Neanderthal-Human Interbreeding Shaped Early Human Survival and Migration
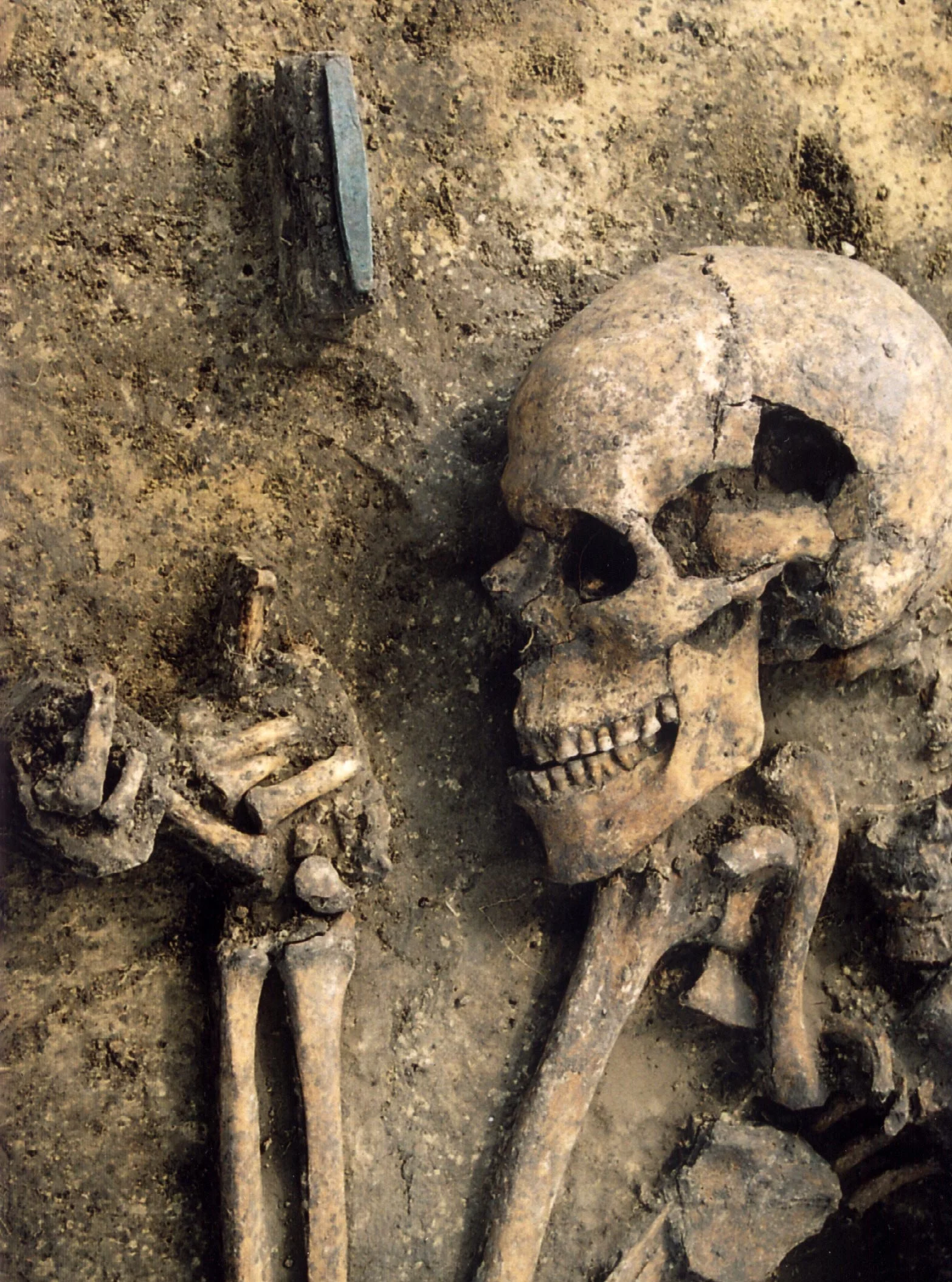
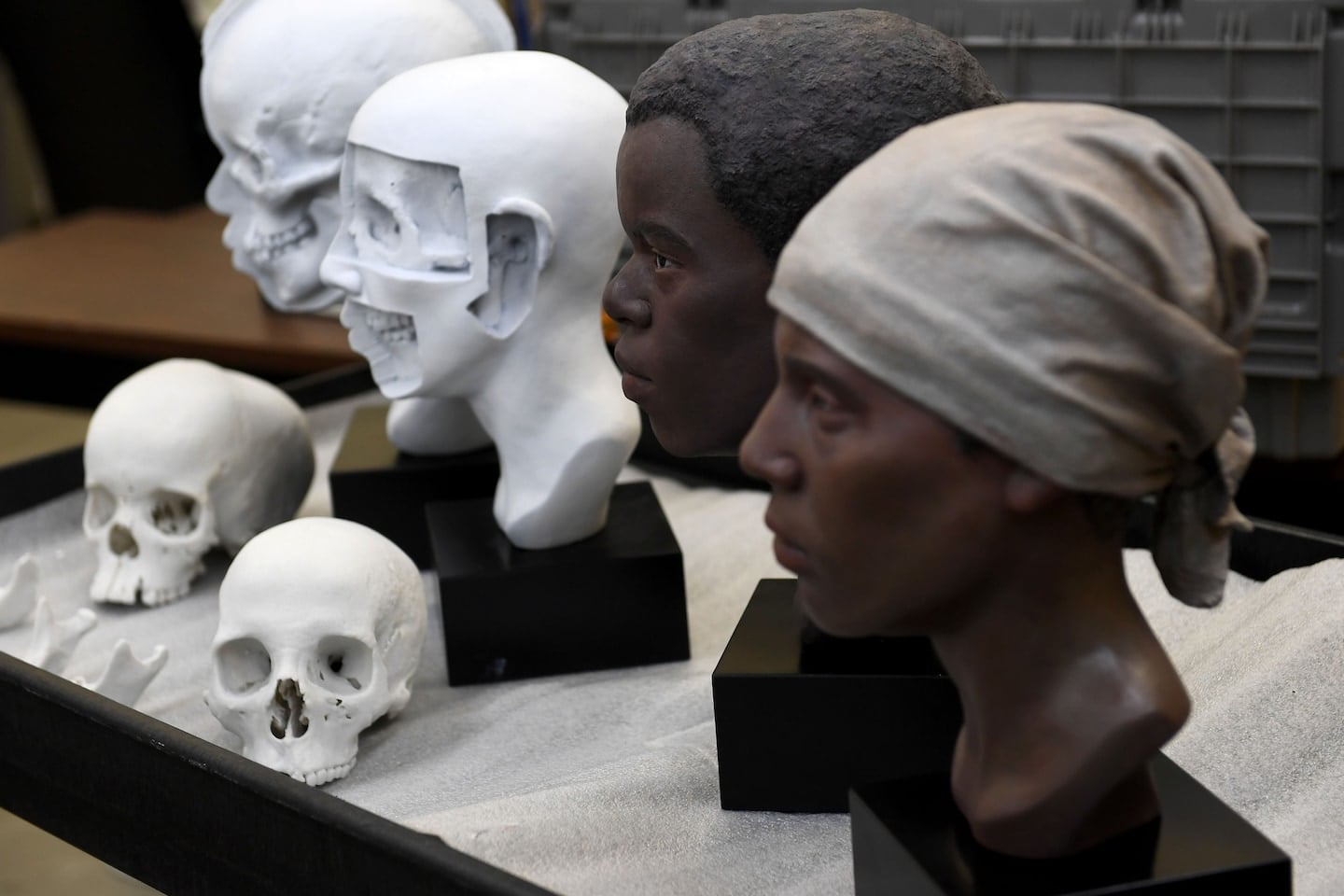
New DNA research reveals that modern humans may owe their survival to interbreeding with Neanderthals, which provided crucial genetic advantages, such as enhanced immune systems, necessary for thriving outside Africa. This challenges the traditional narrative of human evolution as a straightforward success story, showing that early human populations often went extinct before those with Neanderthal genes expanded globally. The findings also suggest that environmental factors, rather than human superiority, contributed to the extinction of Neanderthals.