Medicine News
The latest medicine stories, summarized by AI
Featured Medicine Stories

Selective CAR-T targets IGHV4-34, sparing healthy immunity in lymphoma mice
A CART4-34 CAR-T therapy targets the IGHV4-34 gene in B-cell cancer, destroying lymphoma cells in mice as effectively as CD19 CAR-T while sparing healthy B cells and avoiding immune suppression; the approach could also be used to treat autoimmune conditions such as lupus, but human trials are needed.
More Top Stories
VEXAS Syndrome: UBA1 Mutations Drive Inflammation and Myeloid Bias
Nature•3 months ago
mRNA COVID Vaccines Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy Effectiveness
Nature•4 months ago
More Medicine Stories
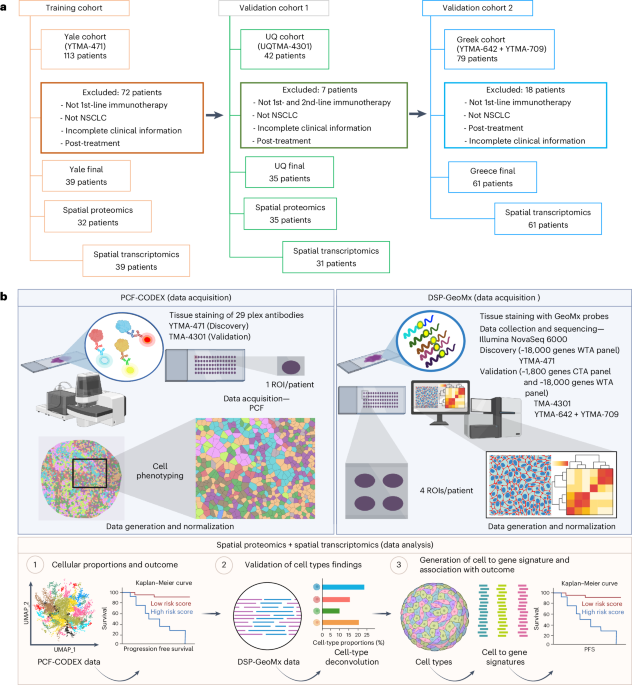
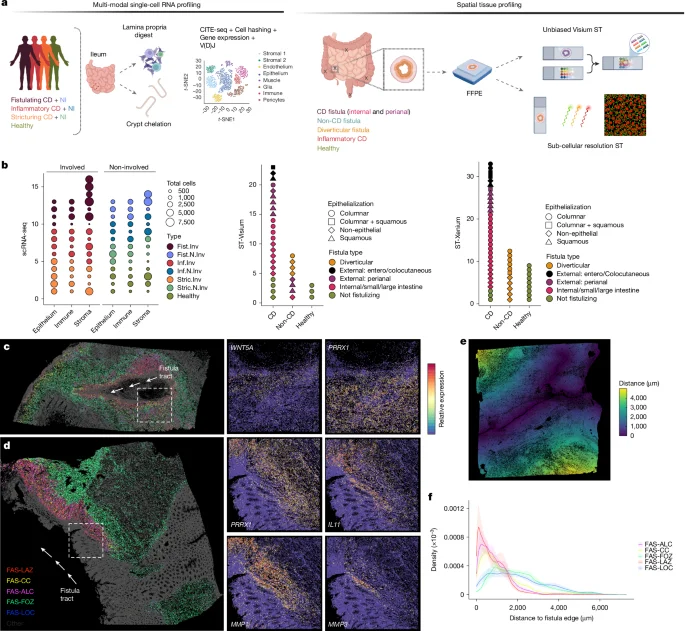
Innovative Multi-Omics and Mapping Techniques Enhance Lung Cancer Treatment Predictions
This study develops spatial multi-omics and machine learning-based biomarkers to predict immunotherapy outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer, highlighting the roles of immune cell spatial organization, macrophage PD-L1 expression, and gene signatures in resistance and response, validated across multiple cohorts.
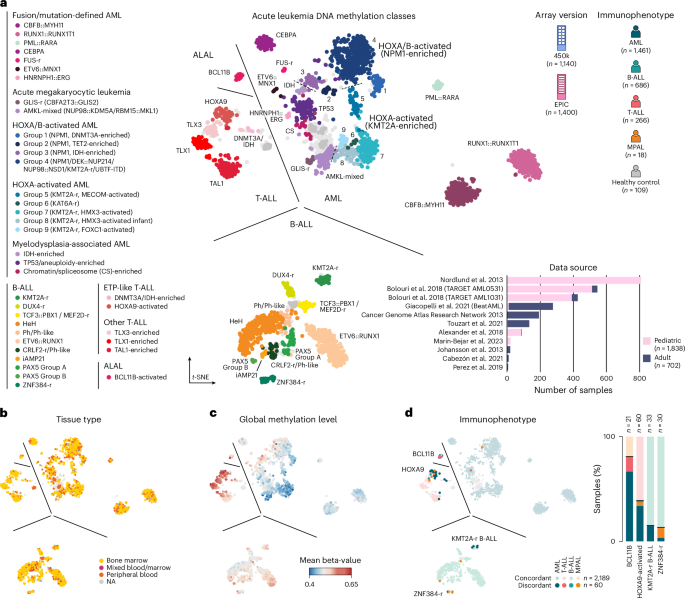
Dana-Farber Develops AI-Powered Tool for Rapid Leukemia Classification
The article presents a rapid epigenomic classification method for acute leukemia using nanopore sequencing and machine learning, based on a comprehensive DNA methylation reference cohort, enabling faster and more precise diagnosis that can complement traditional diagnostic workflows.
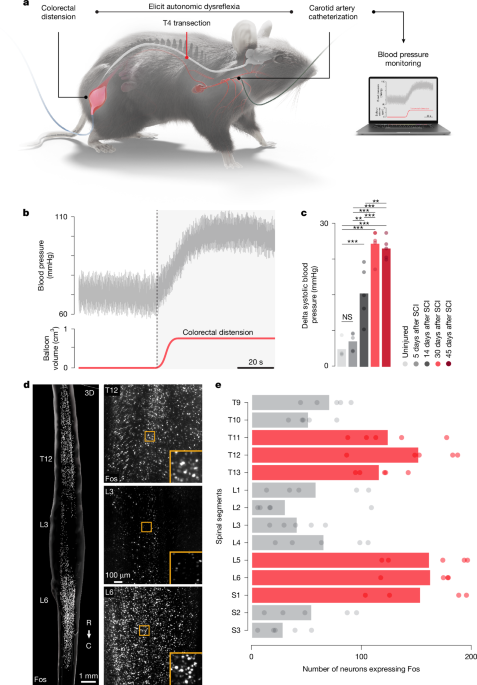
Advances in Blood Pressure Regulation Post-Spinal Cord Injury Using ONWARD ARC-IM Therapy
The article investigates the neuronal basis of autonomic dysreflexia after spinal cord injury, identifying specific neuronal subpopulations and their reorganization that trigger this life-threatening condition, and explores therapeutic strategies like electrical stimulation to modulate these neural circuits.

Bariatric Surgery Outperforms GLP-1 Medications for Long-Term Diabetes and Obesity Outcomes
This study compares the macrovascular and microvascular outcomes of metabolic surgery versus GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with diabetes and obesity, highlighting the potential benefits and data sharing protocols, with references to related research and long-term outcomes.
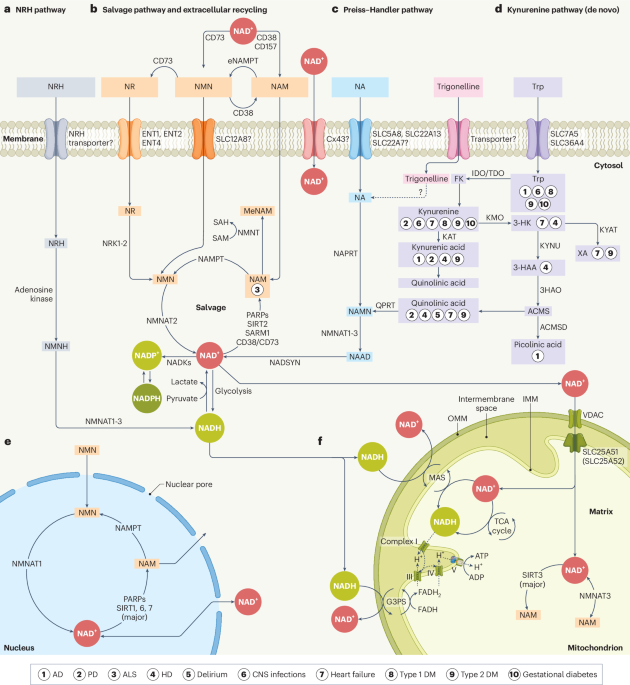
Advances and Challenges in NAD+ Therapy for Longevity and Well-being
The article reviews emerging strategies, applications, and challenges of targeting NAD+ metabolism in clinical settings, highlighting its potential in treating age-related diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer, while discussing current research and therapeutic prospects.
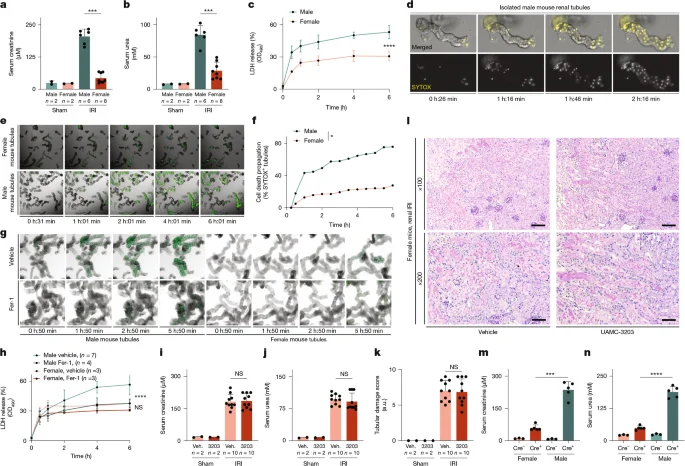
Oestradiol's Role in Preventing Ferroptosis and Kidney Injury
The study reveals that female kidney tissues are resistant to ferroptosis and acute kidney injury due to the protective effects of oestradiol, which acts through non-genomic antioxidant mechanisms and ESR1-dependent pathways, while male tissues are more susceptible due to higher ether lipid plasticity and lower hydropersulfide levels.

"Long-lasting UTI Vaccine Provides 9 Years of Protection for Over Half of Recipients"
A study presented at the European Association of Urology Congress reveals that the MV140 vaccine, administered as an oral spray, has shown to prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs) for up to 9 years in 54% of participants, with an average infection-free period of 4.5 years. The vaccine, containing inactivated whole bacteria of major UTI-causing species, has been well-tolerated and resulted in fewer and less severe UTIs. Researchers believe it could be a game changer for UTI prevention and reduce the reliance on antibiotic treatments, with further research needed to optimize its use.

"The Impact of Breastfeeding on Parental Mental Health: What You Need to Know"
A mother shares her experience of being advised against breastfeeding by her psychiatrist due to the potential impact on her mental health, despite societal pressure and medical guidelines promoting breastfeeding. She discusses the mental health risks of breastfeeding, the challenges she faced, and the importance of considering parental mental health in feeding decisions. The article highlights the need for better alignment of care across specialties and emphasizes that the best feeding choice is the one that allows parents to be the healthiest version of themselves.
"Breakthrough Gene Therapy Offers Hope for Hereditary Angioedema"
A groundbreaking gene therapy has shown promising results in treating hereditary angioedema, a rare disorder causing painful and potentially fatal swelling. Patients in the trial experienced dramatic improvements, with some being able to come off long-term medication and return to normal life. The therapy, using Crispr gene editing, aims to provide a permanent cure by targeting the genetic mutation causing the condition. While larger trials are ongoing, the high cost of one-shot gene therapies may limit accessibility, but the results offer hope for a potential cure for some sufferers.
"Key Takeaways from CHMP Meeting: January 2024"
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) recommended three new medicines for approval, including Exblifep for urinary tract infections, Ryzneuta for neutropenia, and Niapelf for schizophrenia, while refusing marketing authorizations for Nezglyal and Syfovre. The committee also recommended extensions of therapeutic indication for four medicines and confirmed its original recommendation to not renew the conditional marketing authorization for Translarna. Additionally, the CHMP endorsed measures to minimize risks for medicines containing pseudoephedrine and will re-examine its opinion on generic medicines following a request.
