"Stone Age Genetic Strategy for Inbreeding Avoidance Revealed"
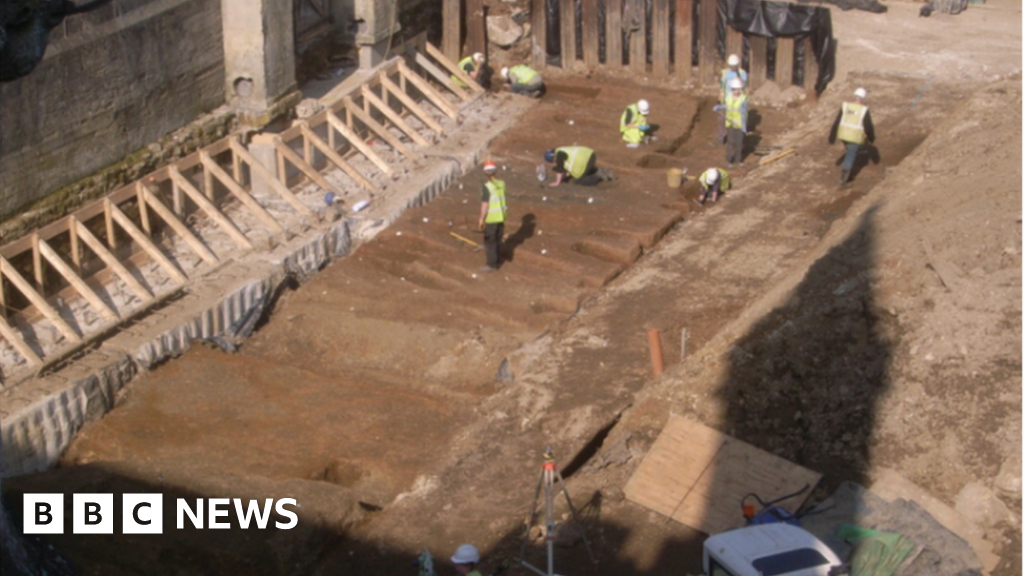
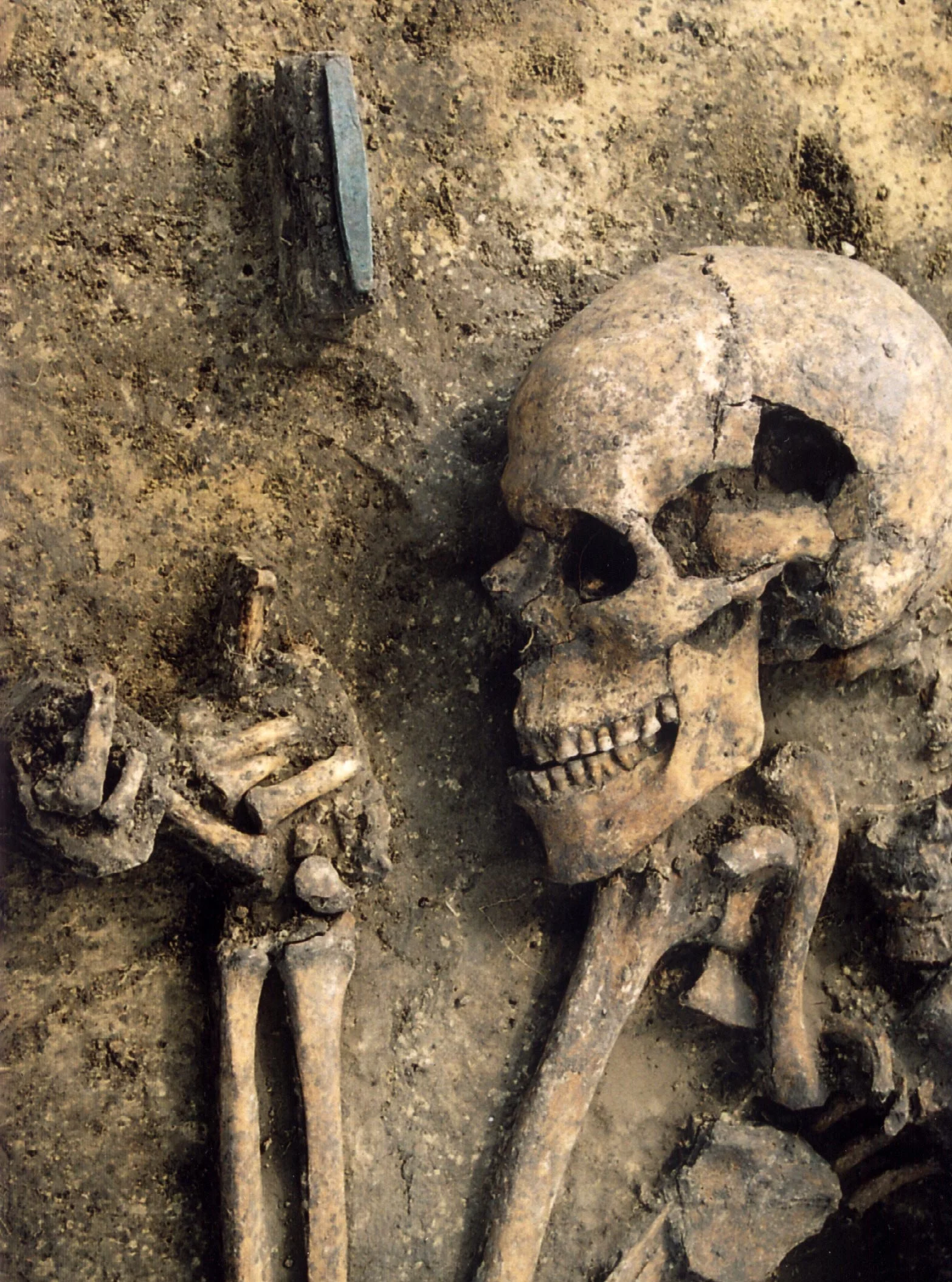
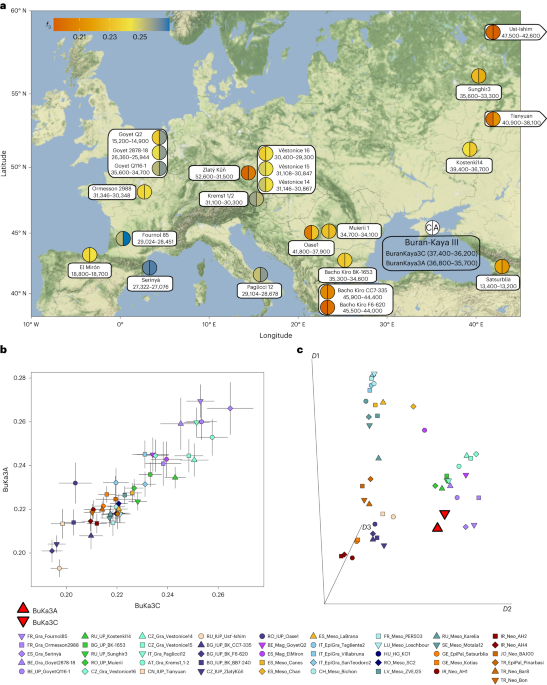
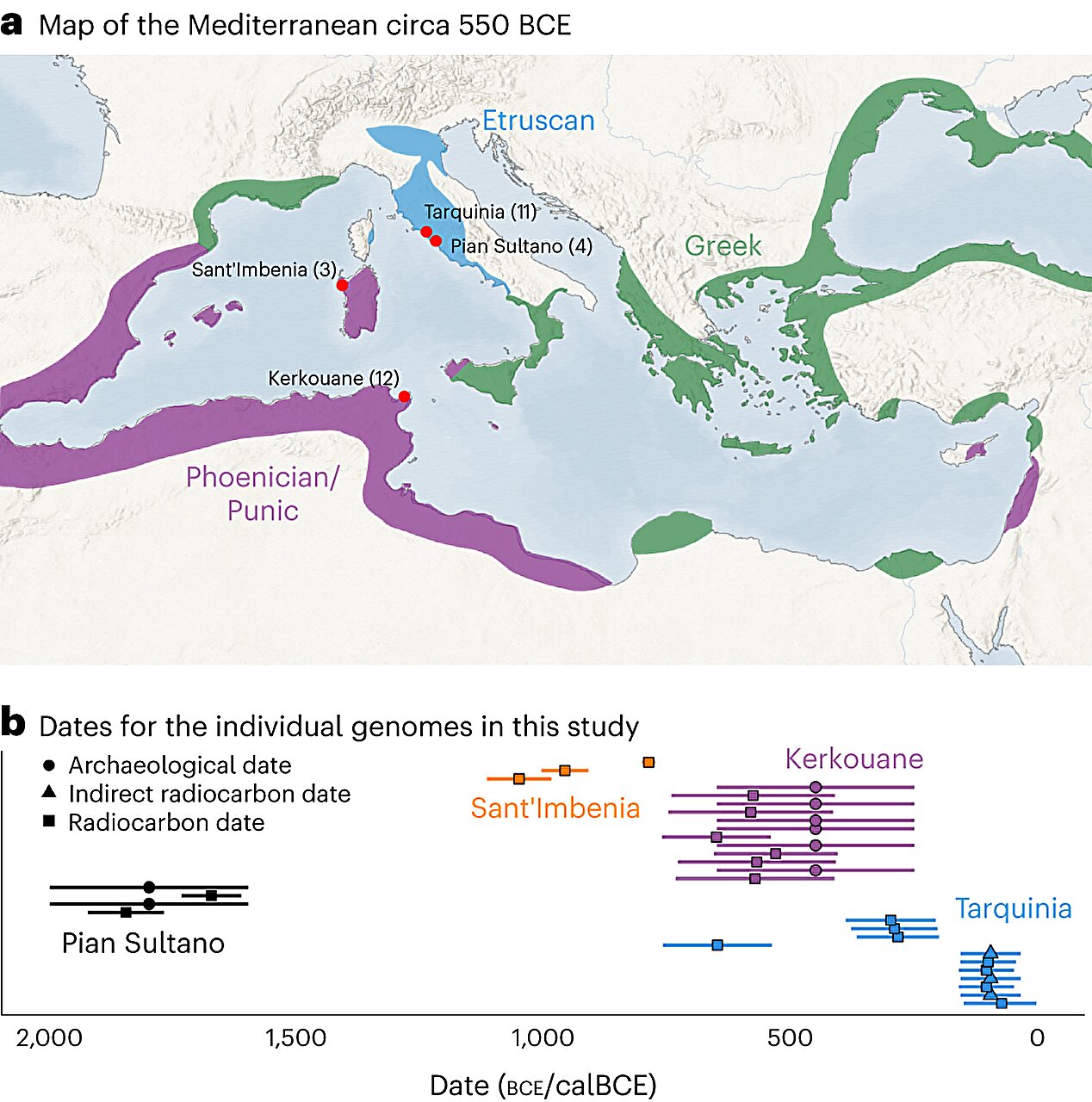
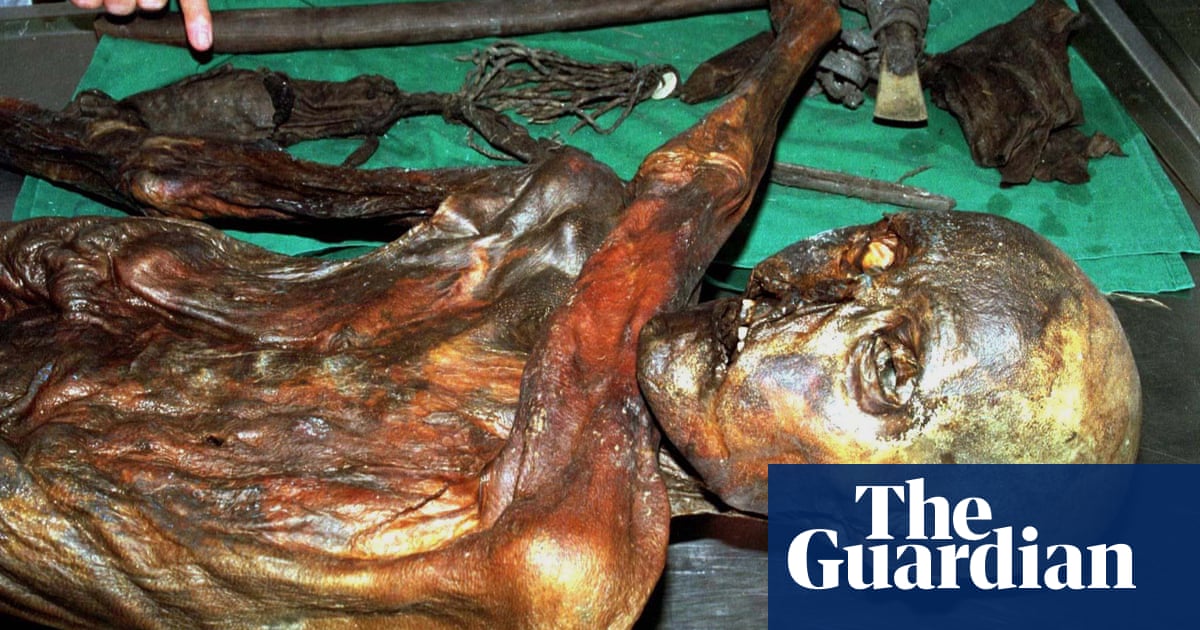
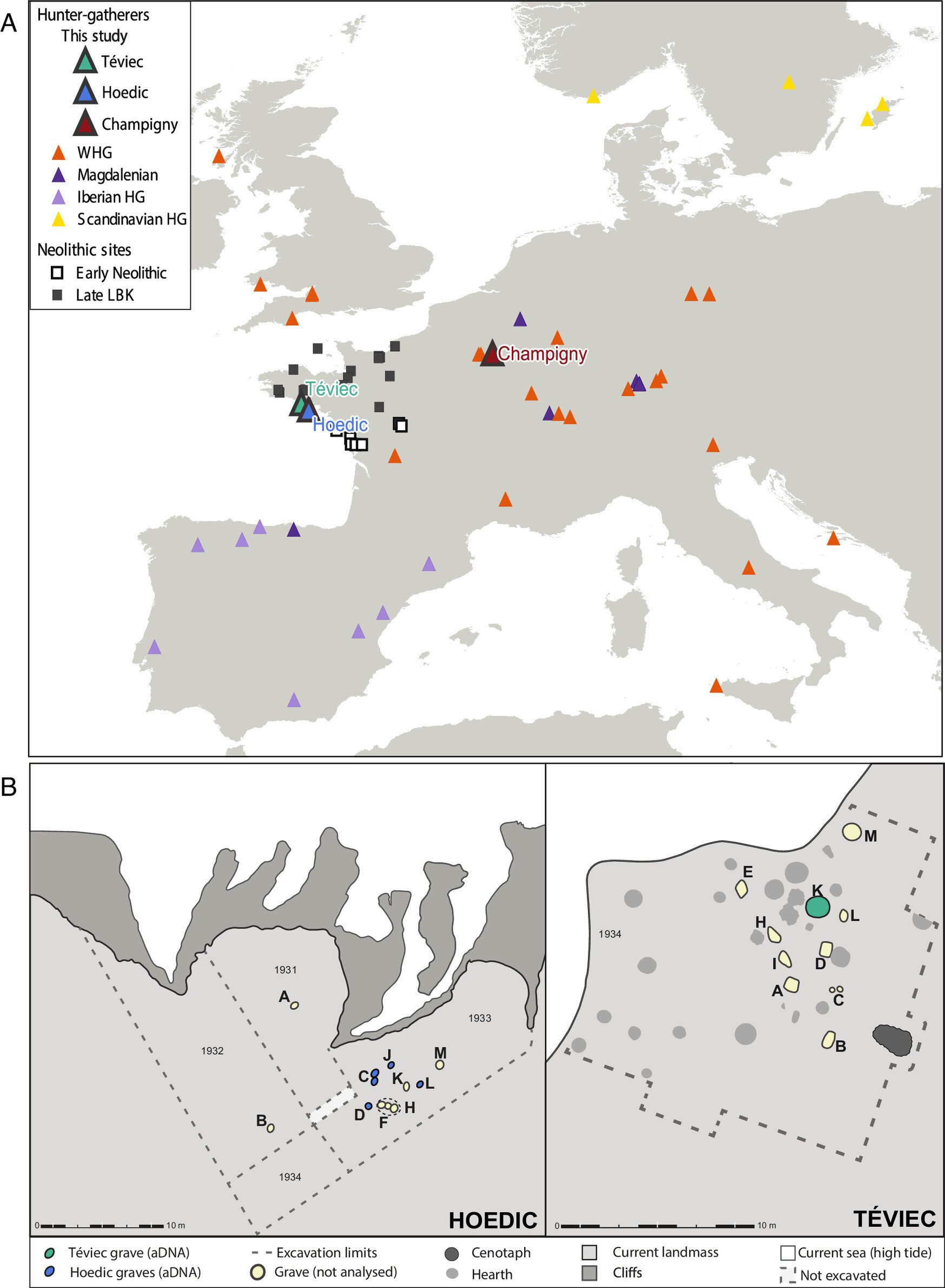
A genetic study of Stone Age burial sites in Western Europe suggests that hunter-gatherer communities deliberately lived together in distinct social units to avoid inbreeding, despite the coexistence of Neolithic farming communities. The study, led by researchers from Uppsala University and French institutions, analyzed the genomes of individuals buried at iconic sites in France, revealing that the groups were generally not closely related and showed no signs of inbreeding. The findings provide new insights into the social dynamics of the last Stone Age hunter-gatherer populations in Western Europe.