
FDA pitches faster path to rare-disease therapies
The FDA, led by Dr. Marty Makary in a White House event with President Trump, proposed a new framework to speed approvals for therapies targeting rare diseases.
All articles tagged with #rare diseases

The FDA, led by Dr. Marty Makary in a White House event with President Trump, proposed a new framework to speed approvals for therapies targeting rare diseases.

The Washington Post WellBeing piece explains situs inversus, a rare condition in which internal organs are mirrored from their usual positions. Catherine O’Hara was born with it, a condition sometimes manifested as dextrocardia (the heart on the right side). For most people with situs inversus, there are few or no symptoms and the condition is often discovered incidentally, with health implications varying depending on any associated anomalies.

At the Undiagnosed Hackathon, DeepMind's AlphaGenome was used to predict how noncoding DNA mutations affect gene activity, helping researchers tie variants to 29 undiagnosed conditions and illustrating AI’s potential to illuminate the genome’s dark matter for hundreds of millions with undiagnosed rare diseases.

Gene therapies are moving from trials toward patient care, with breakthroughs like personalized CRISPR treatments and new gene-editing tools powering hope for many diseases; however, turning lab successes into approved, accessible medicines is hampered by regulatory, manufacturing, safety, and cost challenges, leaving access uneven despite progress.
Menlo Ventures has invested $16 million in Aurora Therapeutics, co-founded by CRISPR pioneer Jennifer Doudna and Fyodor Urnov, to develop personalized CRISPR therapies targeting rare diseases like PKU, leveraging recent regulatory and technological advances to make treatments for ultra-rare conditions more feasible.

BioMarin is acquiring Amicus Therapeutics for $4.8 billion to expand its portfolio in rare disease treatments, including marketed products Galafold and Pombiliti + Opfolda, which generated $599 million in revenue over the past four quarters. The deal aims to accelerate revenue growth, diversify BioMarin's product offerings, and create shareholder value, with the transaction expected to close in Q2 2026 and be immediately accretive to earnings.
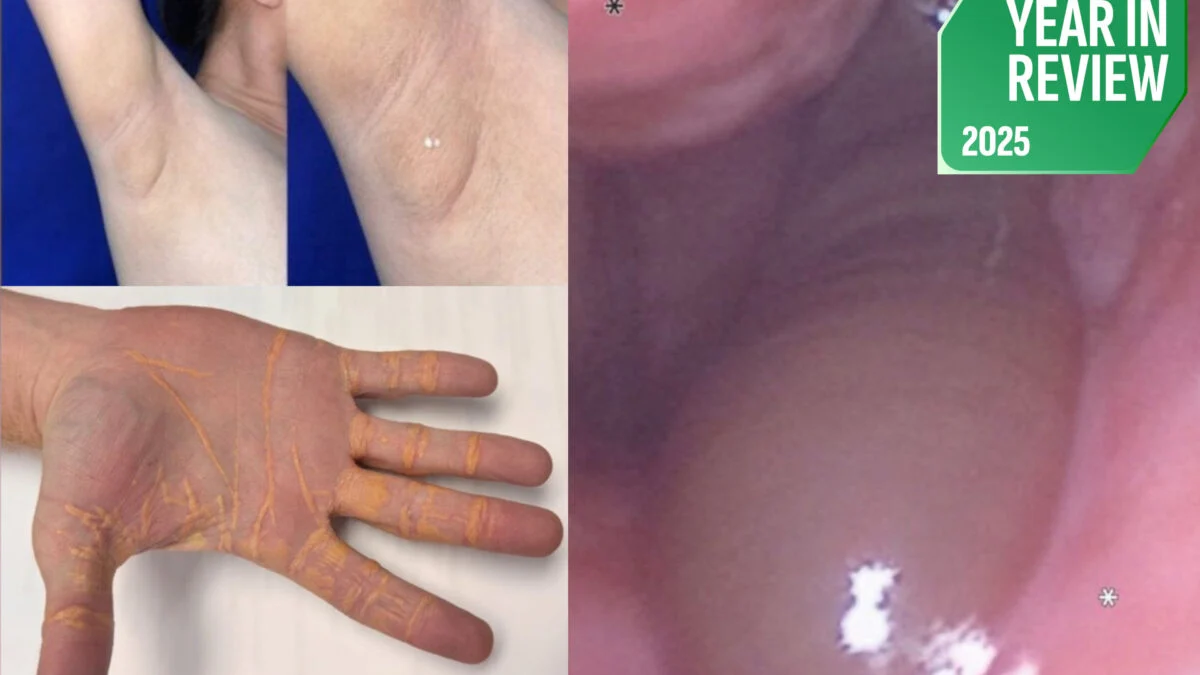
The article reviews some of the strangest medical cases of 2025, including a cholesterol-leaking man from a carnivore diet, a rabies transmission via organ transplant, a brain-eating amoeba infection, accidental THC-laced pizza, and a rare death linked to red meat allergy, highlighting the bizarre and sometimes dangerous surprises in modern medicine.
U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services has approved adding Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Metachromatic Leukodystrophy to the newborn screening panel, enabling earlier diagnosis and treatment to improve outcomes for affected children.

A mother was overjoyed to learn a drug could save her baby's life, but the $2 million cost of the treatment highlights the high prices of new gene therapies, raising concerns about affordability and the impact on the healthcare system.

Novartis is acquiring Avidity Biosciences for about $12 billion to expand its portfolio in rare muscle disorders and strengthen its US presence, with Avidity's early-stage cardiology programs to be spun off into a new company, Spinco.
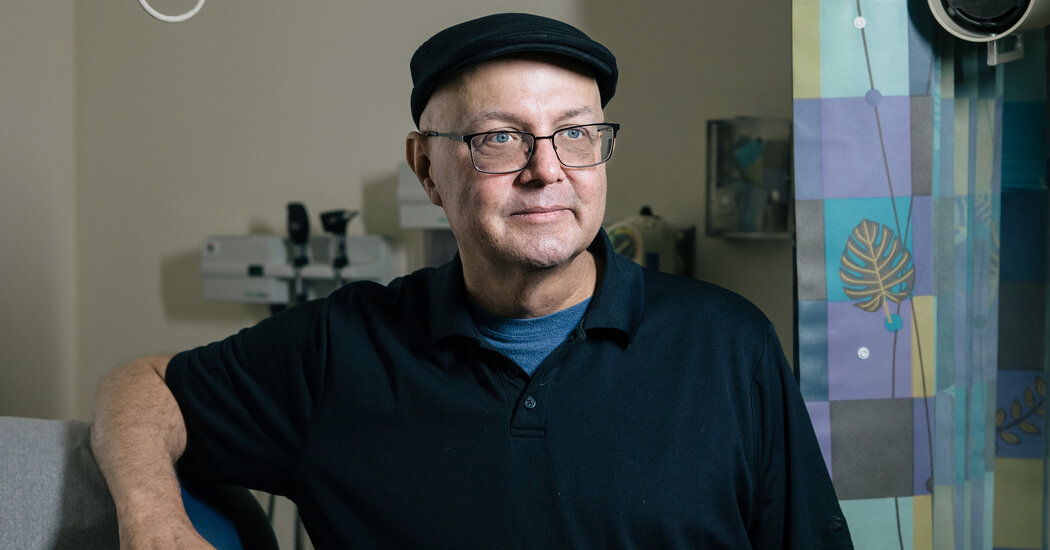

Gene therapies for rare diseases often get developed but are abandoned due to high costs, leaving some patients like Tracy Atteberry with potential cures that are no longer available, highlighting economic barriers in medical innovation.

The FDA has granted accelerated approval to Forzinity (elamipretide) as the first treatment for Barth syndrome, a rare and serious mitochondrial disease, based on improvements in muscle strength that are likely to benefit patients, with further studies required to confirm these benefits.
A rare genetic disorder called complement factor I deficiency, which is more common in the Amish community due to the founder effect, was identified as the cause of brain inflammation in an Amish girl at CHOP, leading to better diagnosis and treatment for similar cases in the community.
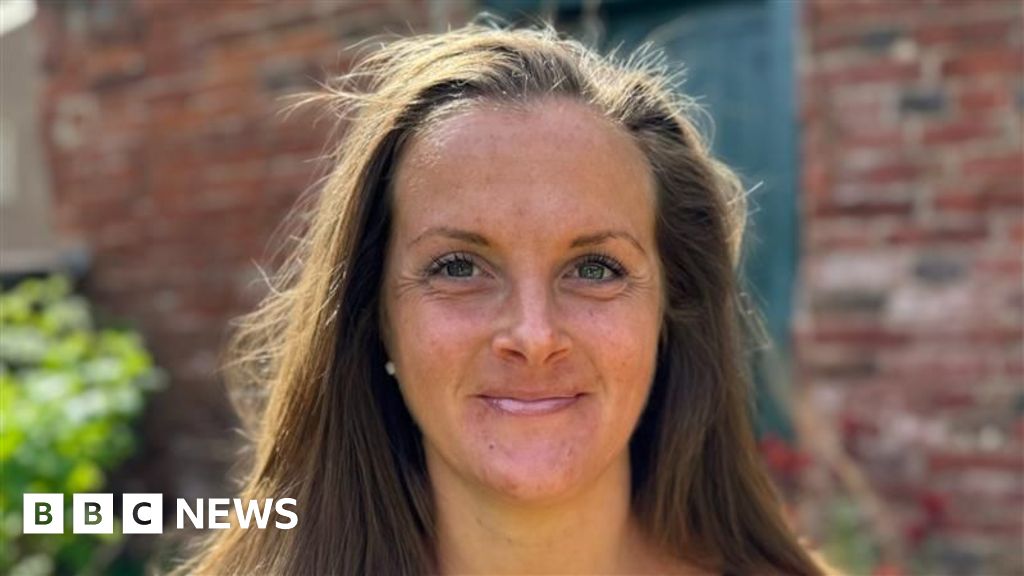

Charlotte Chapman-Hart, a woman with a rare neurological condition, was misdiagnosed with an eating disorder after rapid weight loss caused by medication side effects, leading to traumatic hospital experiences and PTSD. Her story highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis and attentive healthcare for rare diseases.
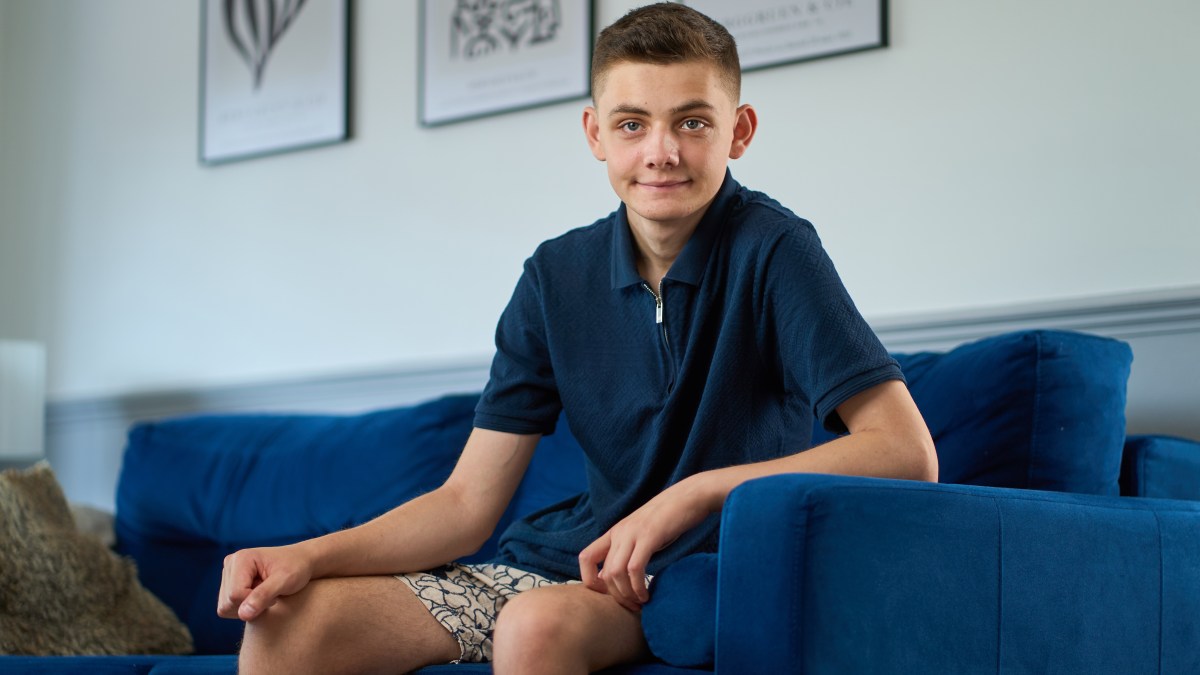

A groundbreaking gene therapy developed by UCL and GOSH has transformed the life of 19-year-old Remi Pereszczak, who suffered from a rare genetic condition called CGD. The therapy, which involves reprogramming his own stem cells, has enabled him to live a healthier, more normal life and attend university. GOSH's new capacity to produce personalized gene therapies in-house promises to accelerate treatment for rare diseases and has broader implications for medicine, including potential cancer cures.