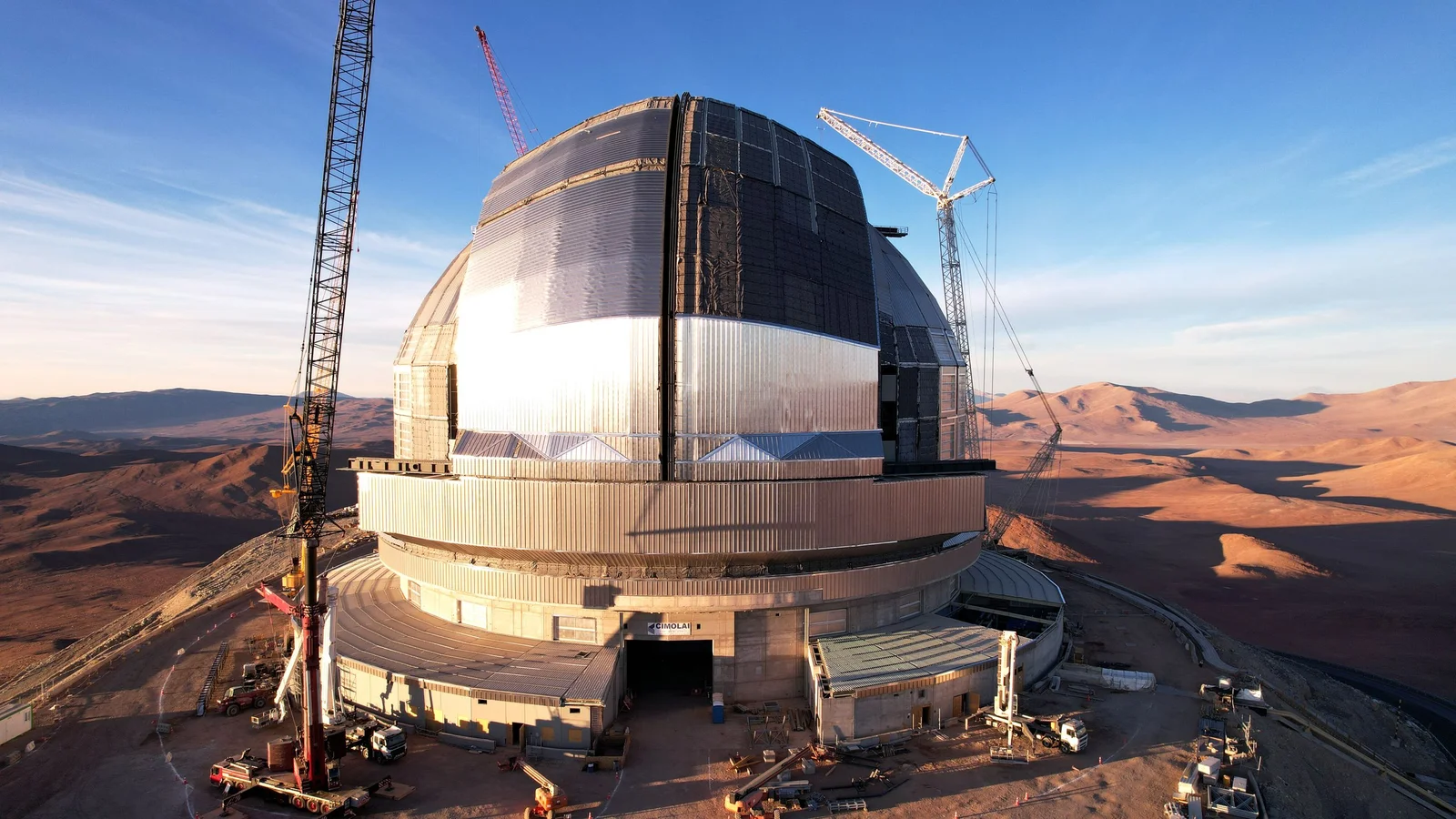
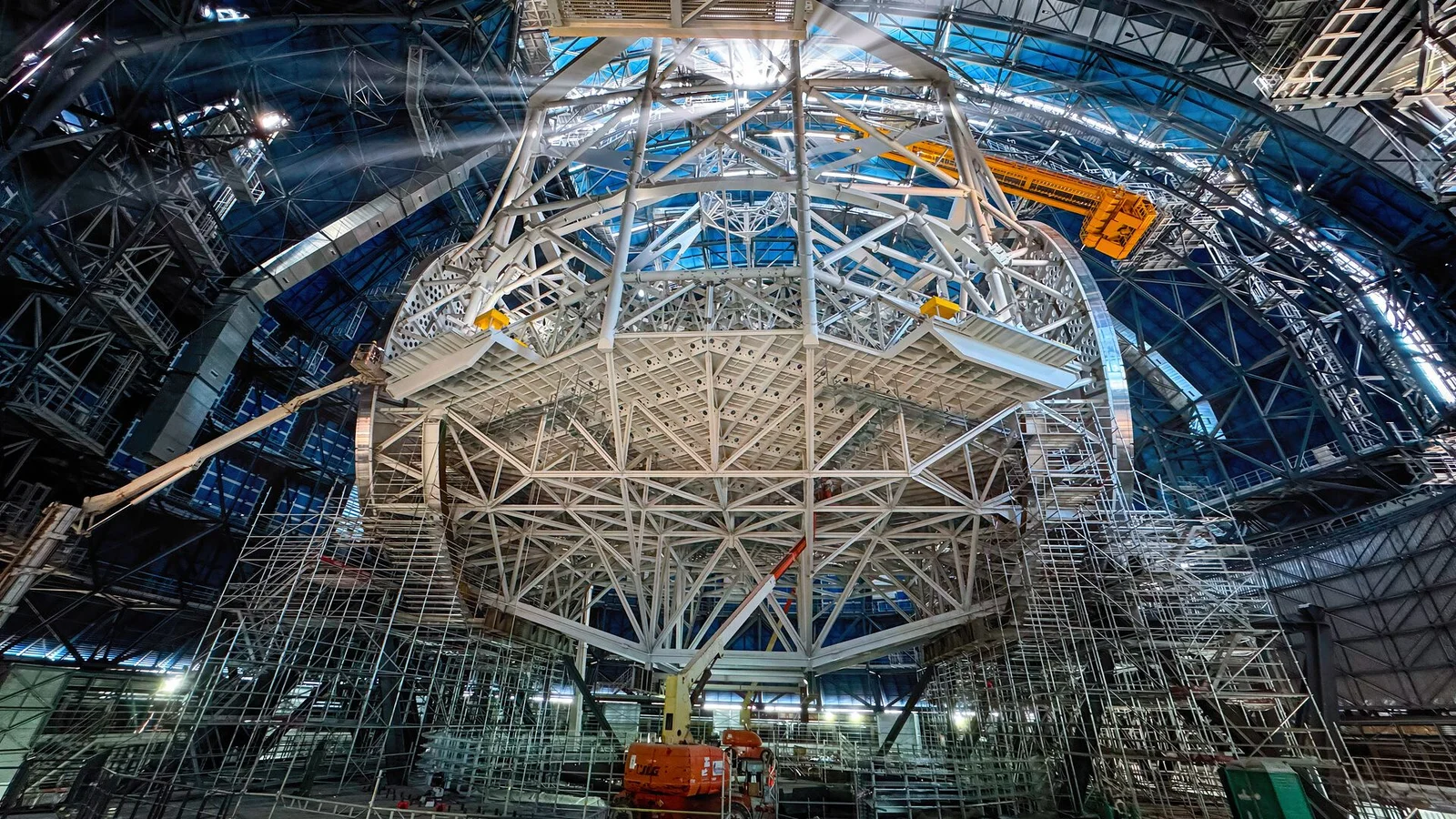
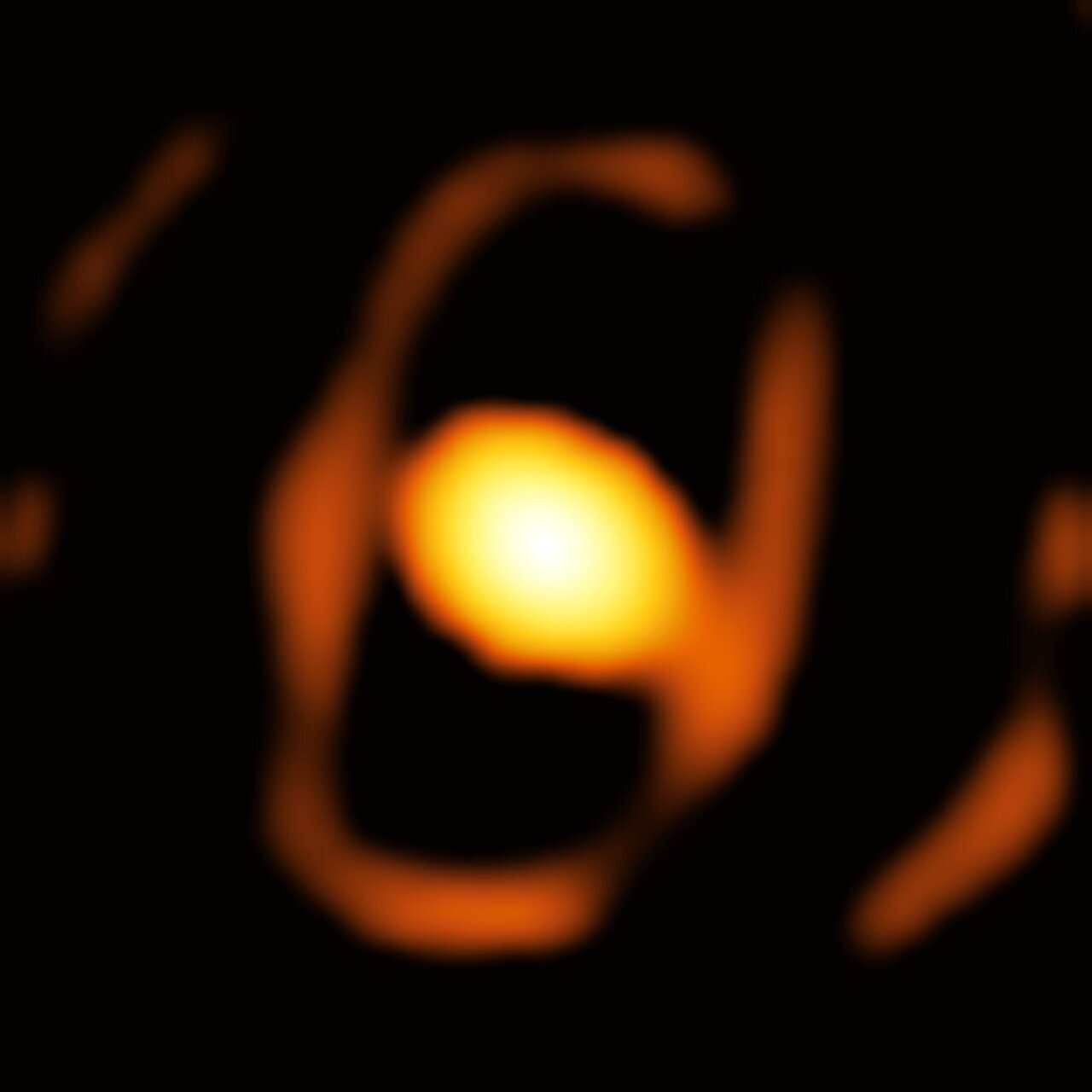Chile’s 80-meter dome gears up to house the Extremely Large Telescope
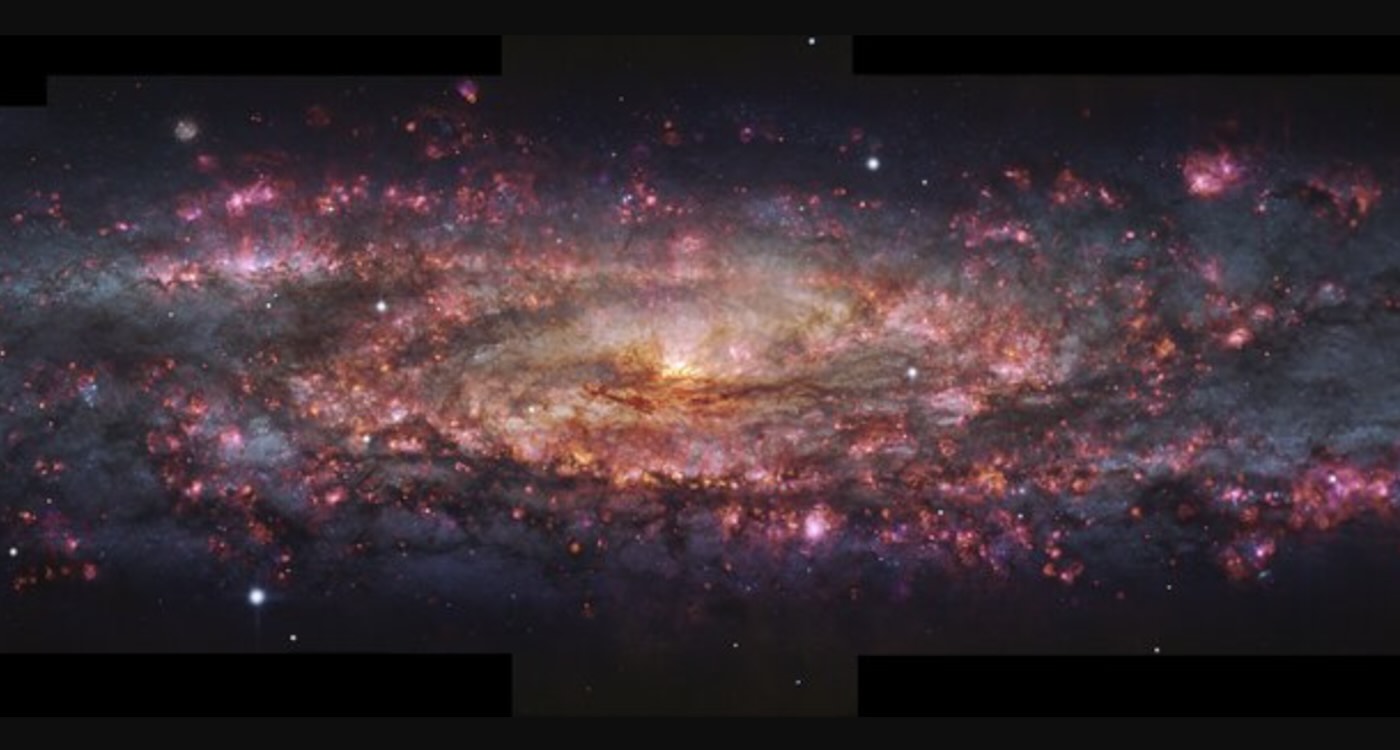
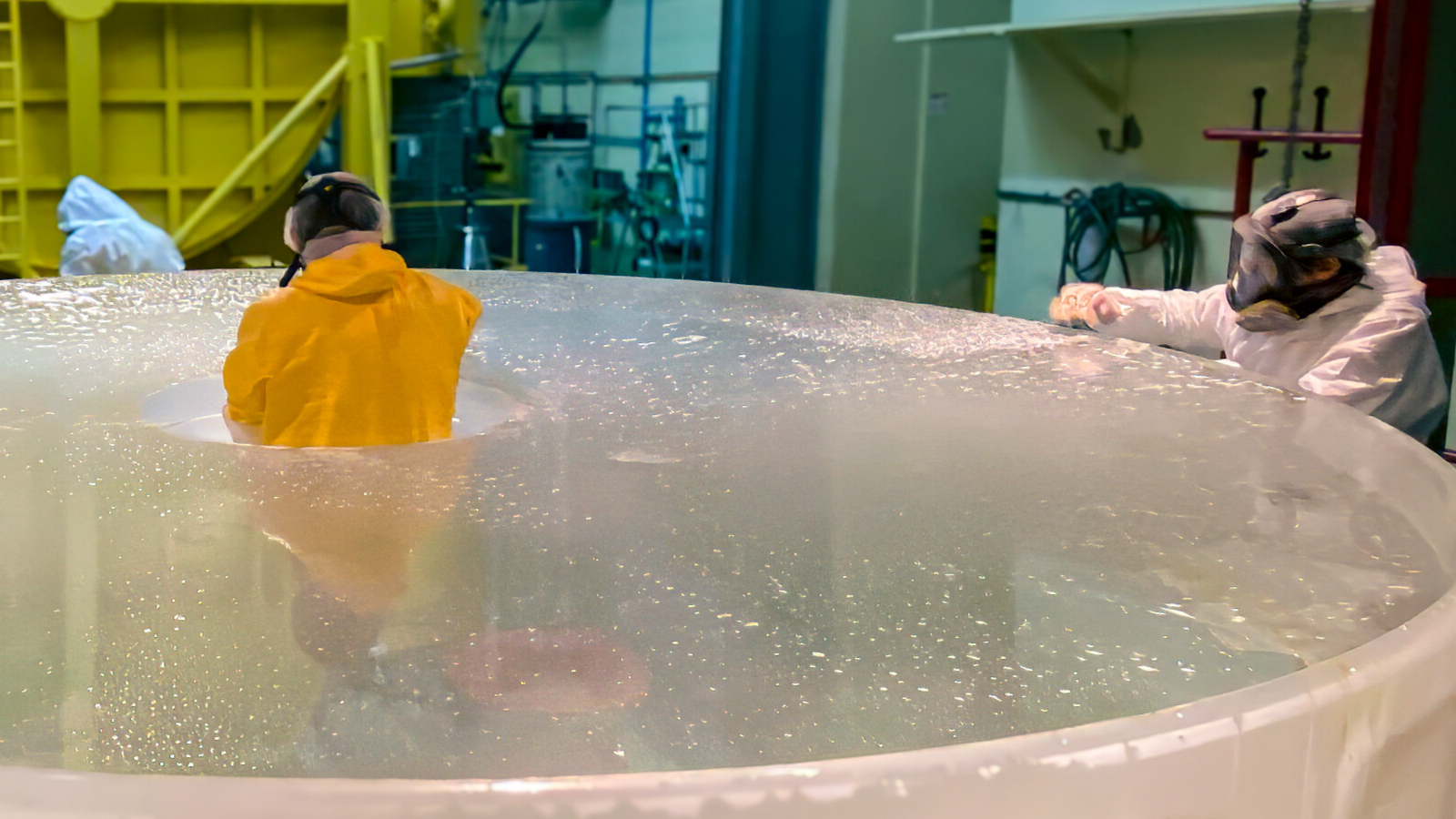
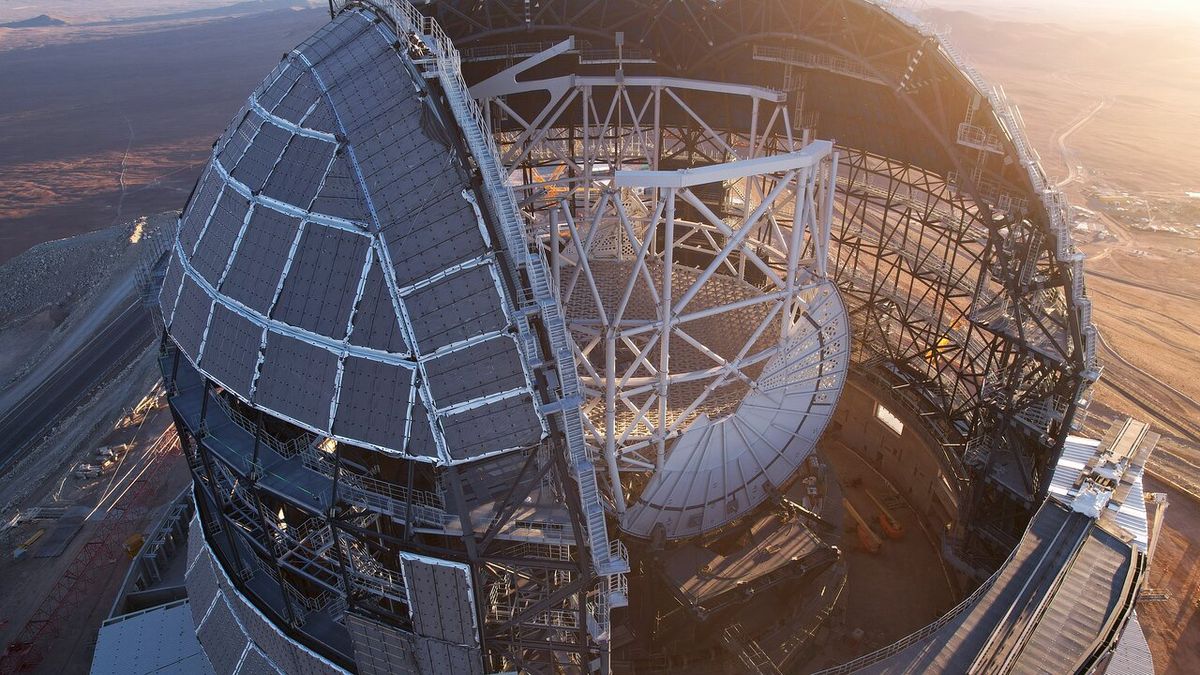
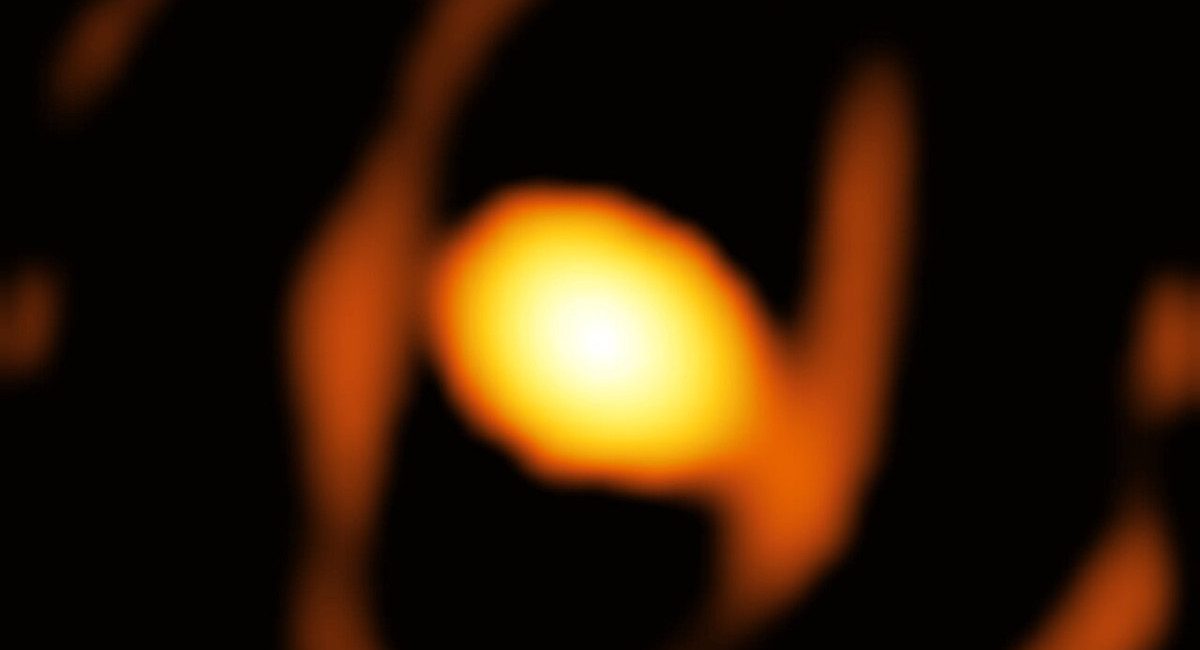
Space agency ESO released imagery of the ELT’s enormous 80-meter outer dome at Cerro Armazones in Chile. The dome will shelter a 39-meter primary mirror, protect optics from desert heat, and feature earthquake-resilient shock absorbers; the upper section will rotate to give the telescope full access to dark skies. The project is slated for completion in 2027, with first light planned for early 2029 and initial science observations in 2030.