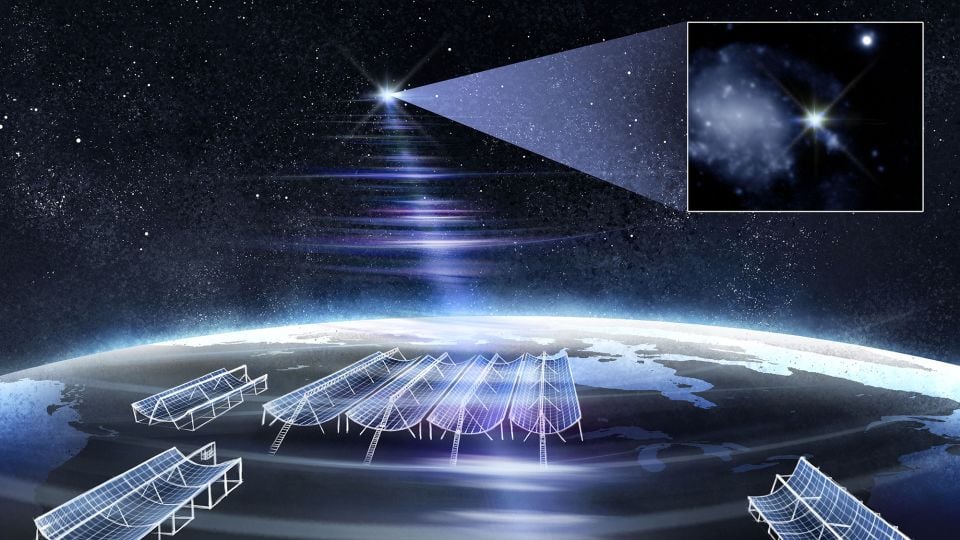
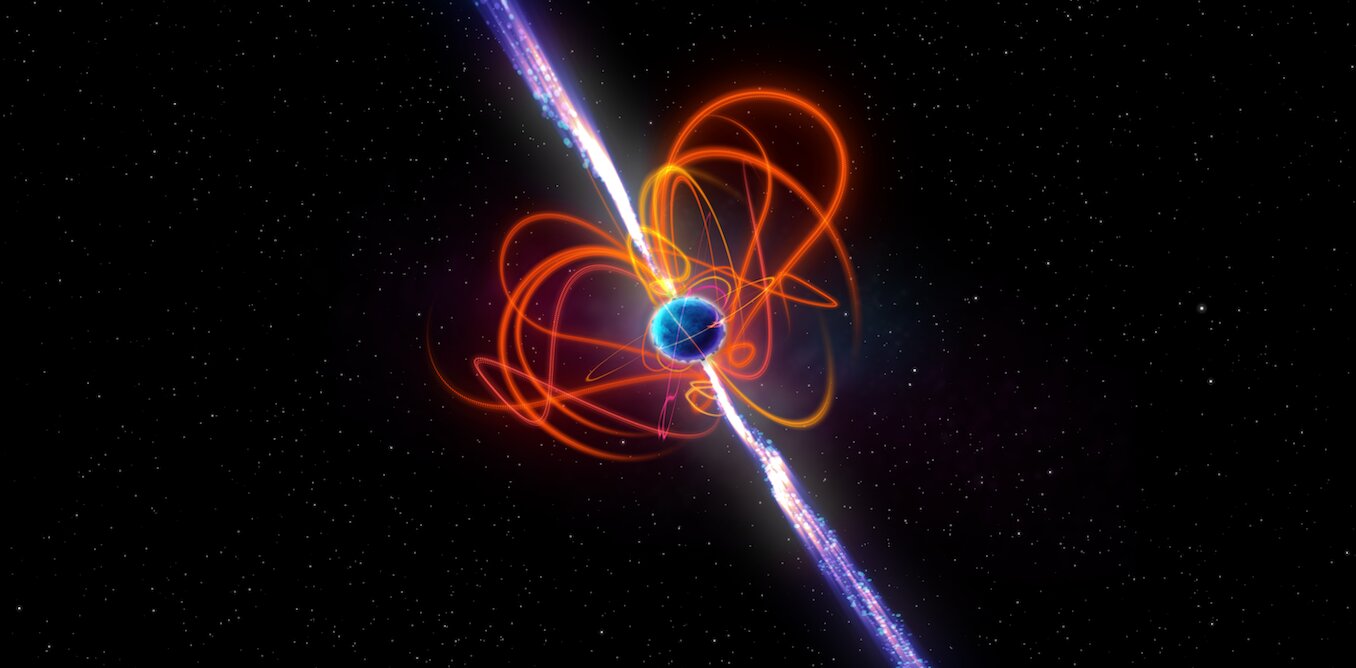
Unprecedented Long-Lasting Gamma-Ray Burst Challenges Space Science
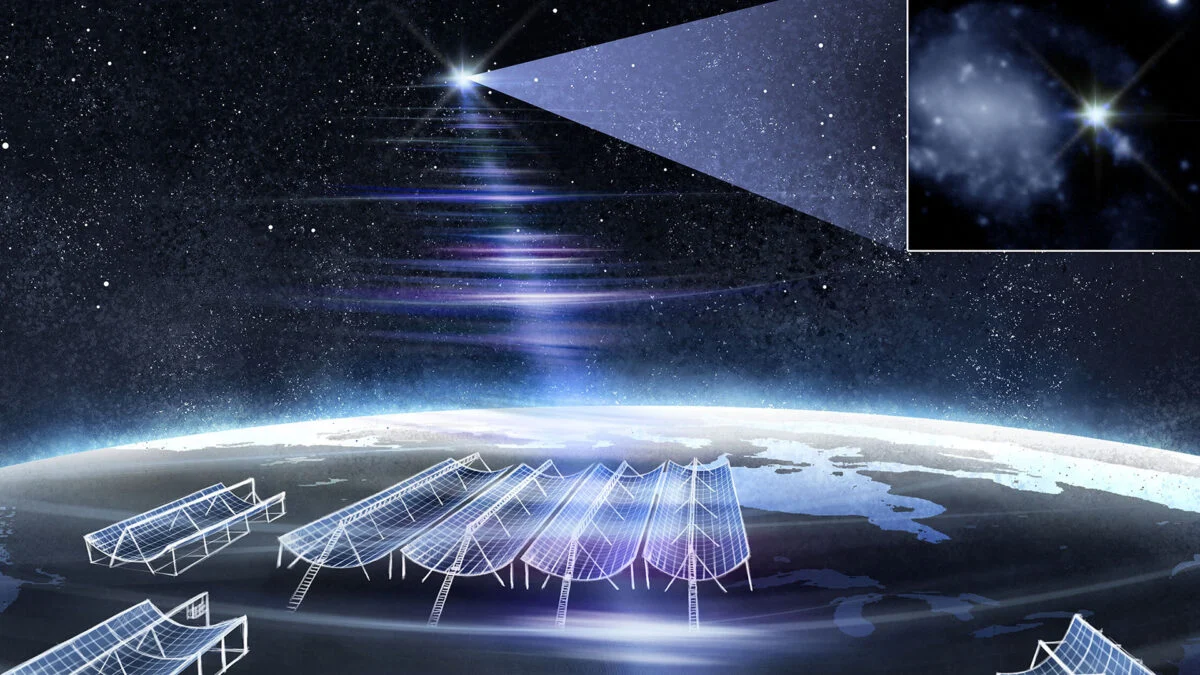
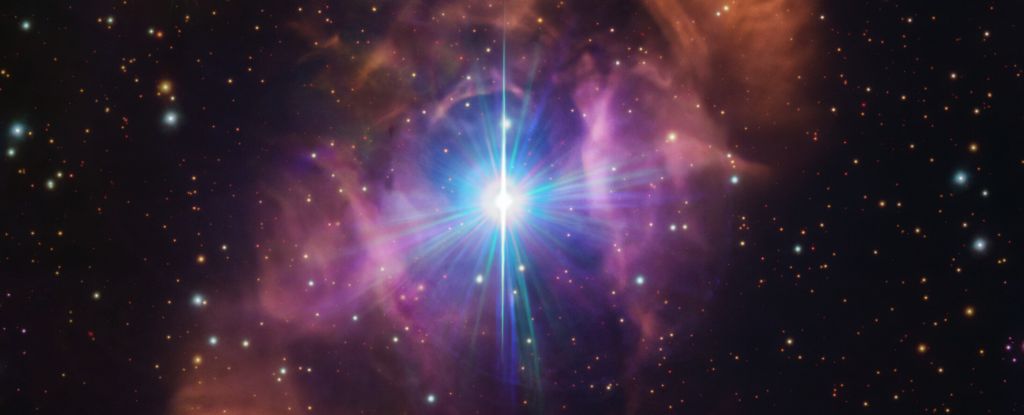
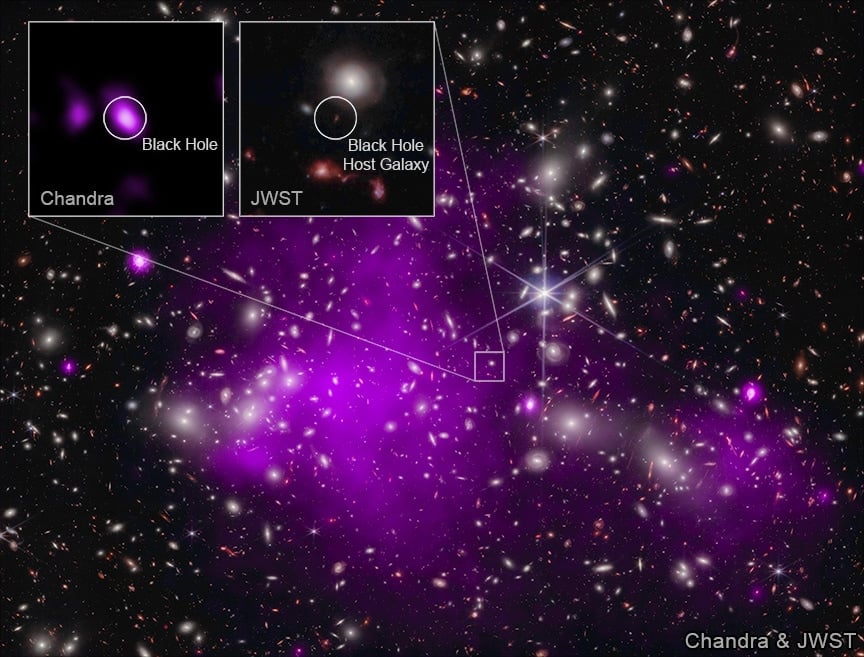
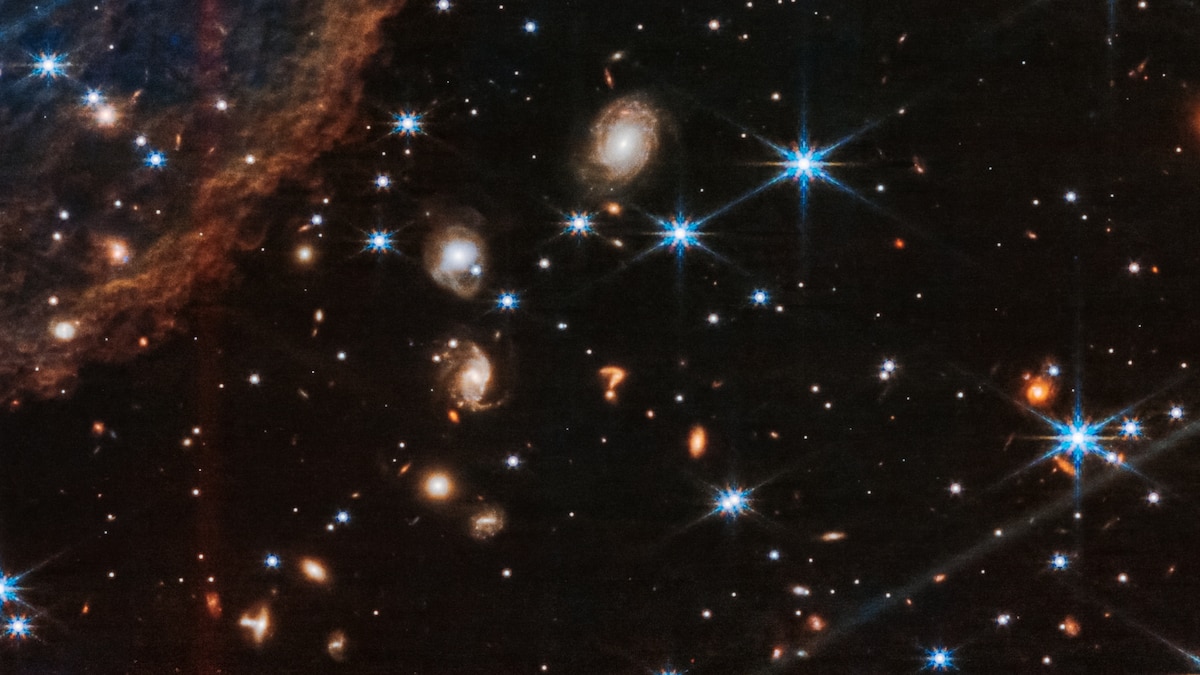
Astronomers observed the longest and most unusual gamma-ray burst ever, GRB 250702B, which repeated and lasted about a day, challenging current models and suggesting the involvement of an intermediate mass black hole or a unique stellar event, marking a significant breakthrough in understanding cosmic explosions.