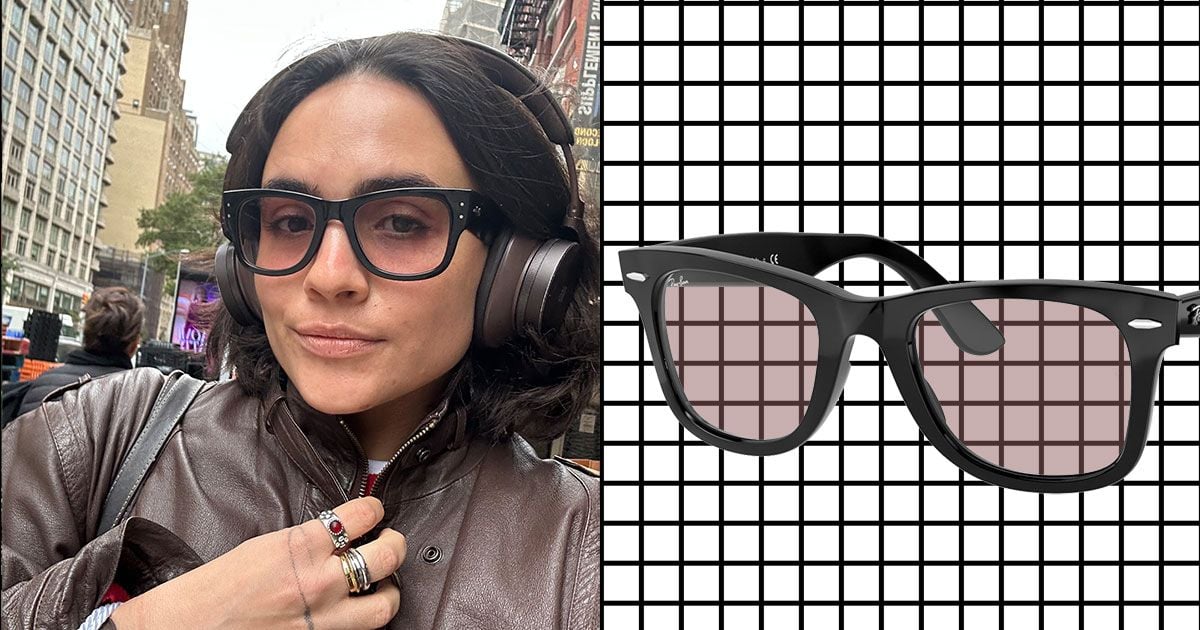
Transition Lenses Make a Stylish Comeback
Ray-Ban's new transition lenses, Transitions GEN S, are highly responsive, offering clear vision and UV protection while adapting quickly to changing light conditions, making them a fashionable and practical choice for daily wear.