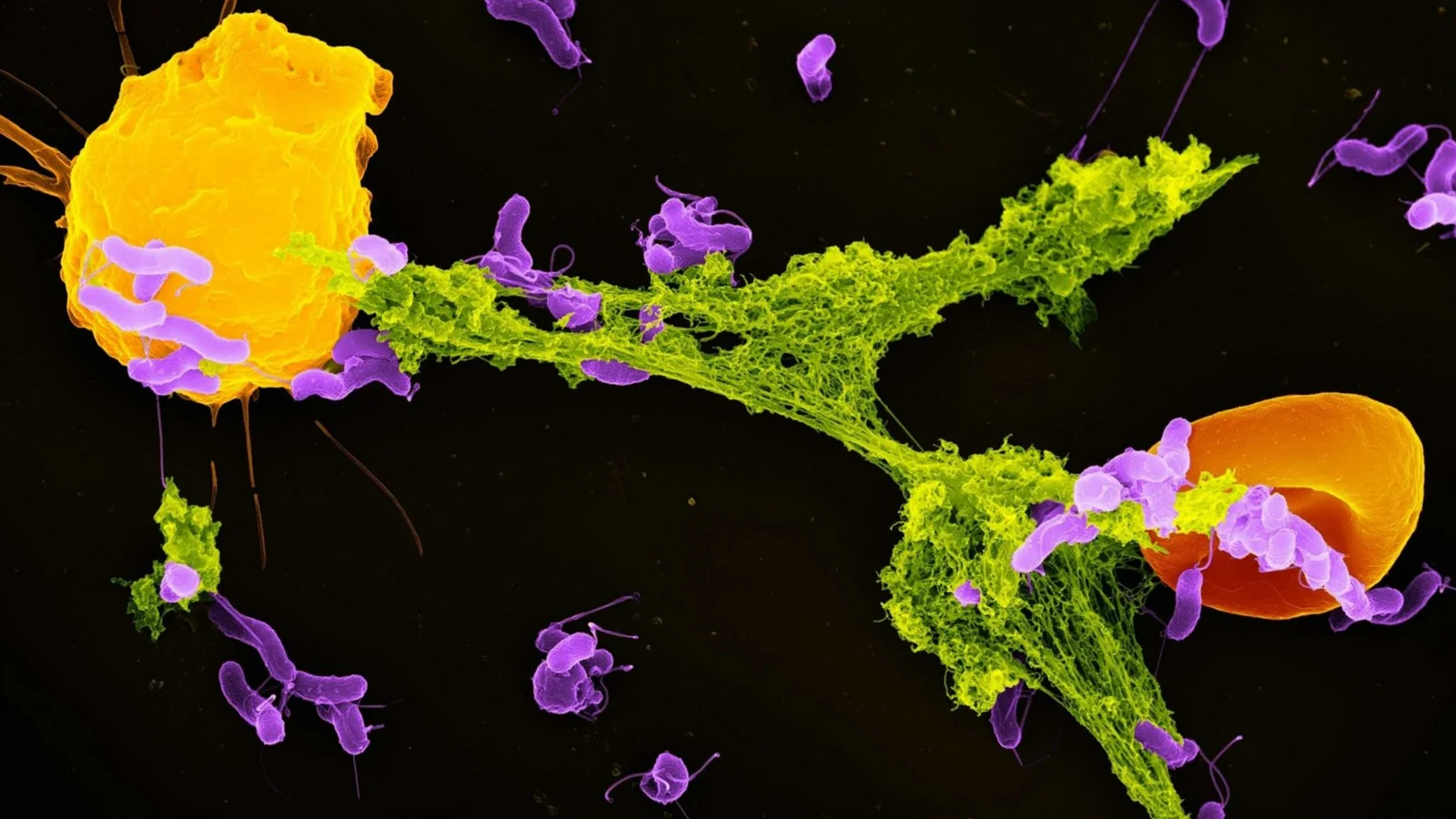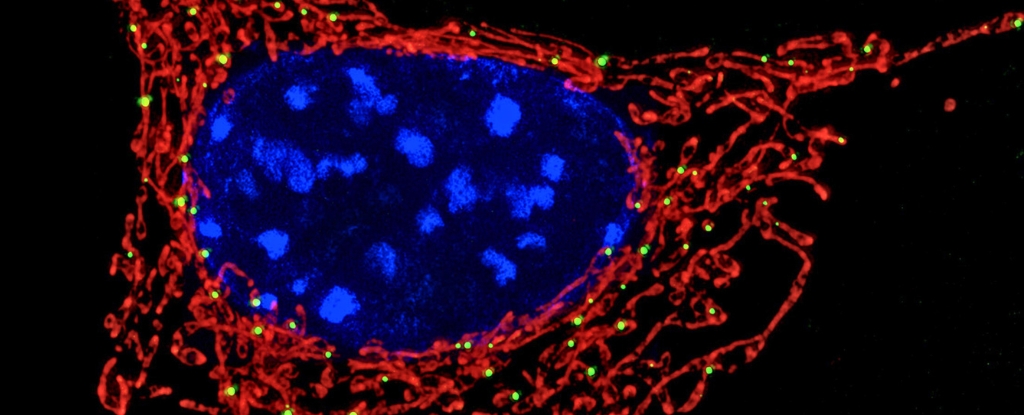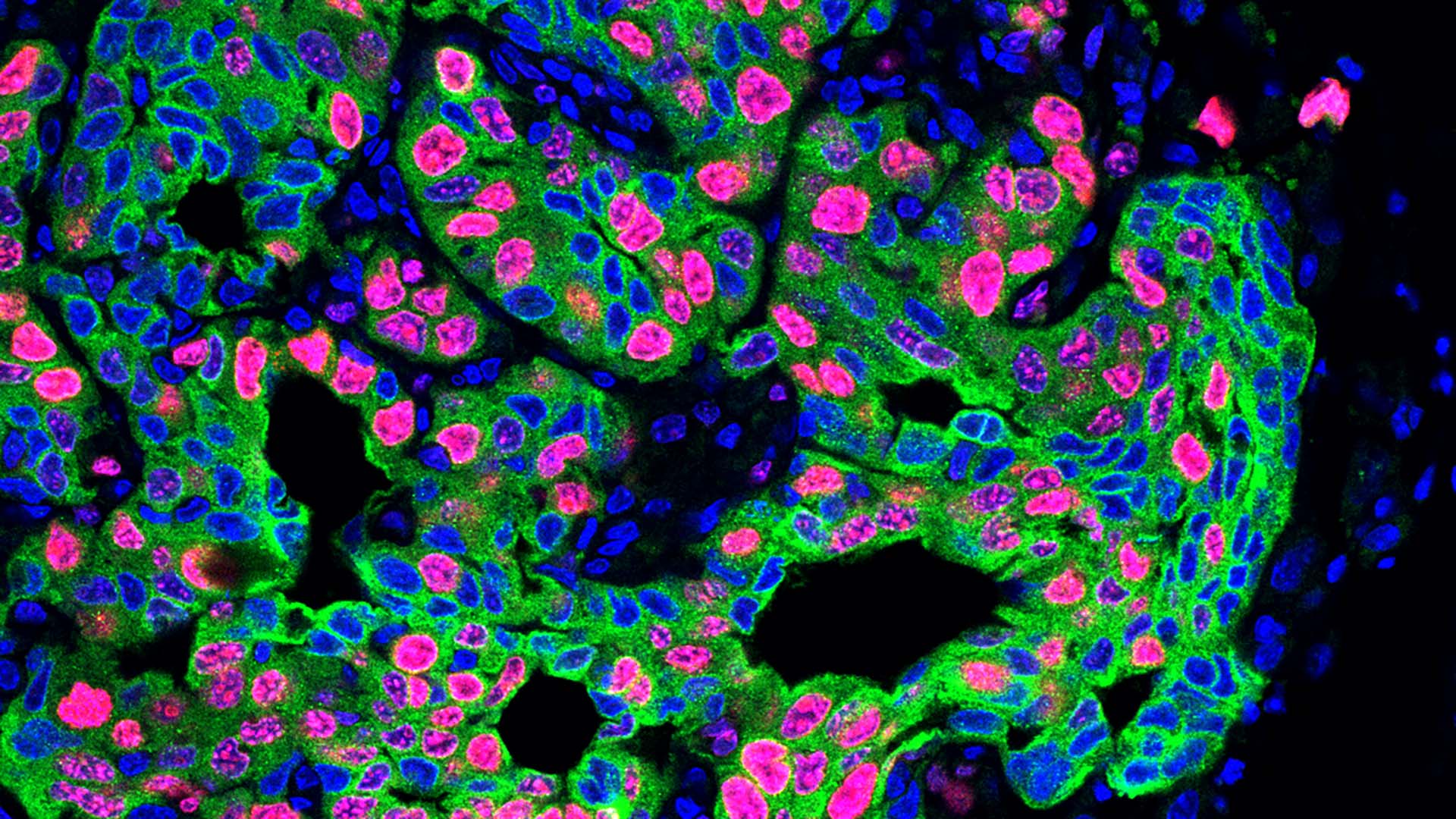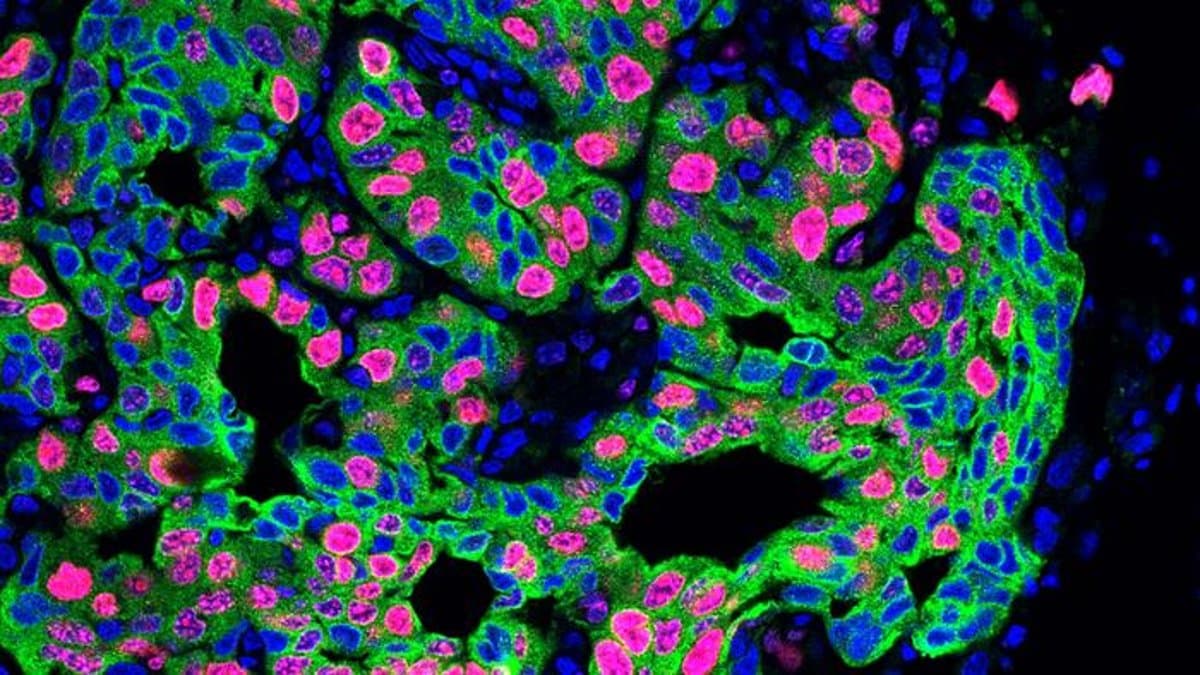
Tumor-Modulated Neutrophils Fuel Cancer Growth via CCL3
University of Geneva researchers find that neutrophils recruited to tumors are reprogrammed to produce the chemokine CCL3, which promotes tumor growth. This shift helps explain why some cancers become more aggressive and points to CCL3 activity in neutrophils as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. The team used genetic tools to selectively suppress CCL3 in neutrophils and reanalyzed multiple studies to confirm the link.