Some PFAS Chemicals May Speed Up Biological Aging in Middle-Aged Men, Study Finds
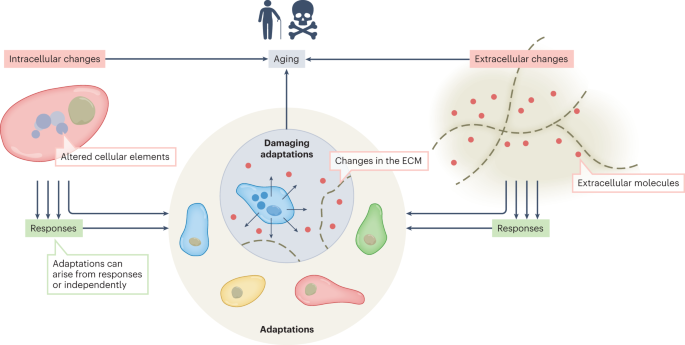
A Shanghai Jiao Tong University–led study using US NHANES data links higher blood levels of PFNA and PFOSA to faster epigenetic aging in men aged 50–64, with no similar effect in women; while it shows association, not causation, the findings suggest some newer PFAS alternatives may pose aging risks and underscore the need to limit exposure and study chemical mixtures.