Unveiling the Intricacies of Cardiac Myosin Filament Structure
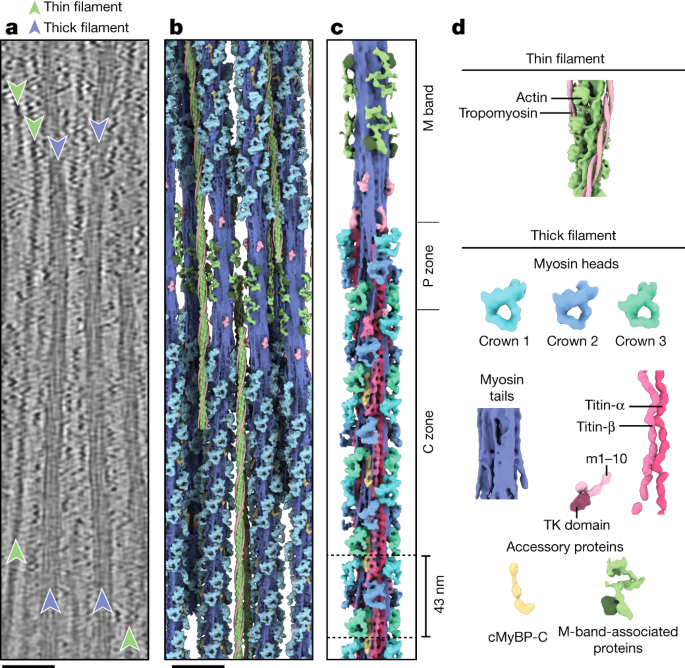
Researchers have determined the structure of the native myosin filament in the relaxed cardiac sarcomere, the basic contractile unit of muscle. The study reveals the arrangement and interactions of key proteins, including myosin, titin, and MyBP-C, within the thick filament. The myosin heads are organized in a quasihelical array with three-fold rotational symmetry, and the myosin tails form a coiled-coil structure at the center of the filament. MyBP-C acts as a mechanical sensor and links the thick and thin filaments, while titin acts as a molecular spring and ruler for myosin assembly. The findings provide insights into the molecular mechanics of muscle contraction and could have implications for understanding and treating cardiac diseases.
- Structure of the native myosin filament in the relaxed cardiac sarcomere Nature.com
- Scientists shoot first true-to-life 3D image of the thick filament of mammalian heart muscle Phys.org
- Cryo-EM structure of the human cardiac myosin filament Nature.com
- Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure Nature.com
Reading Insights
0
1
64 min
vs 65 min read
99%
13,000 → 113 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com