"Neurotransmitters Influence Social Behavior in Economic Exchange"
Originally Published 1 year ago — by Nature.com
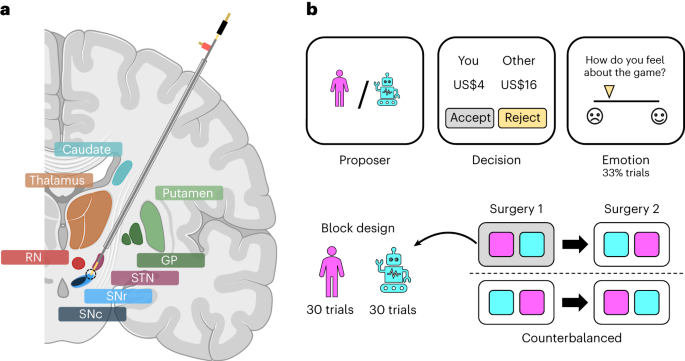
A study using electrochemistry to measure fast dopamine and serotonin fluctuations in the human brain during the ultimatum game found that overall levels of dopamine, but not serotonin, were higher in response to offers from human avatars compared to computer avatars. Additionally, relative changes in dopamine tracked trial-by-trial changes in offer value, resembling reward prediction error signaling, while relative changes in serotonin tracked the current offer value irrespective of the social context. This research provides insights into the roles of dopamine and serotonin in human social interaction at finer biological scales.