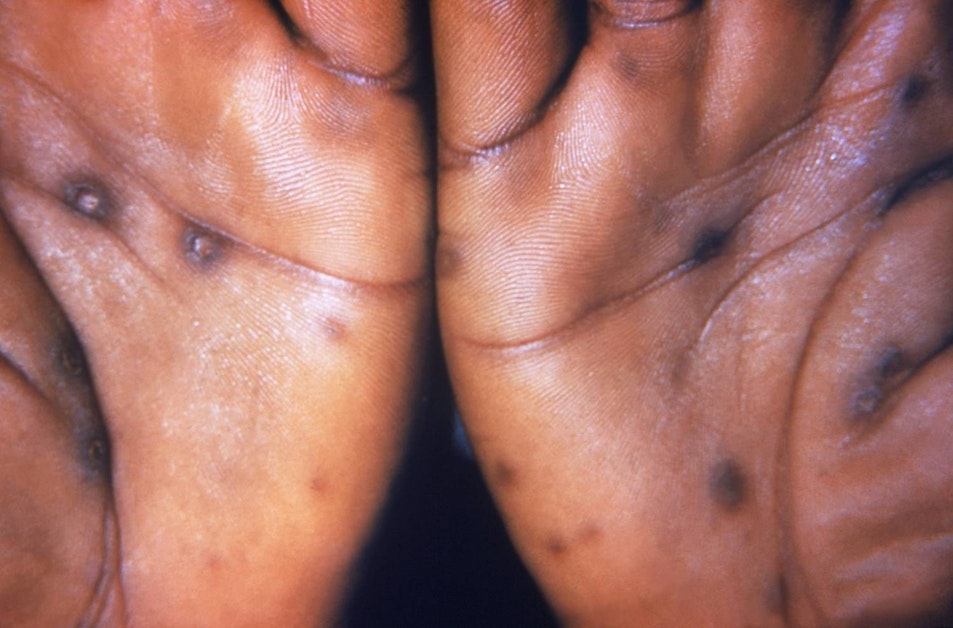
Arlington Faces Sharp Rise in Syphilis, Prompting Expanded Testing Push
Arlington’s 2024 syphilis rate was 31.2 per 100,000, about 50% above Virginia’s average and more than double Northern Virginia’s rate, marking the highest Arlington rate since 2019. Officials cite a younger, highly mobile population and delays in diagnosis and have issued updated testing guidance and engaged clinicians through the Northern Virginia STI/HIV Taskforce to improve detection and treatment. National data show a 42% rise in syphilis from 2020–2024, underscoring the need for routine screening for sexually active people, while Arlington’s STI Clinic provides testing and free services for low‑income residents; prenatal testing to prevent congenital syphilis is also emphasized by Dr. Deidra Parrish, the new public health director.