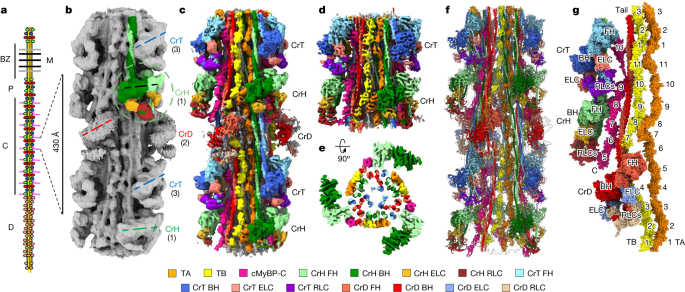
Broadly protective antibody blocks gammaherpesvirus gB fusion across genera
Researchers report Fab5, a broadly reactive antibody that targets a conserved epitope on gammaherpesvirus gB, enabling cross-genus neutralization; it provides protection against authentic virus challenges in mice, non-human primates, and humanized mice, and cryo-EM reveals the epitope is exposed in both pre- and post-fusion conformations, offering a path toward broad-spectrum gammaherpesvirus vaccines.