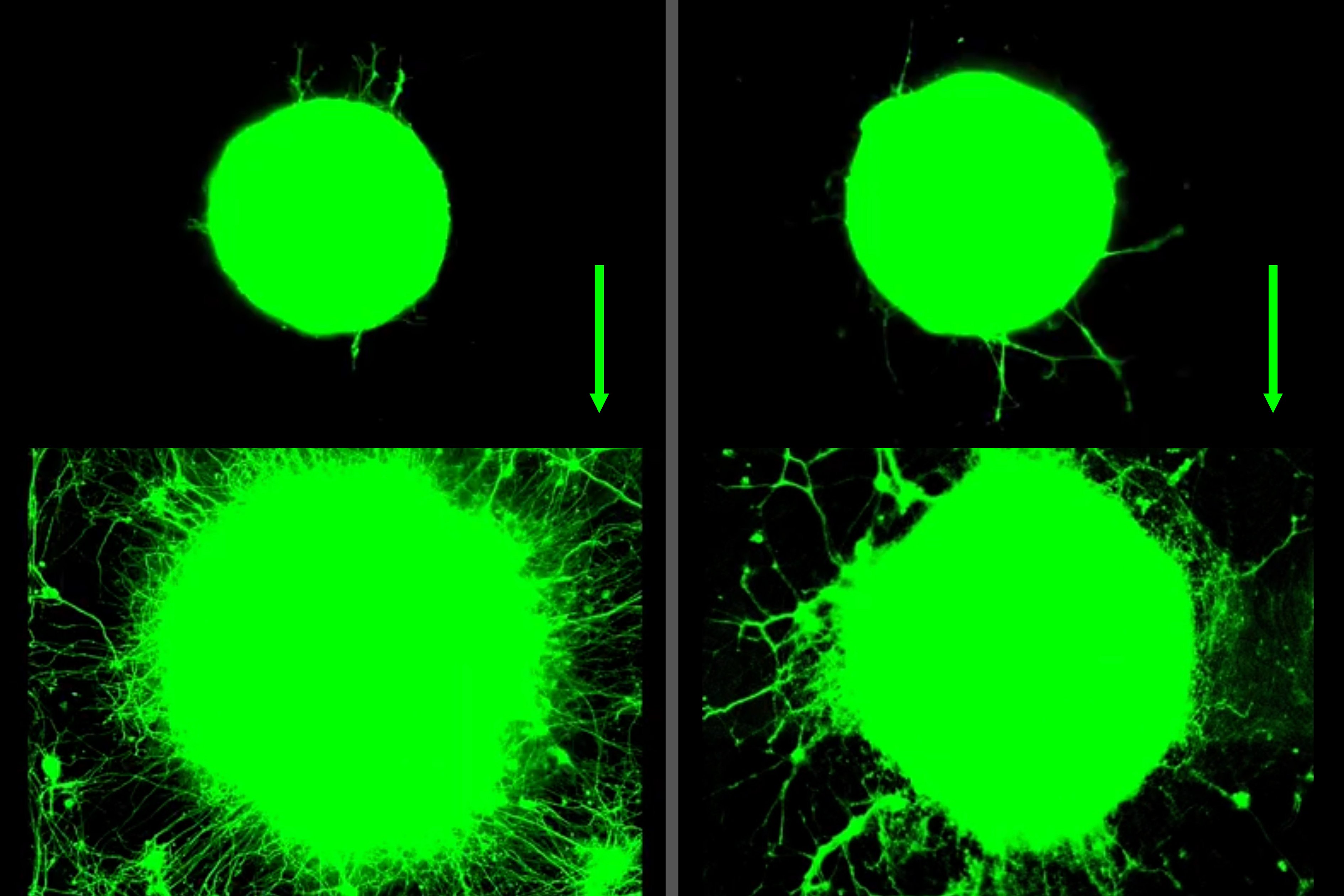
Muscle-Produced 'Exercise Juice' Promotes Nerve Growth
A new study suggests that myokines, chemicals released by muscles during exercise, can promote nerve growth, potentially aiding in nerve repair and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like ALS. Conducted on mouse cells, the research found that both biochemical and mechanical effects of muscle contractions stimulate motor neuron growth. While promising, further studies are needed to explore the therapeutic potential of myokines in humans.