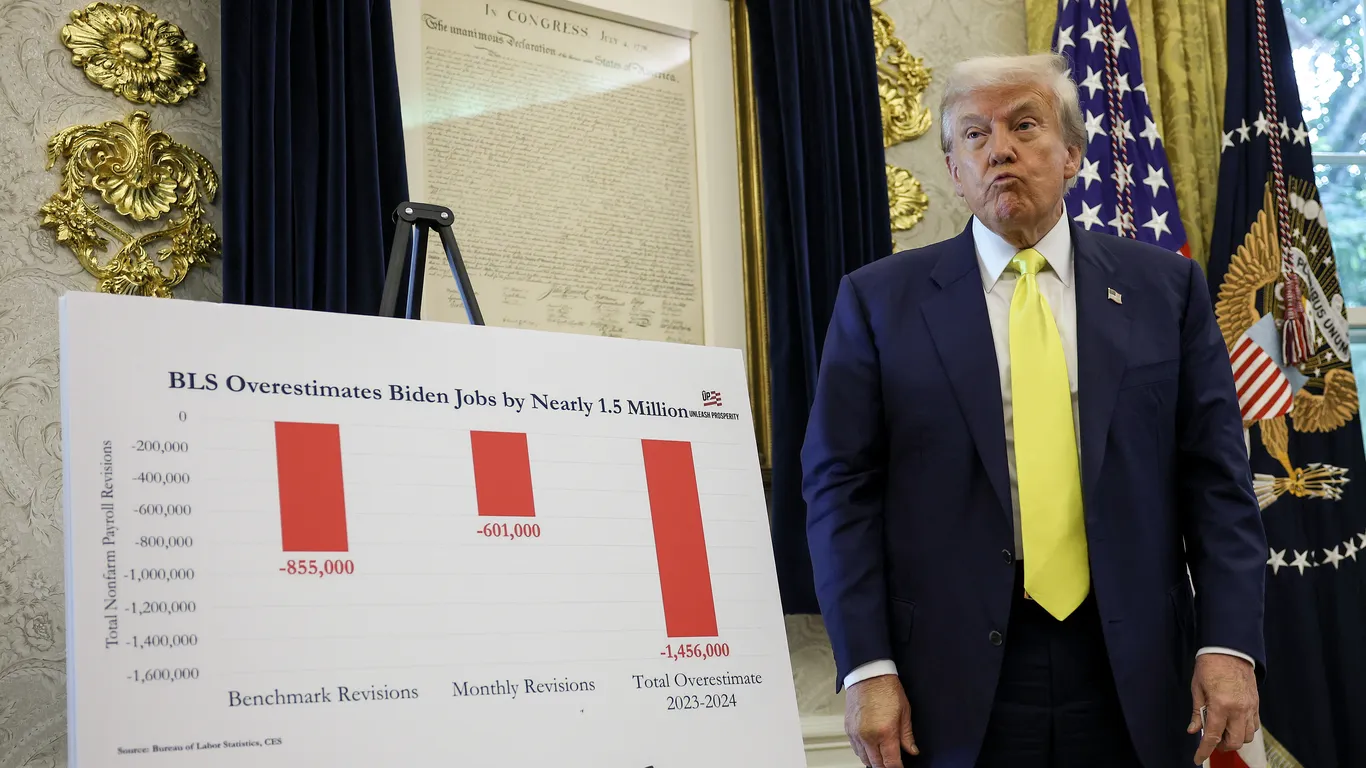
President Trump's nomination of E.J. Antoni as head of the Bureau of Labor Statistics has faced widespread criticism from economists across the political spectrum, who question his qualifications and warn that his appointment could undermine the reliability of vital economic data.

The article discusses the declining job prospects for economists with Ph.D.s, highlighting how the once-booming market for high-skilled economists is shrinking due to budget cuts, technological changes, and economic uncertainty, which could have broader implications for innovation and government research.

President Trump and his allies are attempting to discredit economists and budget experts who warn that their proposed tax legislation could add approximately $2.4 trillion to the US federal debt over a decade, amid political and economic debates over the bill's fiscal impact.

The Federal Reserve is expected to implement a third consecutive interest rate cut this month, reducing the benchmark rate to 4.25%-4.50%, according to economists surveyed by Bloomberg News. This would total a one percentage point reduction since September, with fewer rate cuts anticipated in 2025.

Economists warn that former President Donald Trump's proposed economic plans could exacerbate inflation. His policies, which include significant tax cuts and increased government spending, may lead to higher demand and subsequently drive up prices, complicating efforts to control inflation.

A Wall Street Journal survey indicates that most economists believe a potential second term for Donald Trump could lead to higher inflation, deficits, and interest rates compared to a continued Joe Biden presidency. The survey, conducted with 68 professional forecasters, highlights concerns over Trump's policy preferences on trade and immigration, which could impact the labor supply and economic stability. Despite these predictions, the actual impact of either presidency on the economy will depend on various factors, including Congressional actions and external economic shocks.

Amending the 1974 National Manufactured Housing Construction and Safety Standards Act to remove the requirement for manufactured homes to be built on a permanent chassis could save homebuyers $175,000 and increase the availability of affordable housing, according to economists Lee Ohanian and James Schmitz. This change would make manufactured homes more attractive, safer, and easier to finance, potentially transforming homeownership for millions of Americans.
Economists predict that the Federal Reserve will need to maintain high interest rates for a longer period than what the markets currently anticipate, due to concerns about inflation and the strength of the economy.

Top economists' new forecast shows a decreased likelihood of a recession in the first half of 2024, with a 17.3% chance of negative growth in the first quarter, down from 40.9% in the previous survey. The forecasters predict a soft landing for the economy, with expectations of a 2.1% annual GDP growth rate and a strong labor market, projecting a 4% unemployment rate by the end of the year. Inflation is expected to moderate, and stock markets were mixed while the 10-year Treasury yield rose to 4.16% in early trading on Friday.