Illinois Mom Survives Rare Skin Disease, Loses 87% of Skin and Her Sight
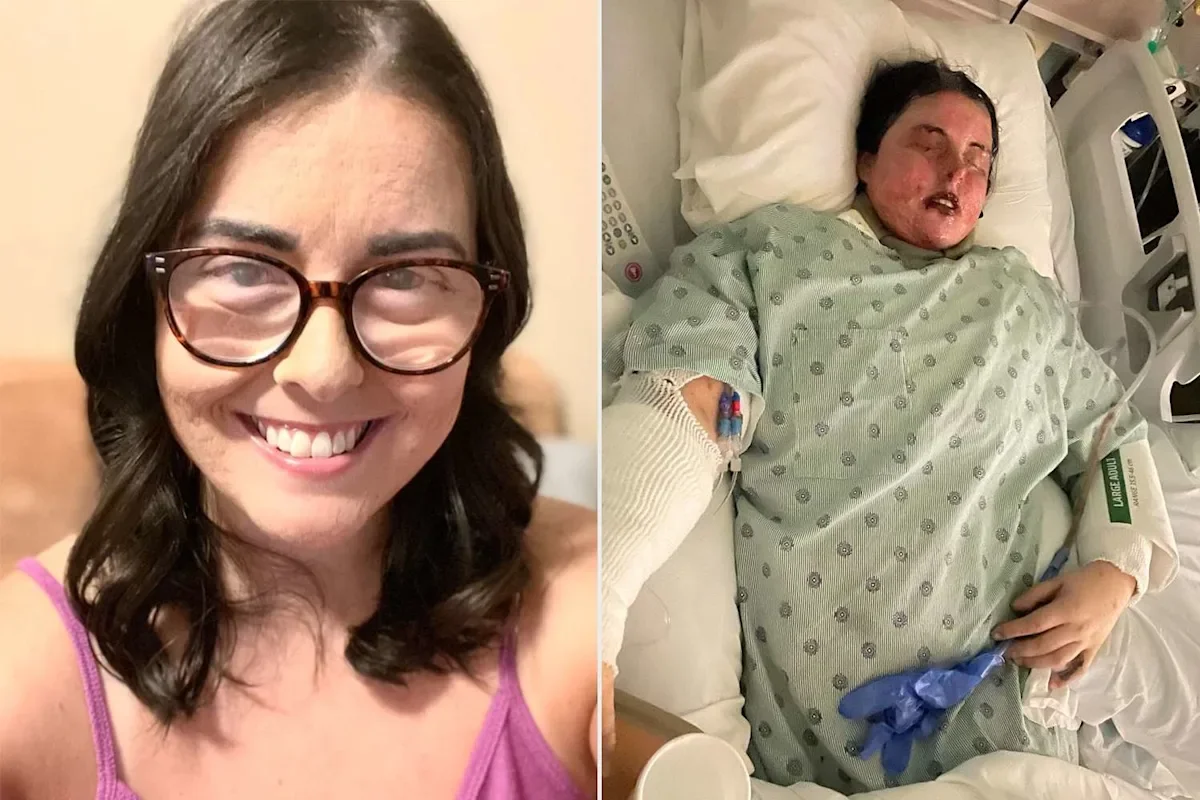
An Illinois mother, Emily McAllister, developed Stevens-Johnson syndrome after starting a new anti‑seizure medication in 2022. The condition caused a blistering rash that destroyed about 87% of her skin, required multiple surgeries (including eyelid reconstruction and a stem cell transplant), and left her legally blind in both eyes. She survived a life-threatening illness but faces permanent vision loss and describes her life as fundamentally changed, while emphasizing she’s lucky to be alive.