Health Neuroscience News
The latest health neuroscience stories, summarized by AI
Featured Health Neuroscience Stories


"Predicting Parkinson's Progression with Eye Tests"
Optical coherence tomography, commonly used in eye exams, can monitor neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease patients by measuring the thickness of the retina, which often precedes cognitive and motor decline. This method offers a potential early indicator of disease progression, suggesting that routine eye exams could become a non-invasive tool for predicting the future severity of Parkinson’s symptoms and aiding in more targeted treatment strategies.

More Top Stories
"Promising Immunotherapy Treatment Target for Alzheimer's Disease Identified"
Neuroscience News•1 year ago
"Rising Brain Sizes in Younger Generations Linked to Lower Dementia Risk"
Euronews•1 year ago
More Health Neuroscience Stories

"Viagra's Potential in Treating Alzheimer's Disease"
A new study led by the Cleveland Clinic suggests that sildenafil, the main component of Viagra, shows potential as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease. The research, which integrates computational models, insurance claims data, and laboratory observations, indicates a 30-54% reduction in Alzheimer's diagnoses among sildenafil users and decreased levels of neurotoxic proteins in brain cells. This interdisciplinary approach highlights the benefits of drug repurposing and offers a promising avenue for new Alzheimer's therapies, with implications for future clinical trials to explore sildenafil's effectiveness in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
"Flickering Light and Sound Waves: A Promising Treatment for Alzheimer's"
Recent research from MIT and other institutions suggests that light and sound therapy at a frequency of 40 Hz may slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by enhancing the release of peptides from interneurons, promoting the removal of Alzheimer’s-related proteins through the brain’s glymphatic system. This study reveals a key mechanism that contributes to these beneficial effects, showing that sensory gamma stimulation increases 40 Hz neuronal activity in the brain, prompting a particular type of neuron to release peptides that drive specific processes promoting increased amyloid clearance via the glymphatic system.
"Breakthrough Sensor Enables Early Alzheimer's Detection"
Researchers have developed a novel fluorescence imaging technique using a sensor array of coumarin-based molecular probes to detect amyloids, key biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. This breakthrough offers a simpler alternative to PET scans and could enable earlier diagnosis and a better understanding of these diseases, potentially paving the way for new treatment strategies. The sensor array showed high sensitivity and selectivity in detecting various amyloids, and it could distinguish between different conditions and stages of Alzheimer’s, offering a non-invasive diagnostic method with significant potential for clinical applications.
"Neuroimaging Study Identifies Brain-Wide Patterns Linked to ADHD Symptoms"
A landmark study using a new technique to analyze brain scans from 6,000 children has identified specific patterns of brain-wide connectivity associated with ADHD symptoms, providing insights into the neurological basis of the disorder. The findings could improve future research into ADHD and other neurological conditions, potentially leading to early diagnosis and better understanding of the disorder's genetic and environmental influences. The study highlights the importance of considering diverse neurological functions and using large sample sizes in neuroimaging research.
"Link Between Toxic Tiny RNA Molecules and Alzheimer's Neuron Death Uncovered"
Toxic strands of RNA have been identified in Alzheimer's and aging brains, leading to cell death and DNA damage. Researchers found that protective short RNA strands diminish with age, allowing Alzheimer's to progress, while 'superagers' have higher levels of protective RNAs. Targeting RNA strands could open new treatment pathways for neurodegenerative diseases, as increasing brain levels of protective RNA may be a new strategy for the treatment of neurodegeneration.
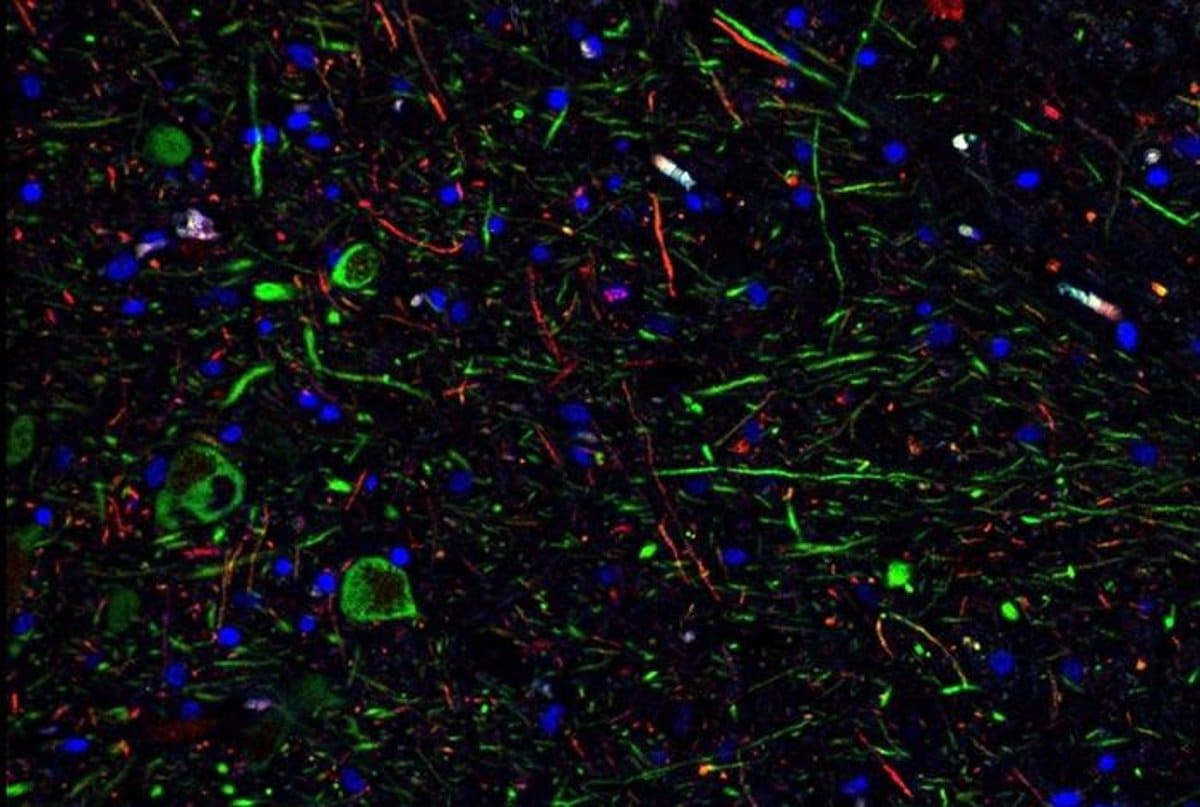
"COVID-19's Impact on Dopamine Neurons"
A study reveals that SARS-CoV-2 can infect dopamine neurons, leading to senescence and inflammation, potentially contributing to long COVID symptoms like brain fog and depression. Approximately 5% of dopamine neurons can be infected, and three drugs have been identified as potential protectors against SARS-CoV-2 infection in these neurons. The findings suggest the need for careful, long-term monitoring of neurological problems in COVID-19 patients and may shed light on the risk of developing Parkinson's-related symptoms.

"Uncovering the Five Biological Variants of Alzheimer's Disease"
Researchers have identified five biological variants of Alzheimer’s disease through cerebrospinal fluid analysis, shedding new light on the complexity of the condition. These variants differ in amyloid production, blood-brain barrier integrity, nerve cell growth, protein synthesis, and immune system functioning. This breakthrough highlights the importance of personalized medicine in Alzheimer’s treatment, as a drug that works for one variant may be ineffective or even harmful for another. The study paves the way for targeted therapies tailored to specific Alzheimer’s variants, potentially improving treatment outcomes.
