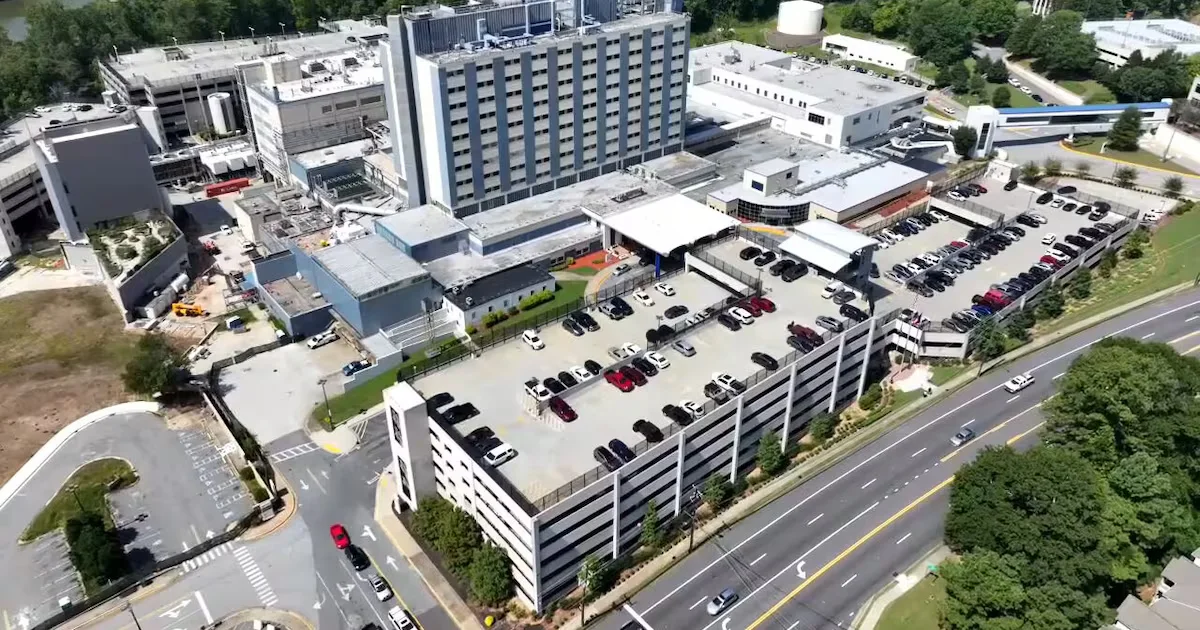
Legionella positive in Atlanta VA patient prompts cleaning and monitoring
An immunocompromised patient at the Atlanta VA Health Care System died after testing positive for Legionella. The facility sampled the patient’s room and a nearby ice machine; routine water-system testing on the seventh floor had been negative for two years. Other patients were relocated, the area disinfected, and investigators consulted federal health agencies. There are no active Legionella cases reported at the facility.