Quadcopter Breaks World Speed Record at 657 km/h
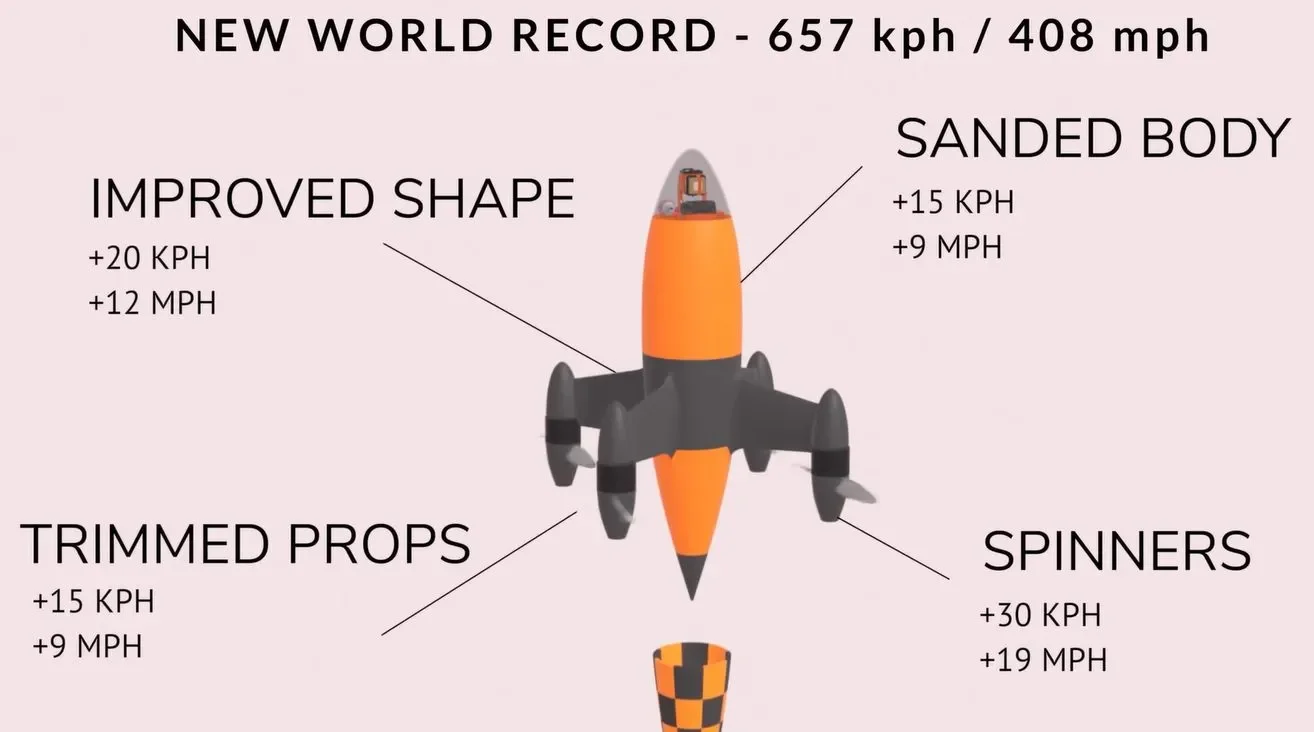
A team led by Luke Maximo Bell set a new drone speed record by achieving an average speed of 657 km/h with a redesigned V4 quadcopter featuring upgraded engines, props, and a larger 3D-printed body, tested via simulations and printed on a Bambu Lab H2D. A follow camera attempt with a 360-degree setup was not finalized, keeping the door open for future challengers while noting that prop airplanes have exceeded 800 km/h.