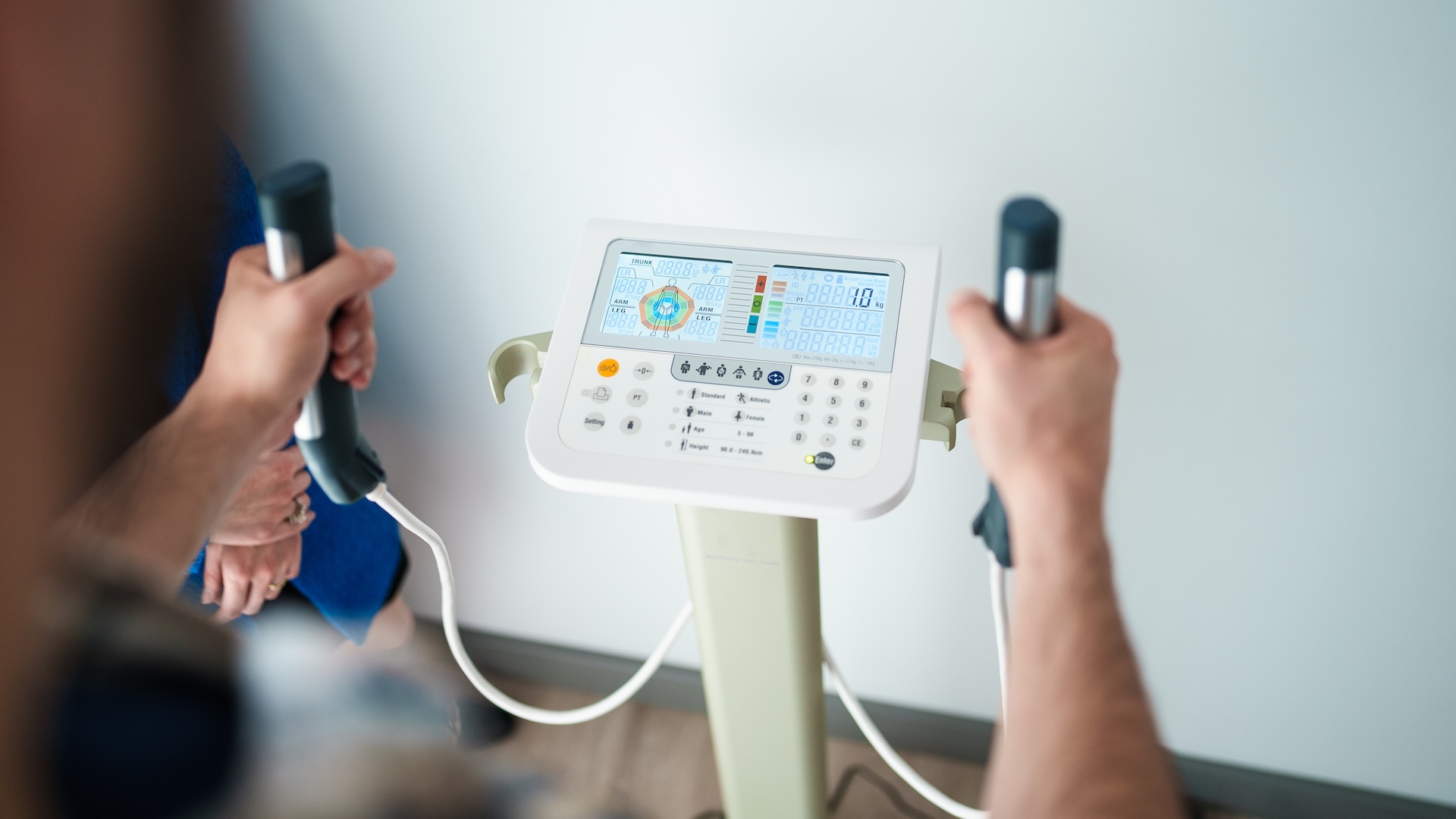
HIIT Could Help Seniors Trim Fat Without Losing Muscle
Australian researchers followed over 120 healthy older adults (average age ~72) for six months and found that high‑intensity interval training (HIIT) reduced fat while preserving lean muscle mass, whereas moderate- and low‑intensity workouts also cut fat but were associated with small or unclear muscle loss. The findings suggest exercise intensity is key for aging body composition, though results apply to healthy individuals and HIIT may not suit everyone; medical or trainer guidance is advised before starting such a regimen.