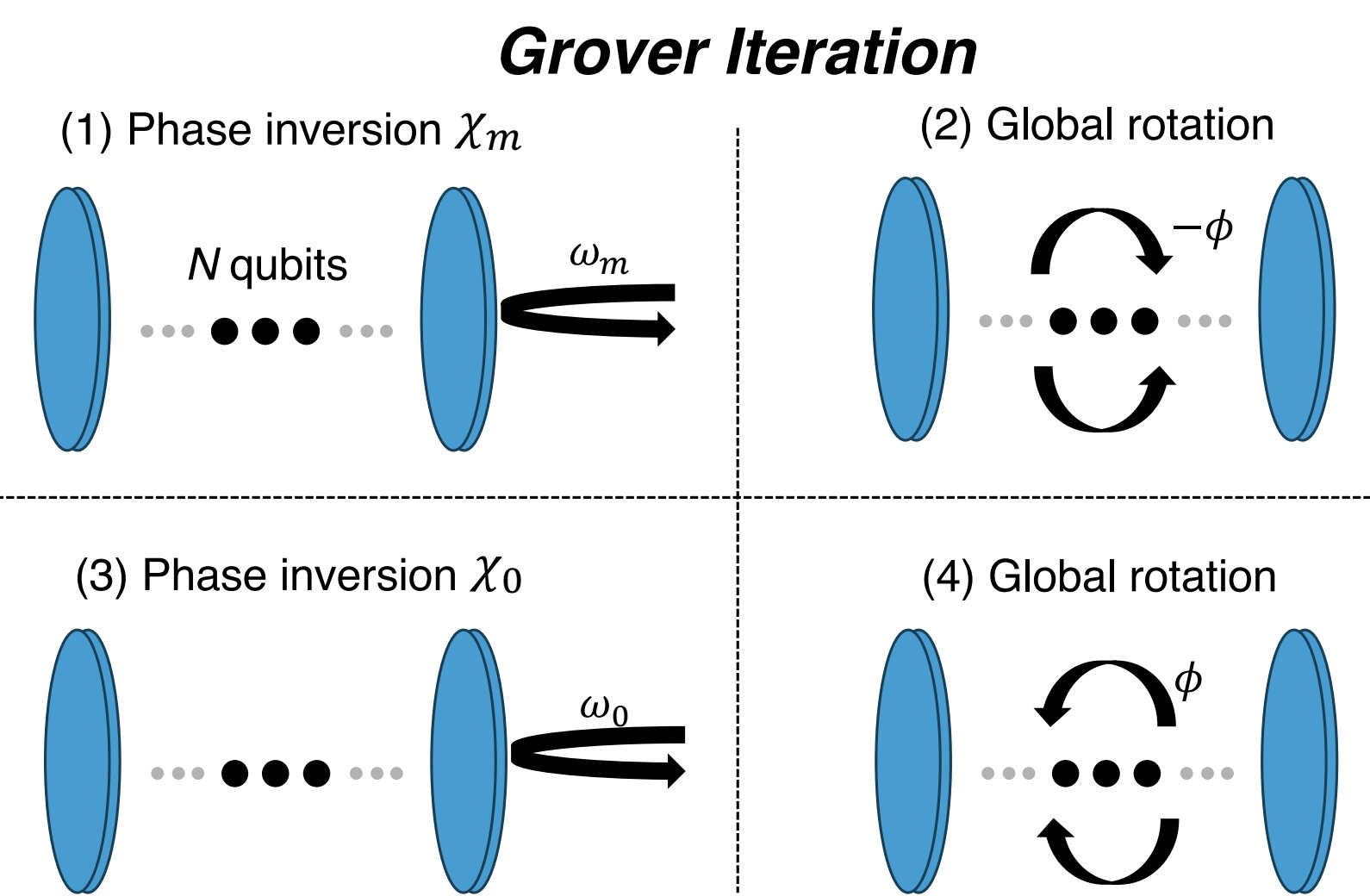
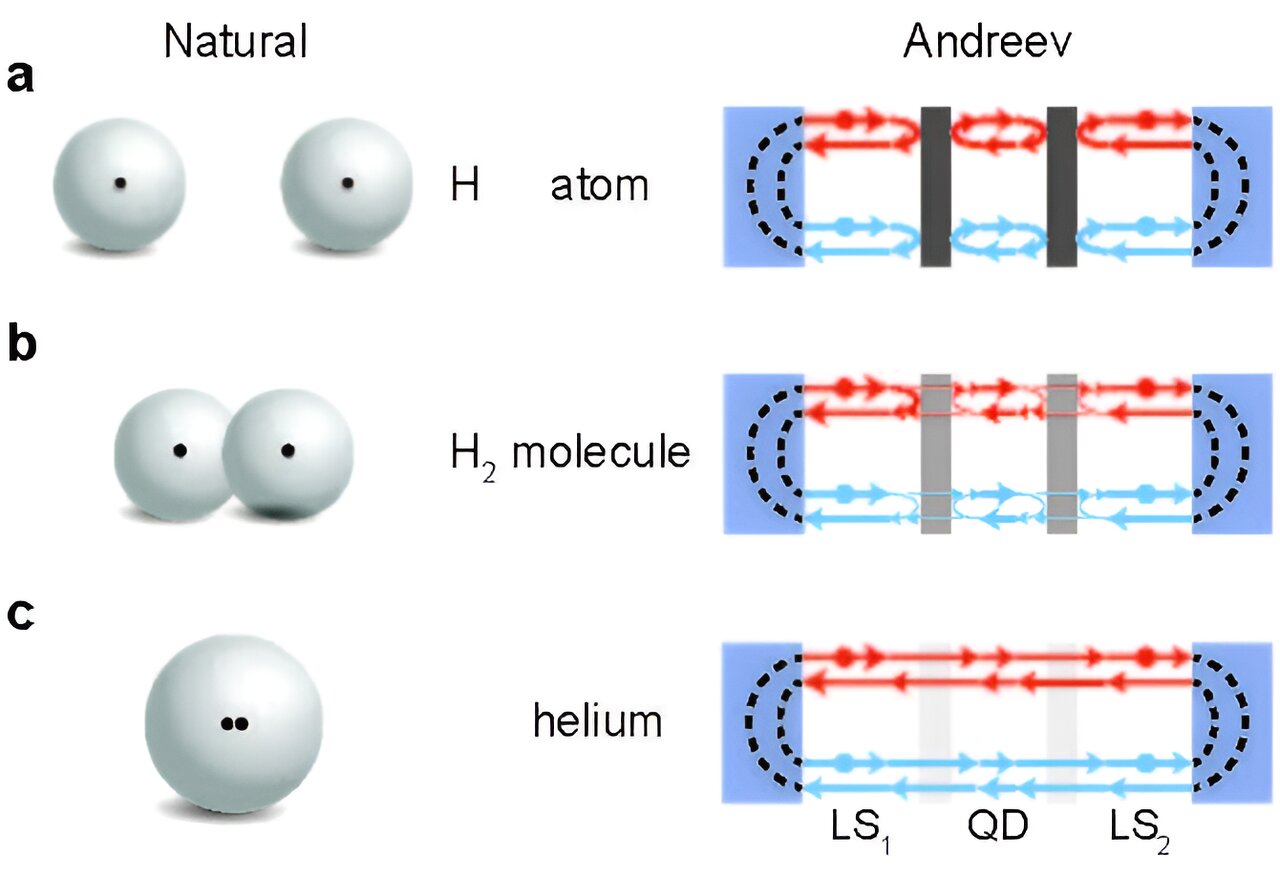
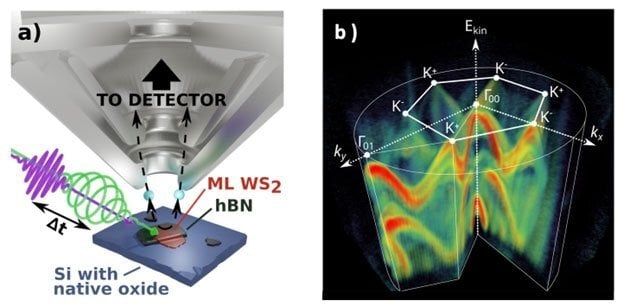
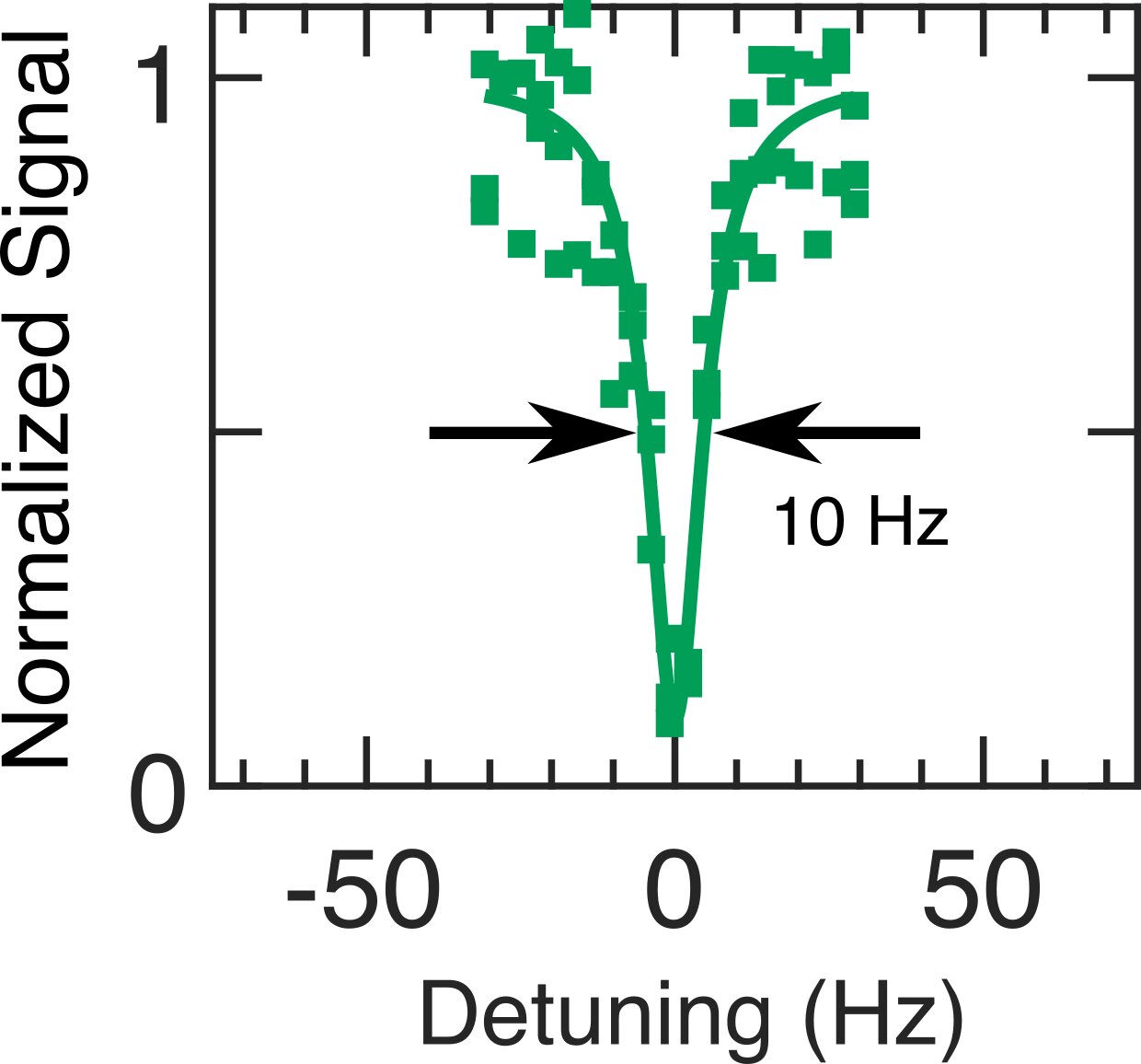
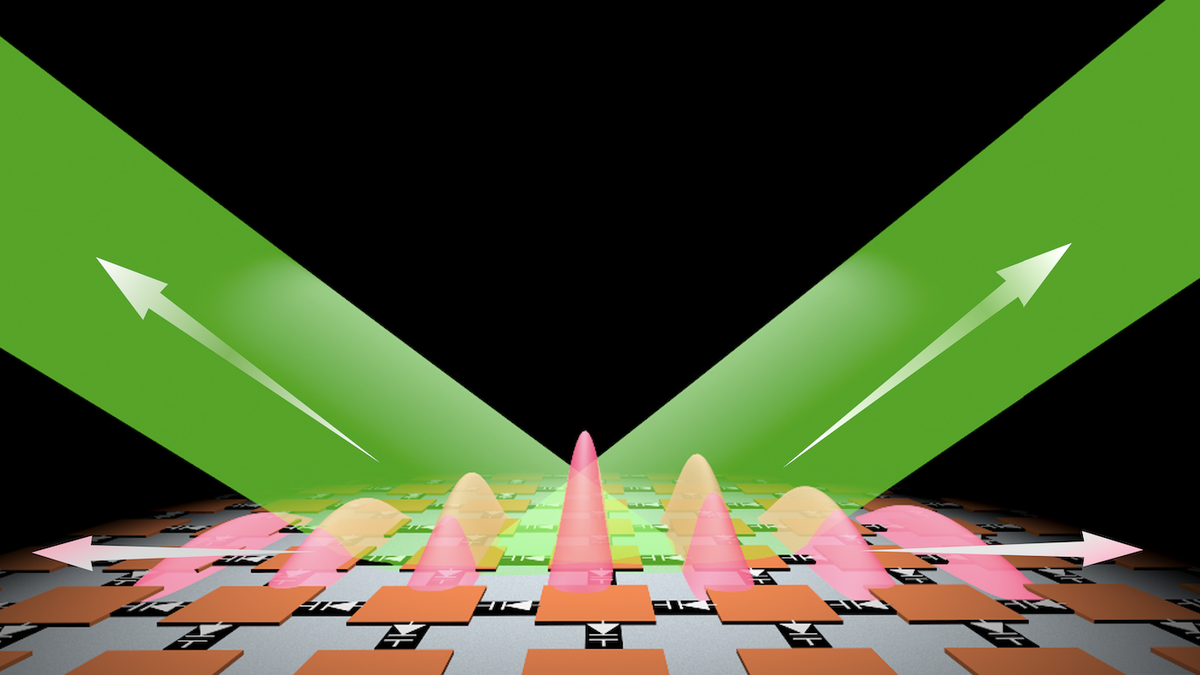
Quantum Computers Struggle with Intractable Problems
Researchers have demonstrated that recognizing phases of matter in quantum states can be exponentially hard for quantum computers, especially as the correlation length increases, making some problems practically impossible to solve efficiently, which raises fundamental questions about the limits of physical observation.