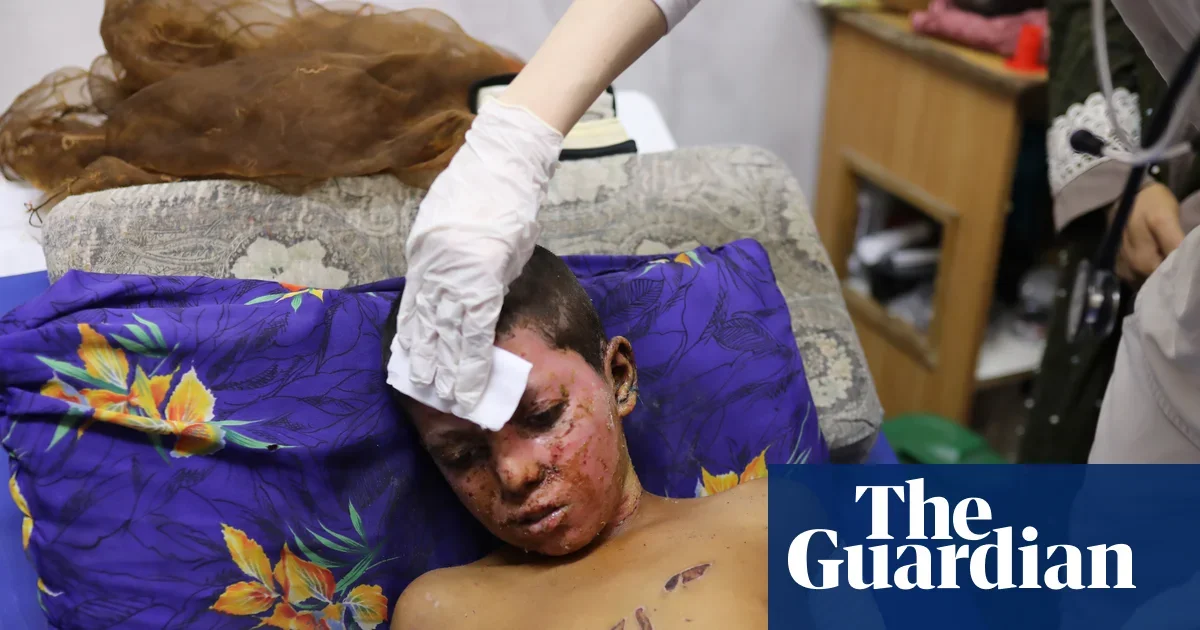
Gaza Civilian Injuries Mirror Battlefield Wounds, Study Finds
A study published in the BMJ reveals that civilians in Gaza are suffering injuries similar to those of soldiers in intense combat, with many experiencing severe burns and blast injuries, highlighting the devastating impact of the ongoing conflict and heavy bombardments on the civilian population.