Understanding and Managing Fatty Liver Disease: Causes, Diet, and New Treatments
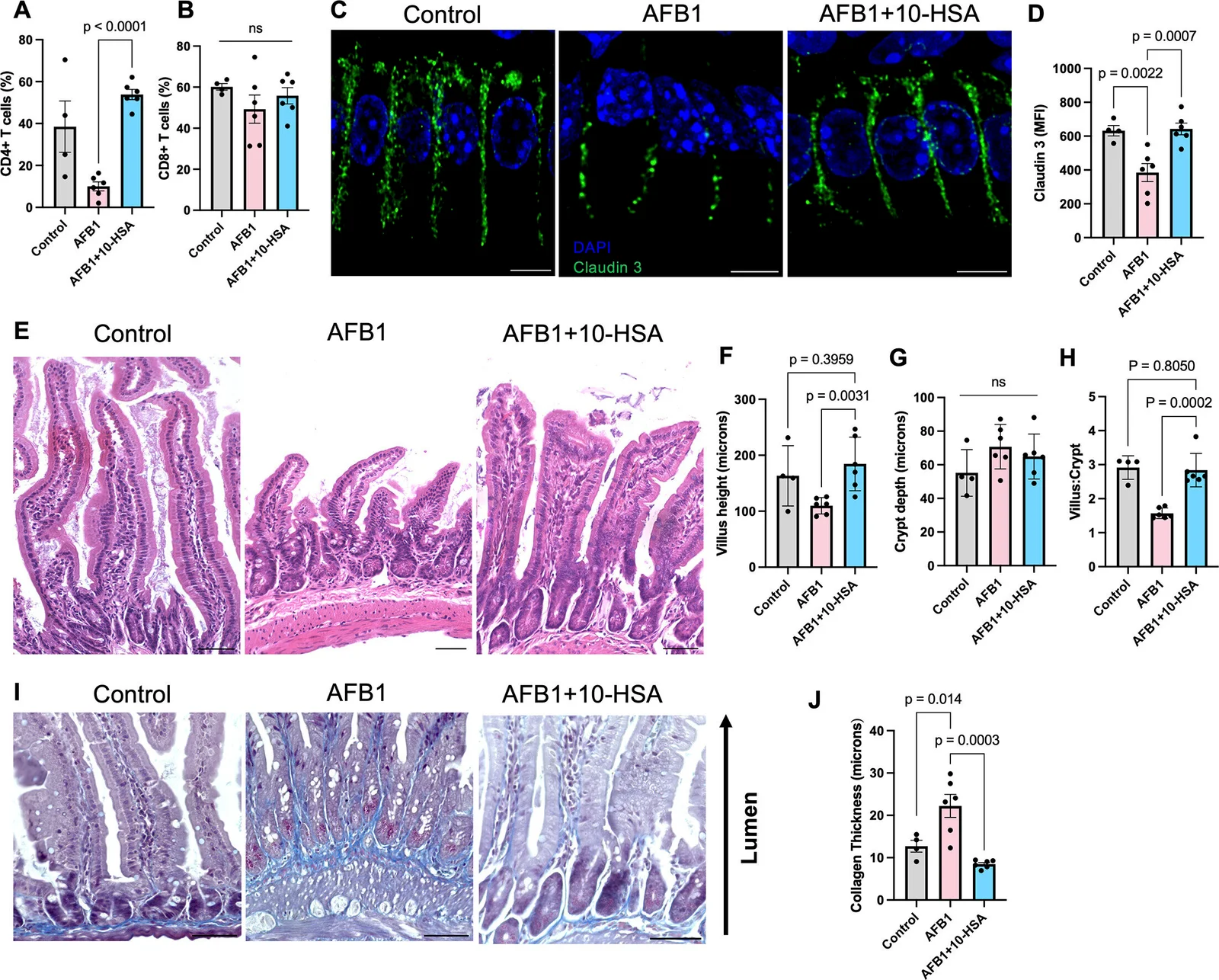
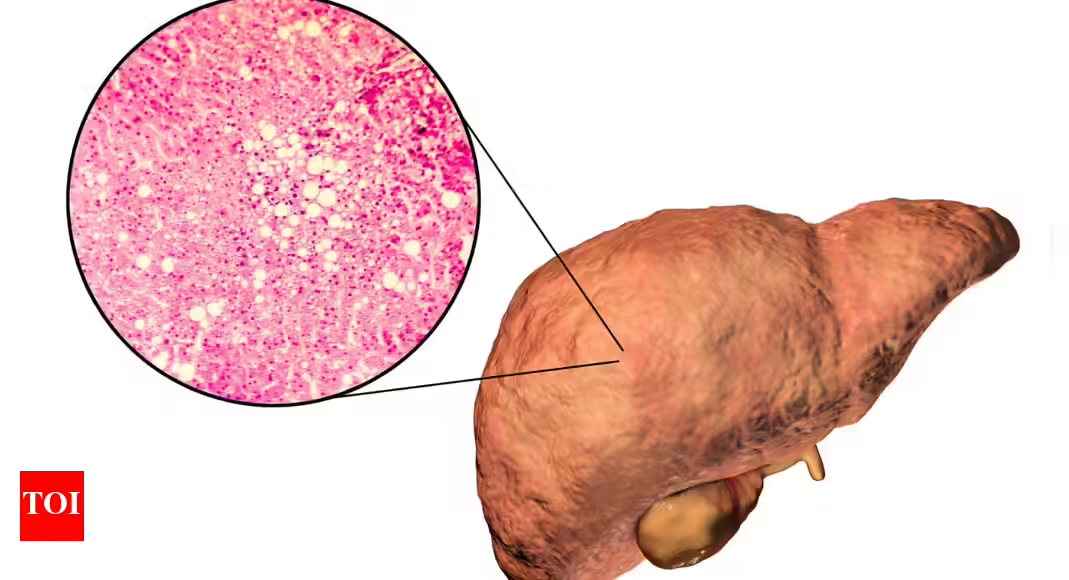
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is linked to nutritional imbalances, particularly deficiencies in copper and vitamin A, and excess intake of fruit sugar (fructose). Dr. DeBease suggests that supporting liver health involves eliminating fruit, reducing carbs, and increasing nutrient-dense foods like organ meats to aid iron processing and repair liver damage. The approach emphasizes internal nutritional support over simply reducing fat intake.