Deadly Fungus Spreads Nationwide Amid Rising Drug Resistance
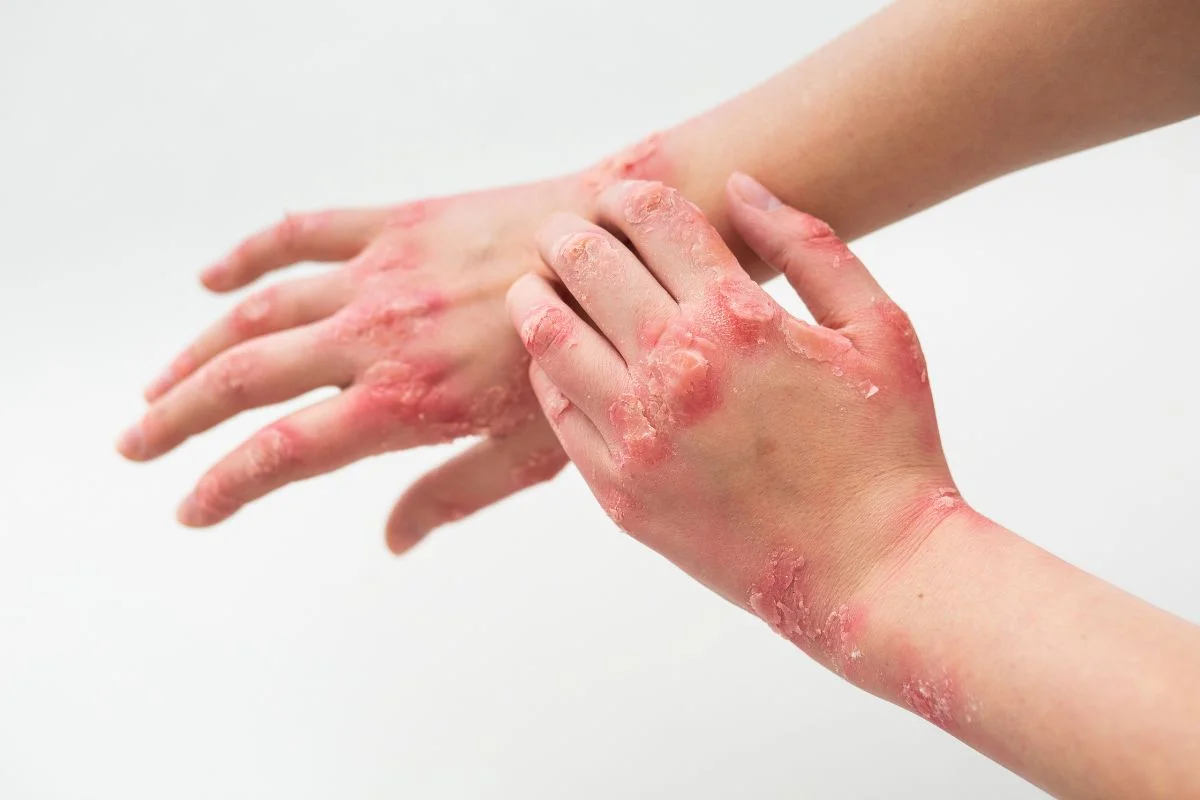
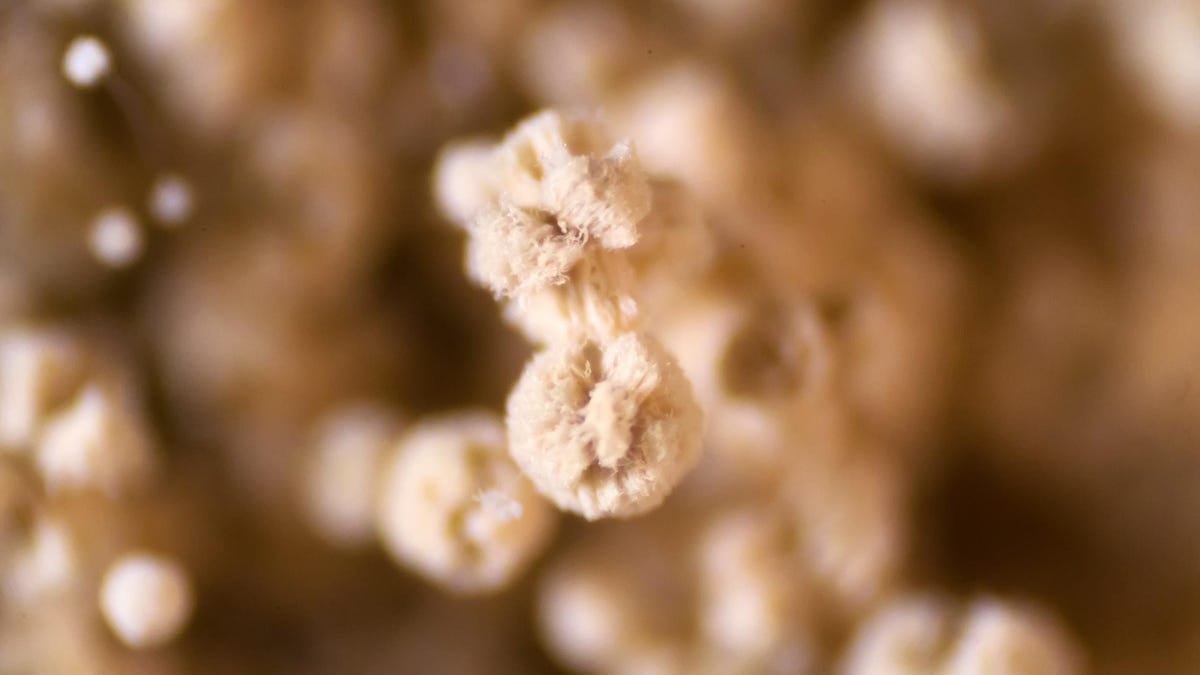
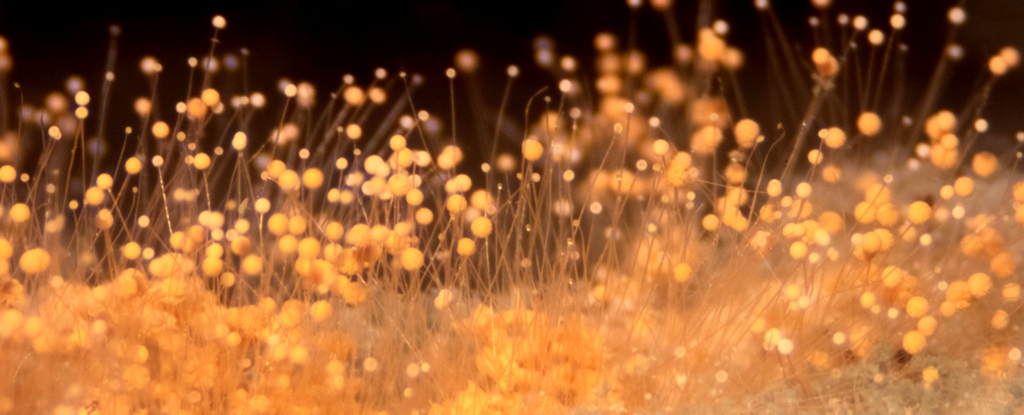
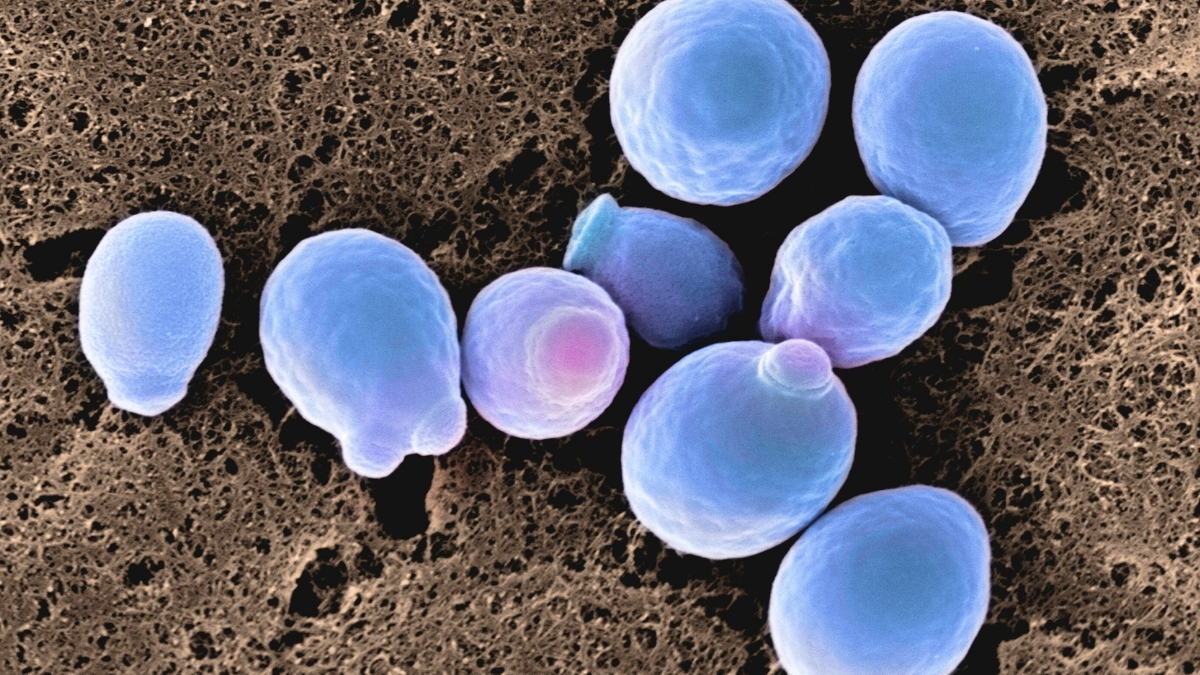
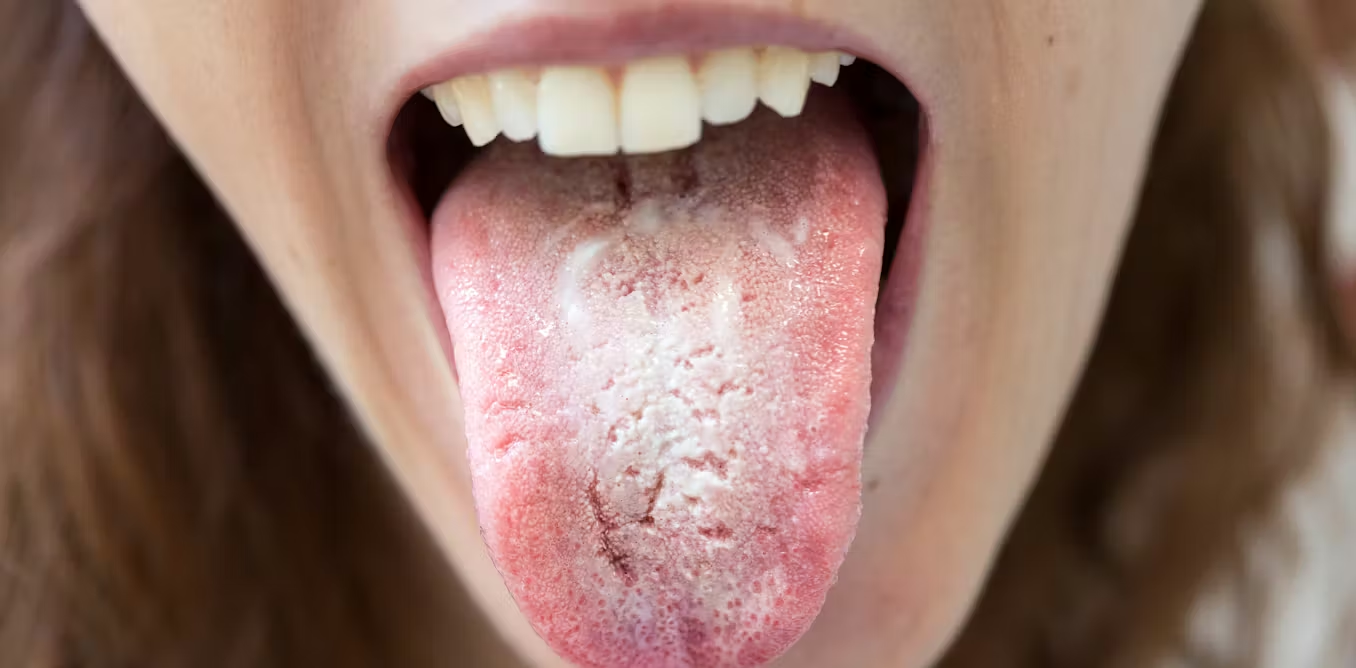
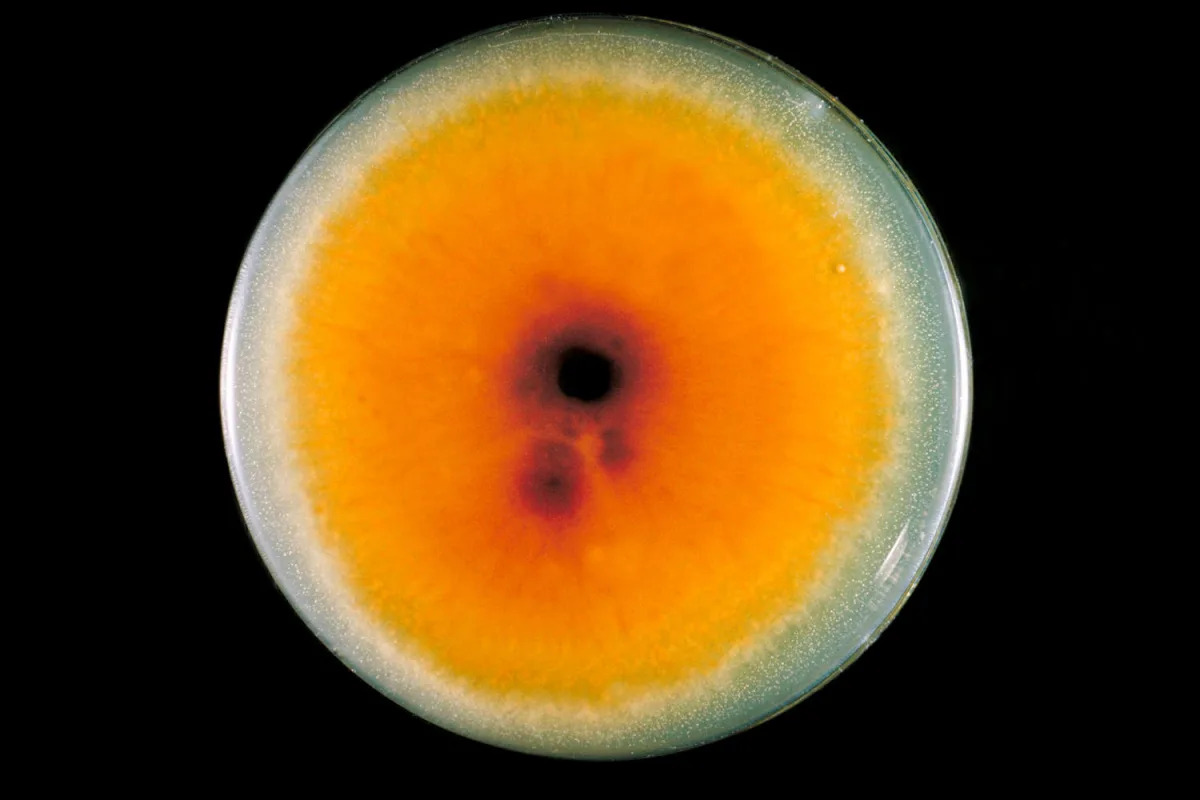
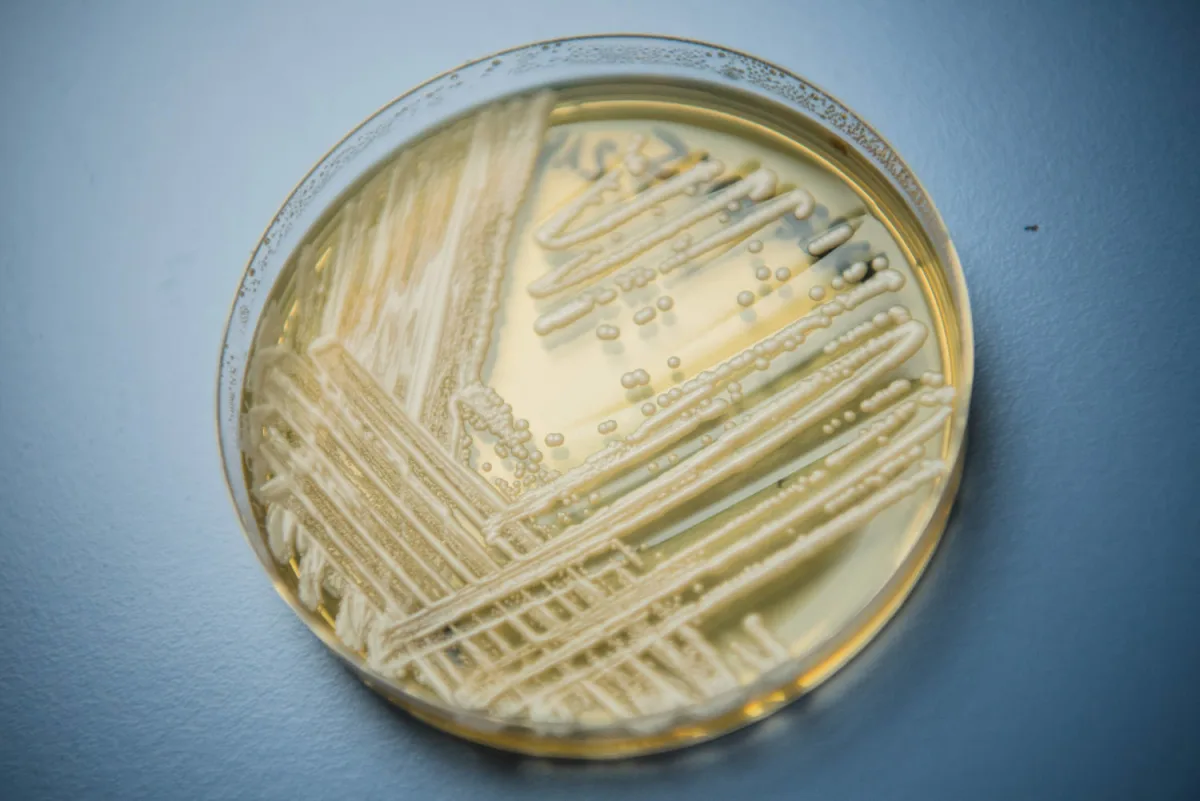
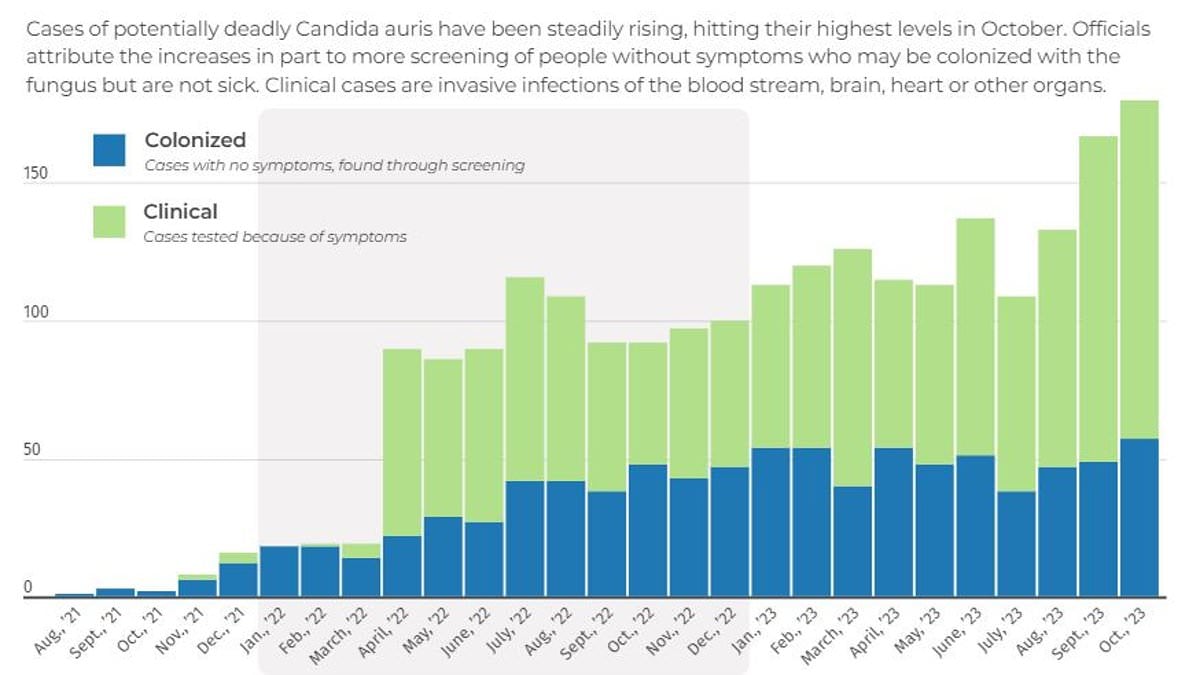
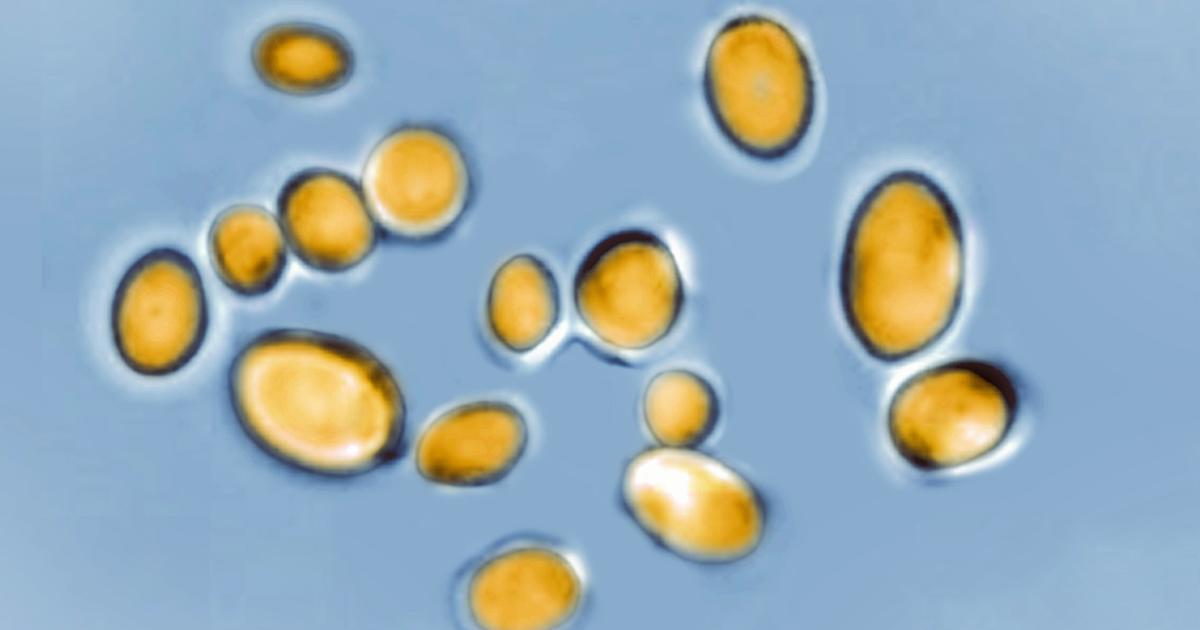
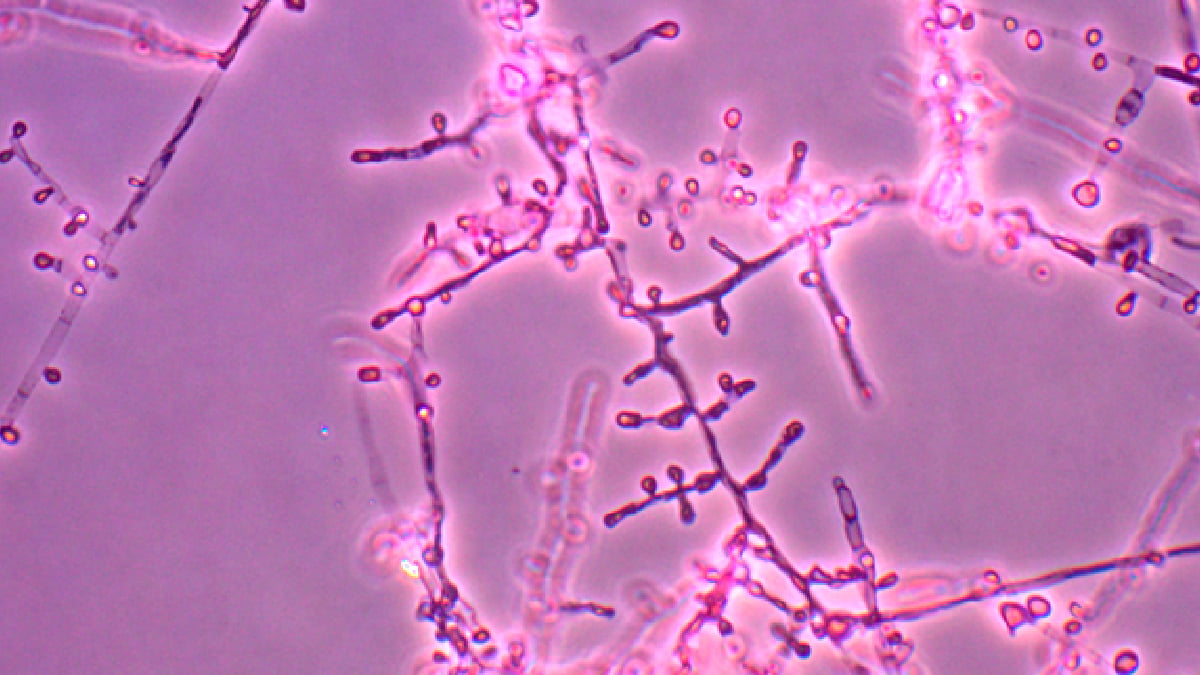
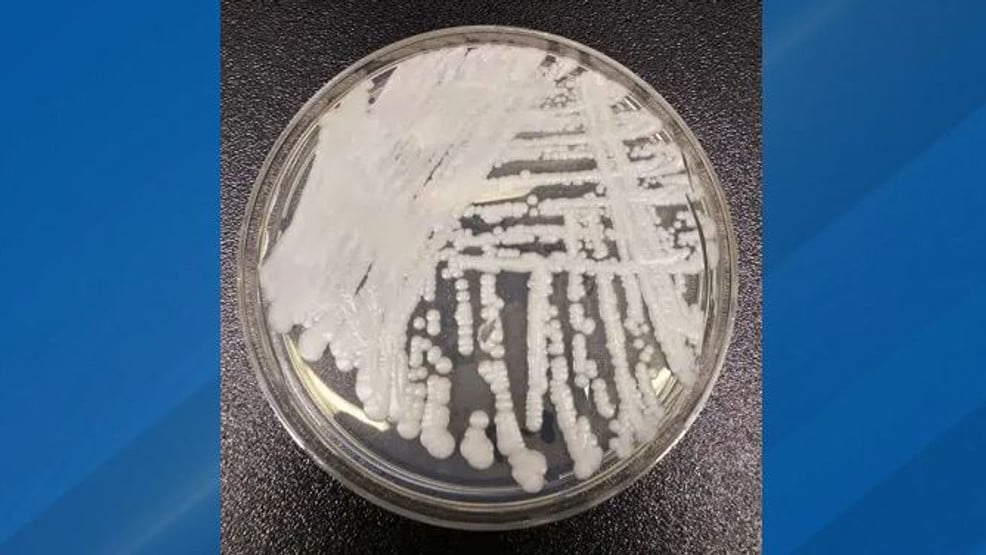
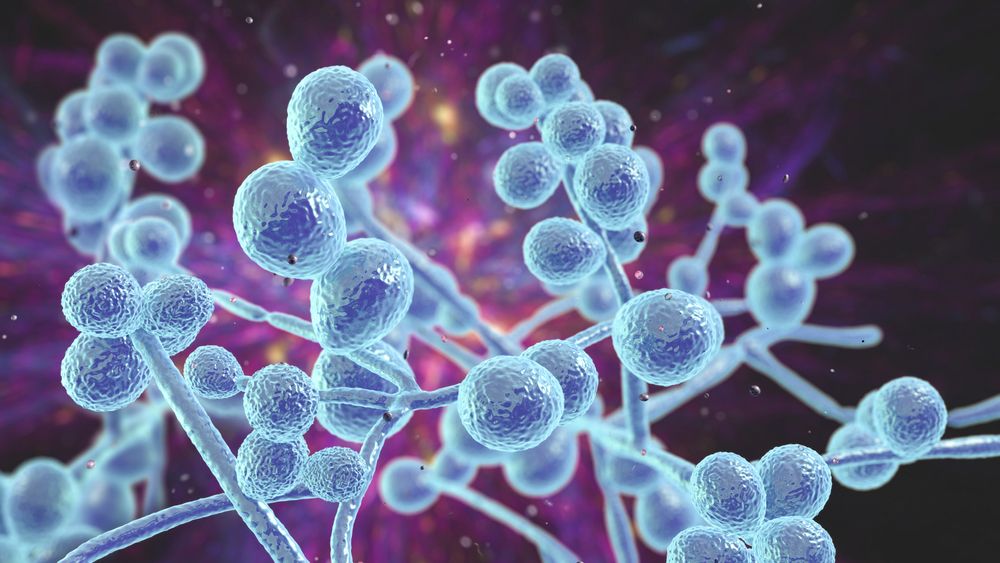
A drug-resistant fungus called Candida auris has been reported in 27 US states with over 7,000 cases, posing a serious threat in healthcare settings due to its resistance to multiple antifungal drugs and ability to spread easily, highlighting a growing global concern about antifungal resistance and the need for strict infection control measures.