Vera Rubin Observatory Captures Massive Stellar Stream Escaping Galaxy
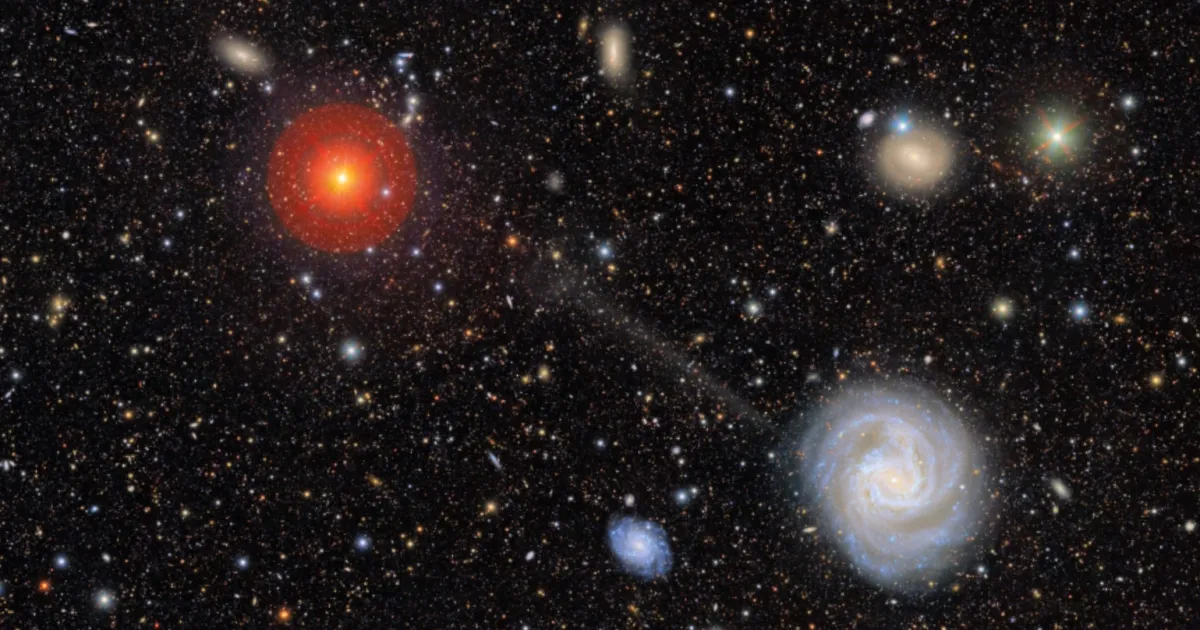
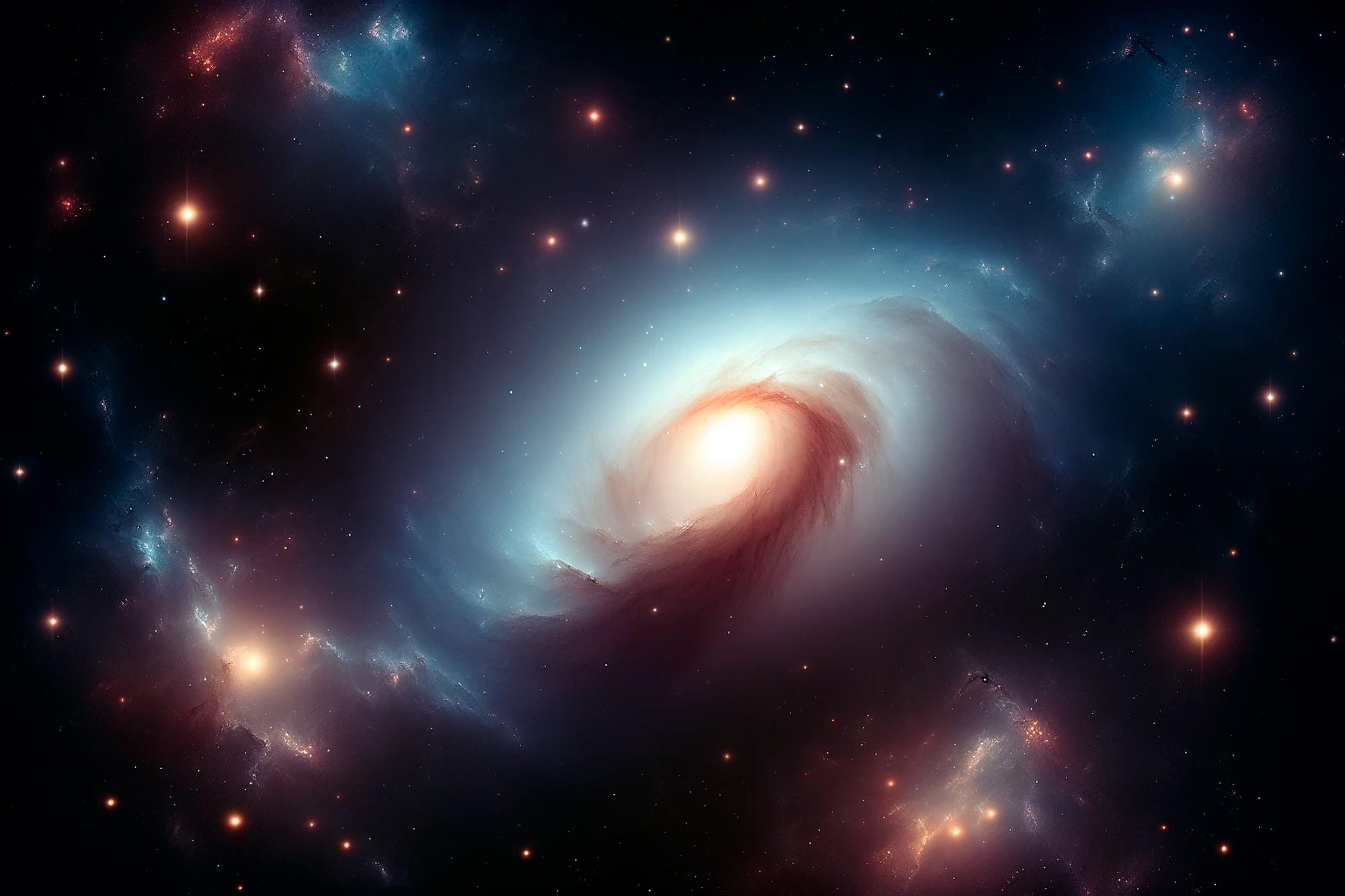
The Vera Rubin Observatory's first observations have revealed a faint stellar stream emanating from the galaxy Messier 61, showcasing its unprecedented capability to detect low-surface-brightness features and opening new avenues for understanding galaxy interactions and evolution.