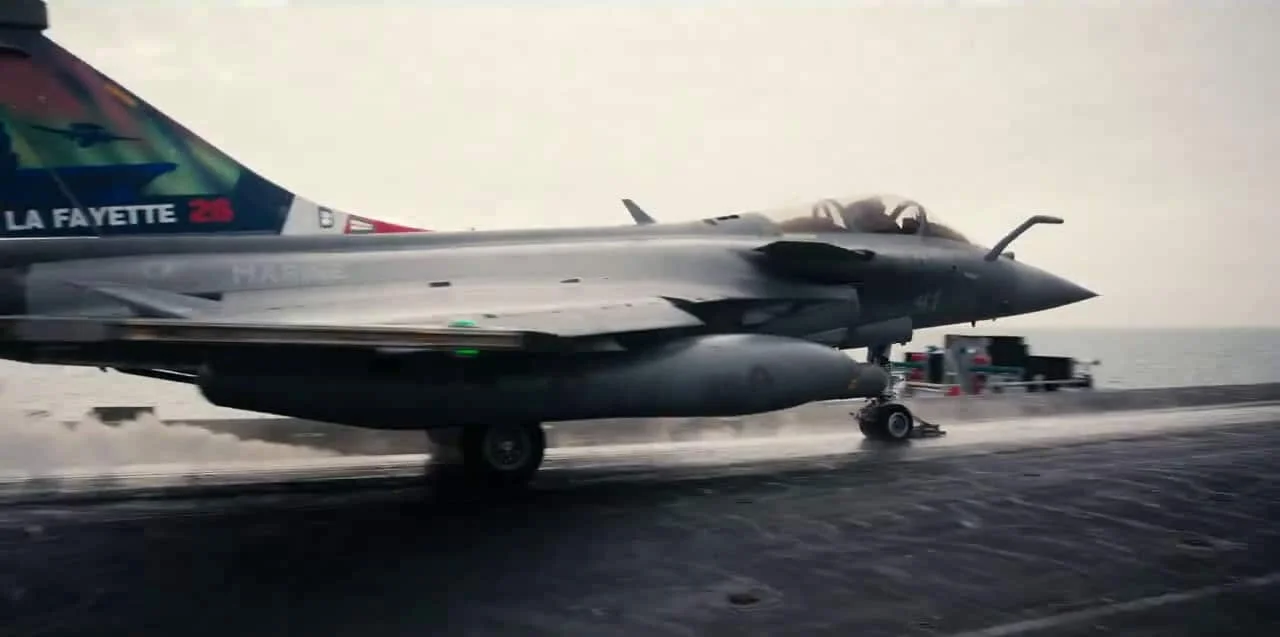
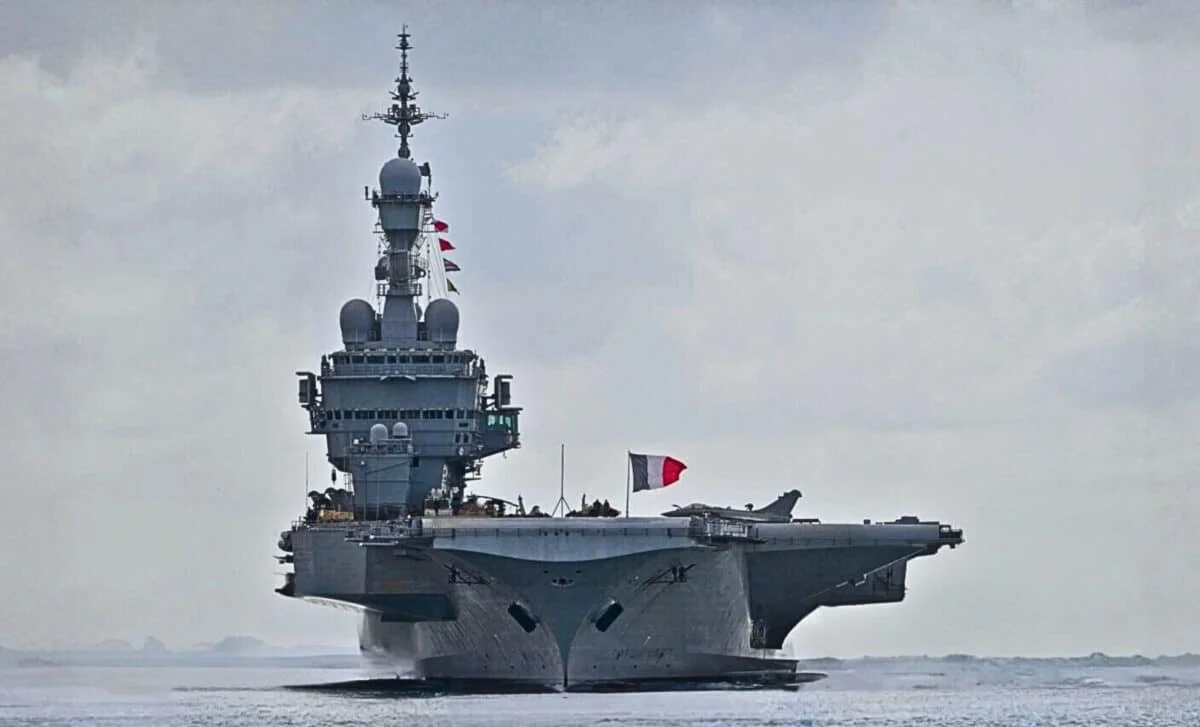
France mobilizes Charles de Gaulle for North Atlantic NATO mission LA FAYETTE 26
France’s carrier strike group led by the nuclear-powered Charles de Gaulle has begun a North Atlantic deployment for mission LA FAYETTE 26, after departing Toulon on January 27 for the Orion 26 exercise, and will participate in NATO drills Steadfast Dart, Baltic Sentry, Neptune Strike, and Cold Response, including a historic port visit to Malmö, Sweden, as France strengthens maritime interoperability amid rising Russian activity and a shifting Arctic focus.