Houston's Black Maternal Health Crisis Reveals Systemic Gaps
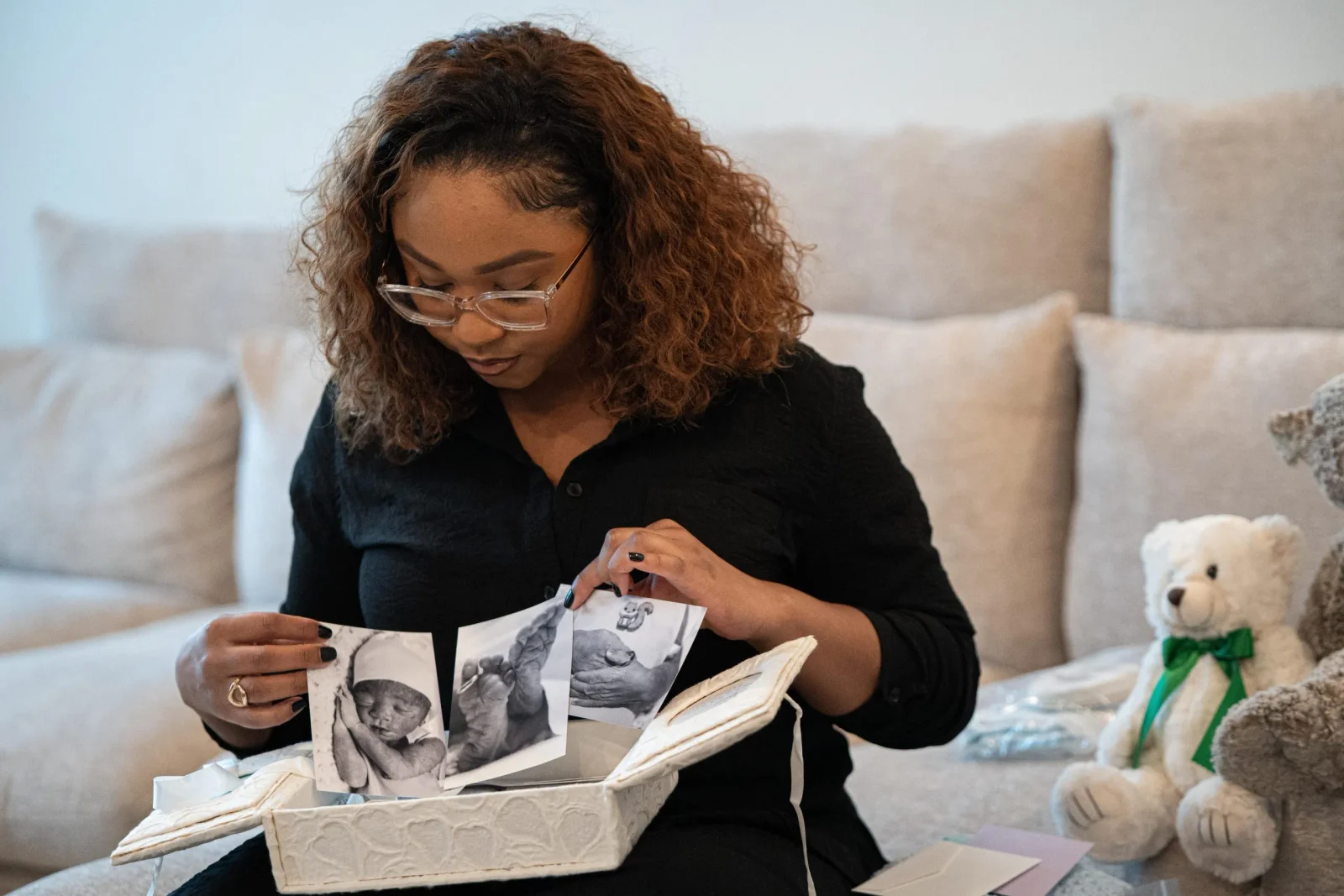
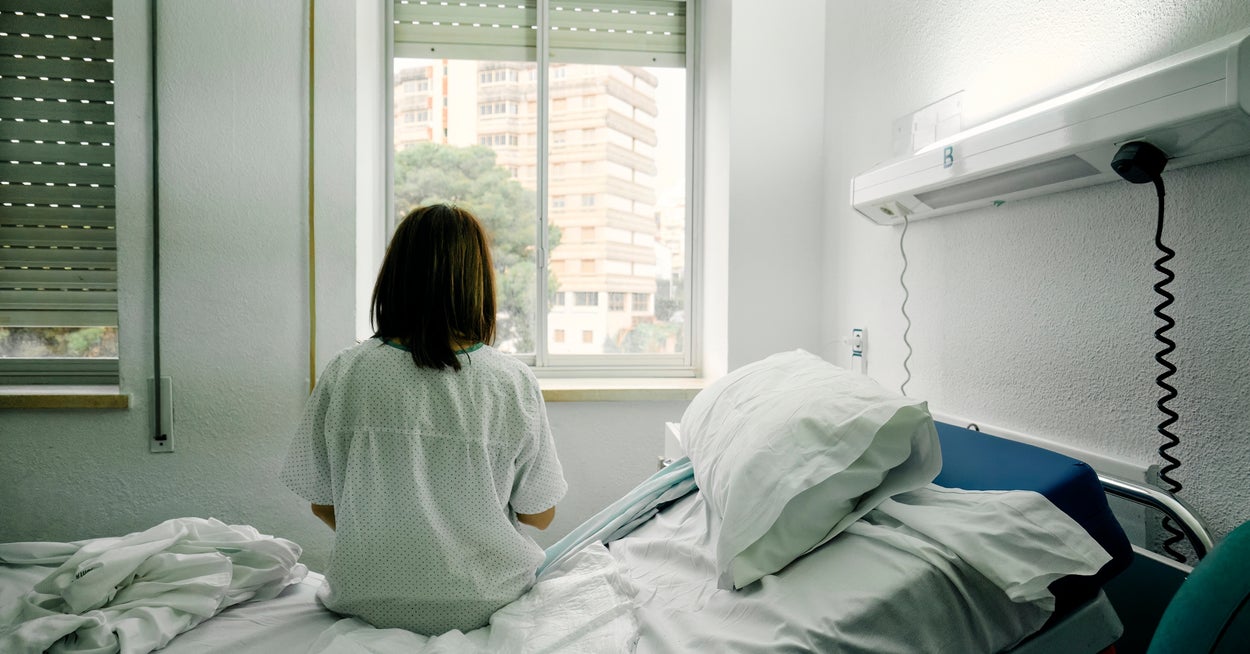
In Harris County, including Houston, Black women face markedly higher pregnancy‑related death and infant mortality rates than white women, driven by social determinants, access gaps, and racial bias. A 2016–2020 study found Black maternal mortality at 83.4 per 100,000 live births—the nation’s highest—while Black infant mortality stood at 11.66 per 1,000. Personal stories, like Moriah Ballard’s fatal preeclampsia and stillborn son, illustrate delayed care, miscommunication, and distrust in the system. Local hospitals and advocates are pushing reforms and funding to expand culturally competent care and improve communication, but experts say racism and systemic gaps must be confronted to save Black mothers and babies.