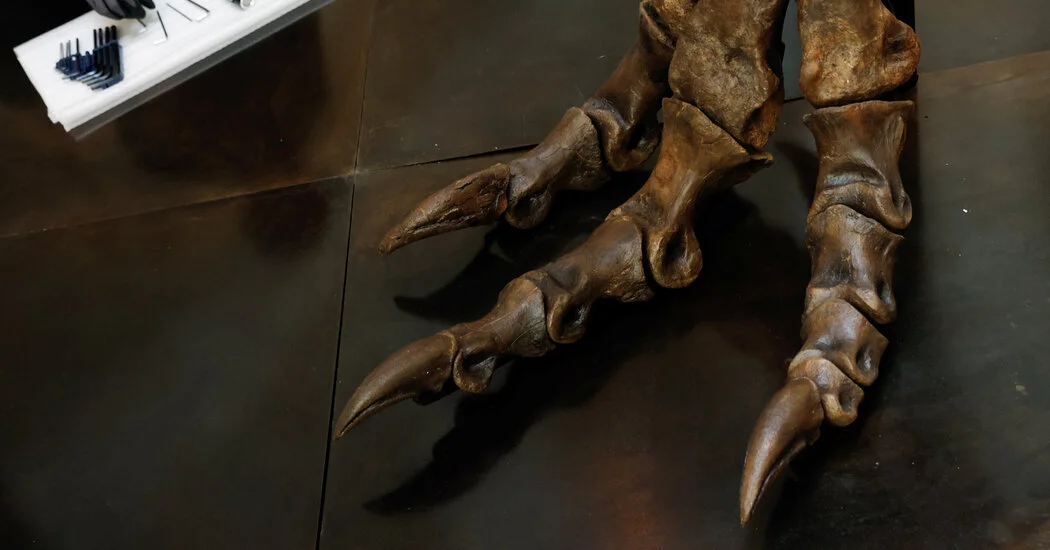
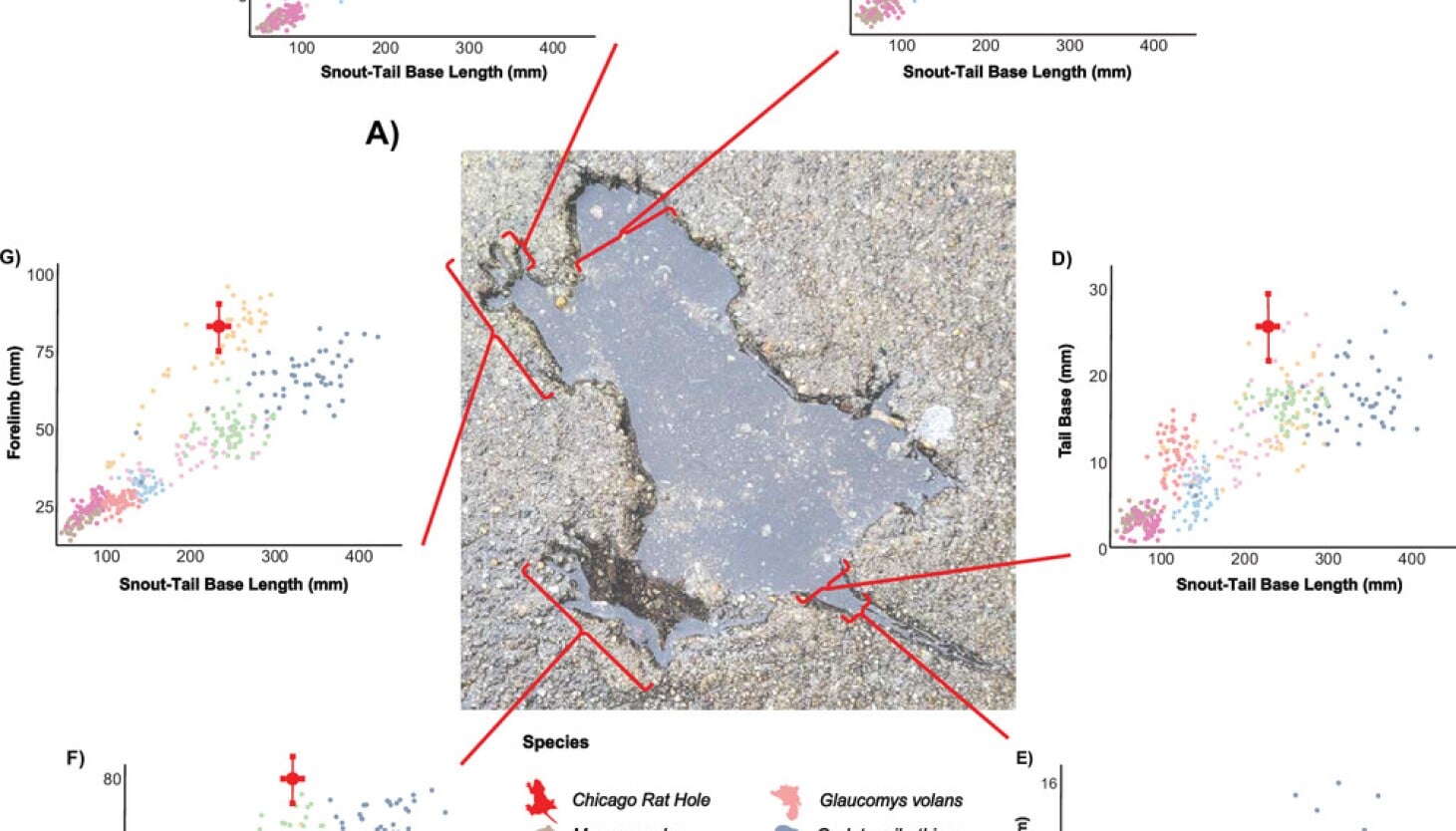
T. rex Tiptoes Like a Giant Bird, New Study Shows
A Royal Society Open Science study analyzing T. rex footprints and leg anatomy finds the giant predator walked on its toes with birdlike, quick strides rather than heel-first stomping. Juveniles could reach over 37 ft/s and adults about 20 ft/s, suggesting different hunting behaviors as they aged and reinforcing the link between tyrannosaurs and living birds.